The Enlightenment - A movement in the 1700s that
advertisement

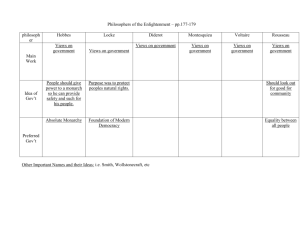
The Enlightenment -A movement in the 1700s that stressed a scientific approach to life. -A revolution in thinking. Brought on by the Scientific Revolution (1500s-1600s) Copernicus- heliocentric theory Jenner- smallpox vaccine Many advancements in physics, chemistry, anatomy, etc… Famous Figures from the Enlightenment Thomas Hobbes John Locke Montesquieu Voltaire Rousseau Diderot Mary Wollstonecraft Thomas Hobbes Leviathan “people are naturally cruel and greedy” “solitary, poor, nasty, brutish, and short” – Hobbes on life without strict laws. Absolute monarchy is best b/c it imposes order and obedience. John Locke “people are basically reasonable and moral” “natural rights” – life, liberty, property Best government- democracy People have the right to overthrow a govt if it is unjust or inept. Montesquieu Montesquieu Best known for the idea of “separation of powers” and “checks and balances” “Power should be a check to power” His book The Spirit of the Laws had a profound impact on the framers of the U.S. Constitution. Legislative, executive, and judicial branches Voltaire Voltaire Francois-Marie Arouet Probably the most influential philosophe Used wit, sarcasm, satire Best known for defending free speech Also argued against slavery, religious intolerance, superstition Targeted corrupt govt officials in his writings His books were banned and outlawed; he was imprisoned twice and exiled to England. Jean-Jacques Rousseau Rousseau The Social Contract Believed society corrupted people Believed titles of nobility should be abolished Disapproved of traditional education of his time – favored more vocational and physical education. Denis Diderot Diderot Published the Encyclopedia. Articles criticized slavery, encouraged free expression and education for all Banned by the Catholic Church Seen as very controversial for the time Helped spread Enlightenment ideas Mary Wollstonecraft Wollstonecraft A Vindication of the Rights of Woman Accepted traditional women’s roles, but… Called for equal education for boys and girls Believed women should be allowed to participate in politics Spread of Ideas Paris was the center of the Enlightenment, and ideas spread from there. How? The Encyclopedia Salons – informal social gatherings (usually at the homes of wealthy or middle-class women) where ideas were exchanged. Wrap-Up So…what was the Enlightenment? An intellectual movement of the 1700s where philosophers held old ways of thinking up to the light of reason to examine them. • Divine Right • Unequal social classes • Women’s lack of rights Periods of Art History Baroque: A style in art and architecture developed in Europe from about 1550 to 1700; a grand, complex style; paintings were huge, colorful, and exciting; this style was made to match the grandness of the lives of absolute monarchs. Periods of Art History Rococo: A style in art and architecture developed in Europe in the mid 1700s; more personal, elegant, and charming; paintings more often showed families and relationships between people. Periods of Art History Neoclassical: A style in art and architecture developed in Europe in the late 1700s and 1800s; a revival of the style from classical Greece and Rome; reflected simplicity, order, balance, and symmetry. This stained glass window is the highly dramatic focal point of The Throne of Saint Peter, 165766, marble, white and gilt stucco, and stained glass, overall height about 100 feet, Saint Peter's Basilica, Vatican, Rome. Vaux-le-Vicomte, France Jean Antoine Watteau (1684-1721) - arguably the greatist French painter of his time. This is entitled "The Embarkation for Cythera" Francois Boucher (1703-70) This is entitled "Venus Consoling Love" (1751) Long Term Effects Belief in progress A more secular outlook Importance of the individual Views toward Children View of nature (sinful to good) Discipline (strict to relaxed) Increased demand for toys and children’s goods Jigsaw puzzles, rocking horses, games, baby clothes