Motion and Force
advertisement
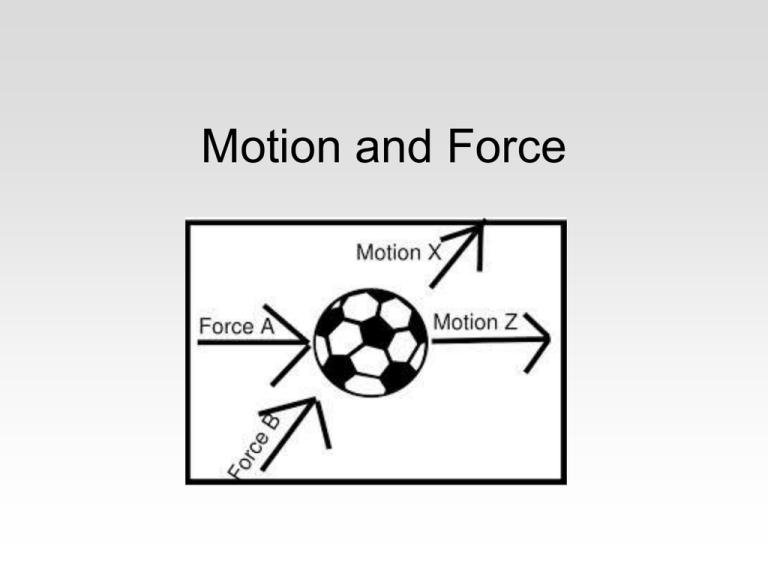
Motion and Force What is force? • Any action that can change the state of motion of an object. (A push or a pull!) • Has a magnitude and direction Fundamental forces • Vary in strength. – SN is strongest, holds nuclei of atoms together, effective over a very short distance – EM force is about 1/100 of the SN force – Gravitational force is much weaker. • Can act through contact or at a distance . – Contact push, pull – Field gravity, magnetic Balanced vs Unbalanced Forces • Net force – combination of all the forces acting on an object *When there is a net force acting upon an object, the object accelerates in the direction of the net force. - No acceleration occurs if net force is 0! • Balanced forces (no net force) do not change motion. • Unbalanced forces (net force > 0) do not cancel completely, objects will accelerate in the direction of the greater force. • Think of tug-of-war! Friction • Force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. • Occurs because the surfaces of objects are not perfectly smooth. Types of Friction • Static friction resists motion between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest. • Kinetic friction opposes the movement of two surfaces that are in contact and are moving over each other. • Static friction is greater than kinetic friction. • Different types of kinetic friction – sliding, rolling, fluid, etc. Friction and Motion • Friction is necessary for many everyday tasks! – Think of your typical day! • • • • • Tires push against ground to make your car move. Brakes use friction to stop your car. Friction between hands & steering wheel. Friction between pencil and paper allows you to write. Friction between your feet and floor allow you to push off when you walk. Check for understanding... 1. Describe a situation in which unbalanced forces are acting on an object. How is it affected? 2. Identify the type of friction. a. Two students push a box that is at rest. b. Box pushed by students is now sliding. c. Students put rollers under box and push it forward. Newtons? • Force is measured in N. – Newton is the force required to cause a mass of 1kg to accelerate 1 m/s/s • Force is calculated using: F = ma – Force is equal to mass x acceleration.