Partial equilibrium analysis: q y Some game theory
advertisement

Partial equilibrium
q
analysis:
y
Some game theory
Lectures in Microeconomic Theory
Fall 2010, Part 19
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
1
Game theory studies multi-person decision
problems, and analyzes agents that
are rational (have well-defined preferences)
reason strategically (take into account their
knowledge and beliefs about what others do)
Applications
Industrial organization (incl. oligopoly theory)
g
g andd auction
c
theoryy
Bargaining
Labor market and financial economics
Macro economics
International economics
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
2
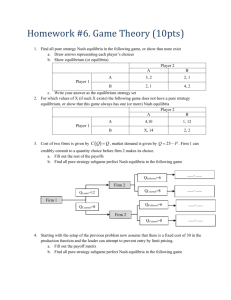
1
Game matrix
The players choose strategies.
Each player’s payoff depends on the strategy profile.
2 Demand 1 Demand 3
1
for self for the other
Demand 1 for self
1, 1
Demand 3
for the other
0, 4
4, 0
Prisoners’
dilemma
If the players do not choose strictly dominated
strategies, both will demand 1 for themselves.
07.07.2010
3, 3
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
3
Solving games through iterated elimination
of strongly dominated strategies
r
T 1,, 1 1,, 0
B 0, 0
0, 1
The game is solved
through
h
h iiter. elimi.
li i
of str. dom. strat.
1 does not choose a str. dom. strategy 1 chooses T
2 believes that 1 does not choose a str. dom. strat. &
2 does not choose a str. dom. strat. 2 chooses
r
Battle of the
No strategy is str.
T 2, 1 0, 0
sexes
B 0, 0 1, 2
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
dominated. for
any of the players!
4
2
Nash equilibrium
Are there strategies for the two players so
that no player will regret his own choice
when
hen being told of the other pla
player’s
er’s choice?
If yes, then such a strategy profile is a
Nash equilibrium.
r
Battle of the
T 2, 1 0, 0
sexes
B 0, 0 1, 2
(T, ) and (B, r) are Nash equilibria.
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
5
The strategic form specifies
Players: {1, ... , i, ... , n}
For each p
player, a strategy set: Si
For each player, a payoff function: ui
G ( S1 ,, Sn ; u1 ,, un )
Payoff for each player i :
ui ( s1 , , sn ) ui ( si , si )
where, for all j , s j S j ,
and where we write si ( s1 , , si 1 , si1 , , sn )
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
6
3
Definitions
Definition : si is strongly dominated by si if
ui ( si, si ) ui ( si, si ) for all si .
Iterated elimination of str. dom. strategies requires
that it is commonly believed that players are rational.
Definition : ( s1 , , sn ) is a Nash equilibrium for
G ( S1 , , S n ; u1 , , u n ) if, for each player i ,
it holds that ui ( si , si ) ui ( si , si ) for all si .
Nash equilibrium requires that players are rational and
have correct conjectures conc. the opponents’ choices.
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
7
Examples
C
L
U 1, 0 1, 2
D 0, 3
R
0, 1
0, 1 2, 0
Iterated elimination of
strongly dominated
strategies works well in
some examples.
C
R
L
T 0, 4 4, 0 5, 3
In other games, no
strategy is str. dom.
M 4, 0 0, 4 5, 3
Even in games w/only
one Nash equil., incorr.
conjectures can be held.
B 3, 5 3, 5 6, 6
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
8
4
Some games have no Nash equilibrium
Monitoring (of
traffic)
I
L l Illegal
Legal
Ill l
Monitoring - 1, 0 - 1, - 4
No
monitoring 0, 0 - 3, 1
1
3
Player 2’s
2 s best
response fn
Player 1’s best
response fn
Such games have a
L
Nash equilibrium in
1
M
N
5
mixed strategies. Interpretation
as a steady state.
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
9
Some games have multiple equilibria
Will the players coordinate, and if yes, on which
equilibrium?
A game of trust
Each of you is to choose 1 or 2 indep. of each other.
A player who chooses 1, receives 100 kr from UofO.
A player who chooses 2, receives 200 kr from UofO
if allll others
h also
l choose
h
2 but
2,
b must pay 500 kr
k if at
least one other player chooses 1.
Write 1 or 2 on a piece of paper!
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
10
5
Multiple equilibria (cont.)
A game
of trust
2
1
Choose 1 Choose 2
100, 110
Choose 1 100, 100 100,-500
Will a
guarantee
help?
Choose 2 -110,
500,100
100 200, 200
Conclusion:
C
l i
S
Some
games (e.g.,
(
the
h battle
b l off the
h sexes
and the game of trust) have multiple Nash equilibria.
Will the players coordinate on a particular Nash equil.?
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
11
Multiple equilibria (cont.)
In some games the Nash equilibria require
that the players choose differently.
Chicken
2
1
Not
R&D R&D
Not R & D 2, 2
R&D
3 0
3,
0, 3
- 1, - 1
Will the players coordinate on a particular Nash equil.?
07.07.2010
G.B. Asheim, ECON4230-35, #19
12
6