Name:_____________ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam

Name:_____________
Chemistry 114
First Hour Exam
Remember- Show all work for partial credit
1. You have probably heard of Nitrous oxide. It has several uses in the real world; it is the so called ‘laughing’ gas you might get in an dentist’s office, and it is used boost could describe two different compounds, one with atoms arranged NNO and the other with the atoms arranged NON.
A. (4 points) Draw Lewis structures for these two different arrangements of atoms.
B. (2 points) Show any resonance structures possible for one or both structures.
C. (2 points) What is the hybridization of the central atom in each of these structures
D. (2 points) What is the bond angle around the central atom is each structure?
E. (2 points) Determine the polarity of each structure. (the N-O bond is polar)
F. (1 point) The real compound is polar and linear, which one is it?
(A)
(B)
(C) Sp in both
(D) 180 in both
(E) NNO Polar, NON nonpolar
(F) NNO
2. (12 points) What is the difference between
A B bond and a F bond A B bond is an orbital in which the electrons are located along the line that connects the atoms, a F bond is one in which the electrons are located to either side of the line connecting the atoms
A F
2s
and a F
2p
orbital A F
2s
orbital is a molecular orbital that is made by hybridizing two 2s atomic orbital together, a F
2p
orbital is a molecular orbital that is made by hybridizing two 2p atomic orbitals together.
set of four molecular orbitals that are obtained when an s and three p atomic orbitals are hybridized together.
A B orbital and a B * orbital Here a B orbnital refers to a bonding B type orbital that has a lower energy than the atomic orbitals that it was hybridized from, so filling it with electrons tends to stabilize a molecule, B *refers to an anti-bonding B type orbital that has a higher energy than the atomic orbitals that it was hybridized from, so filling it with electrons tends to destabilize a molecule.
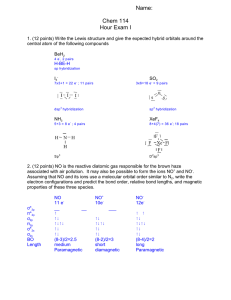
orbital energy level diagrams for these two compounds. Use the diagram to answer the following questions: What is the Bond Order for each ion. Would you predict that the ion would be stable? Is the ion attracted to a magnetic field or is it repelled.
BN + # electrons=3+5-1=7
__ F
2p
*
__ __ B
2p
*
__ F
2p
89 8 _ B
2p
89 F
2s
*
89 F
2s
__ F
2p
*
89 89 B
2p
*
89 89 B
2p
98 F
89 F
2p
2s
*
89 F
2s
B.O. = (5-2)/2 = 1.5
More stable
B.O. = (8-6)/2 = 1
Less stable
Paramagnetic, so attracted to magnetic field Diamagnetic, so repelled by magnetic field
2
4. (20 points) Draw structures for the organic compounds. The name I give may not be correct. If the name is wrong, give a more correct name
2-ethyl-3-methylpentane cis -2-hexene
Proper name: 3,4-dimethylhexane
Name is correct
6-chlorophenol 3,4-diaminocyclohexanol
Name is correct
Proper name:
2-chlorophenol
5. (12 points) What chemical reaction would I use to change:
(For each reaction give the structure of both reactant and product, the name of the reaction, and the reagents you would use to make the reaction work)
Propane to 1-chloropropane
Substitution
1-Propene to 1,2-dichloropropane
Addition
Benzene to Chlorobenzene
Substitution
6. (12 points) Locate the different functional groups in the following molecules:
(There are some function groups we didn’t cover in class, don’t worry about them, find all the ones we did cover)
3
4
7. (10 points) Name and give an example of one natural polymer (biopolymer) and one man-made polymer (a plastic) For each polymer give the structure of the monomer, and tell whether the polymerization reaction is classed as a an addition reaction, a condensation reaction, and why.
For a biopolymer I was looking for Carbohydrates, Proteins, or Nucleic acids and the appropriate monomer, all are made via a condensation reaction.
For the plastic I accepted any of the plastics discussed in class. Most, but not all of these are examples of addition type polymerization reactions.
8. (9 points) Name the four different intermolecular forces, rank the forces by relative strength, range (long distance or short distance), tell what kind of molecule would exhibit this kind of force and give an example molecule.
Strongest
Charge/charge interaction- Long range- displayed by charged ions, NaCl
H-Bonding - Medium range - Displayed by polar compounds that have F,N, or O
Dipole/Dipole interaction - Medium range - Displayed by polar compounds,
3
London Force or induced dipole - Short range - observed in nonpolar compounds
Example: He
Weakest