Name:_____________ Chemistry 114 Fourth Hour Exam
advertisement
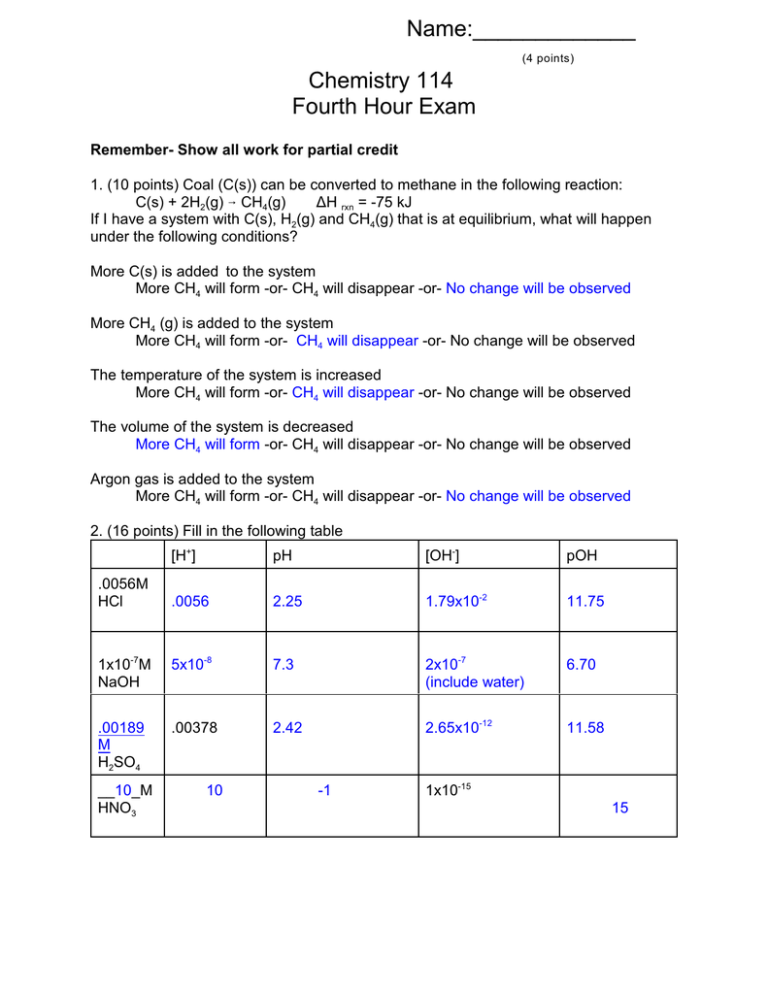
Name:_____________ (4 points) Chemistry 114 Fourth Hour Exam Remember- Show all work for partial credit 1. (10 points) Coal (C(s)) can be converted to methane in the following reaction: C(s) + 2H2(g) 6 CH4(g) ÄH rxn = -75 kJ If I have a system with C(s), H2(g) and CH4(g) that is at equilibrium, what will happen under the following conditions? More C(s) is added to the system More CH4 will form -or- CH4 will disappear -or- No change will be observed More CH4 (g) is added to the system More CH4 will form -or- CH4 will disappear -or- No change will be observed The temperature of the system is increased More CH4 will form -or- CH4 will disappear -or- No change will be observed The volume of the system is decreased More CH4 will form -or- CH4 will disappear -or- No change will be observed Argon gas is added to the system More CH4 will form -or- CH4 will disappear -or- No change will be observed 2. (16 points) Fill in the following table [H+] pH [OH-] pOH .0056 2.25 1.79x10-2 11.75 1x10-7M NaOH 5x10-8 7.3 2x10-7 (include water) 6.70 .00189 M H2SO4 .00378 2.42 2.65x10-12 11.58 .0056M HCl __10_M HNO3 10 -1 1x10-15 15 2 3.(12 points) What is the pH of 4.5 mM Ammonia (KB = 1.8x10-5) B + H2O WBH+ + OHX = [OH-] = [BH+] [B] = .0045 -X ..0045 KB = 1.8x10-5 = X2/.0045 1.8x10-5 x .0045 = X2 X=sqrt(1.8x10-5 x .0045) = 2.8x10-4 pOH = -log (2.8x10-4) = 3.55 pH= 14-3.55 = 10.45 4. (12 points) In the following pairs of compounds, circle the compound that is most acidic. A. HCl or CH3COOH B. NaOH or NH3 C. HClO2 or HClO4 D. Sodium Acetate E. Chromium(VI) oxide F. Sulfur dioxide or Ammonium chloride or or Chromium(VI) nitrate Strontium oxide 3 5. (12 points) I am going to mix 25 mls of a .15M solution of benzoic acid (a weak acid, KA =6.4x10-5) with 20 mls of a .10M solution of sodium benzoate (the sodium salt of this weak acid). What is the pH of the resulting solution? Mixture of acid and conjugate base = buffer, use Henderson-Hasselbach Equation pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA] pKa = -log(6.4x10-5) = 4.18 [HA] =(.025 l x .15M) / .045 l = .0833 [A-] = (.02 l x .10M) /.045 l = .0444 pH = 4.18 + log (.0444/.0833) = 3.91 6. (12 points) Define the following terms A. Entropy- (S) a measure of randomness. B. Spontaneous process - A process that will occur without outside intervention. C. Second law of Thermodynamics - The entropy of the universe is always increasing. D. ÄSsystem The change in entropy of a system, S final - S Initial E. Buffer - A solution that resists changes in pH when either acid or base is added. F. Lewis acid - An electron acceptor or electrophile. 4 7. The chemical reaction for the burning of ethane is: 2 C2H6 (g) + 7 O2(g) 64 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O(g) A. (4 points) Should this process have a + or - ÄS? Explain: 10 gas molecules as products, 9 gas molecules as reactants, the number of gas molecules increase so the randomness of the system increases, so ÄS should be +. B.(8 points) From the data table below, calculate the actual ÄS for this reaction. S (J/K@mol) C2H6(g) 266.9 O2(g) 205 CO2(g) 214 H2O(l) 70 H2O(g) 189 ÄS = 3n Product Sproduct - 3n Reactant S Reactant =[4(214)+6(189)] - [(2(266.9) + 7(205)] = +21.2 J/K@mol 8. (12 points) Tin has two solid forms, called white tin and gray tin. ÄH for the transition Tin(white) 6Tin(gray) is -2 kJ/mole ÄS for the transition Tin(white) 6Tin(gray) is -8 J/mole At what temperature are white tin and gray tin in equilibrium? At equilibrium ÄG = 0 = ÄH -TÄS 0 = -2000 J/mol - X(-8) J/mol 2000 = 8X X = 2000/8 X = 250 K = -23oC = -9.4o F Note: White tin is the normal metallic tin seen at room temperature. If tin is exposed to temperatures below -9.4 F it starts turning into gray tin that crumbles away. This is called ‘tin disease’






