CE 473/573 Groundwater Fall 2012 Homework 9 Due Friday November 2
advertisement

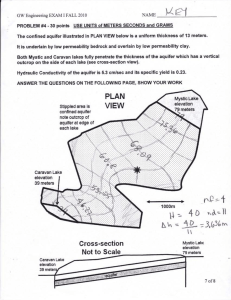
CE 473/573 Groundwater Fall 2012 Homework 9 Due Friday November 2 *53. A pump test is conducted in a leaky confined aquifer. The confining layer has a thickness of 1.5 m, while the aquifer has a thickness of 10 m. The well is pumped at 1000 m3 /d, and it has a radius of 0.6 m. The drawdowns at 30 and 75 m from the well are 0.4 m and 0.25 m, respectively. Determine the hydraulic conductivities of the aquifer and the confining layer. 54. (From 2008 final) A well pumps water at 0.1 m3 /s from a aquifer with transmissivity 0.09 m2 /s that is overlain by a leaky layer of thickness 5 m. The radius of the well is 0.6 m. a. The drawdowns measured at 50 and 150 m from the well are 0.36 and 0.18 m, respectively. What is the hydraulic conductivity of the leaky confining layer. (Hint: You might find the graph below to be useful.) b. If the pumping rate were increased to 0.15 m3 /s, what would be the drawdown at 50 m after a long time? c. If the confined layer were an aquifuge, would the drawdown at 50 m (say) be larger or smaller than the value in part a? Explain your answer. 0.7 0.6 0.4 0.3 0 0 K (150/λ) / K (50/λ) 0.5 0.2 0.1 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 λ (m) 350 400 450 500 *55. An aquifer with storativity 0.003 lies below an aquitard with thickness 5 m and conductivity 0.05 m/d. The unconfined aquifer above the aquitard has a head of 30 m for a long time, and rain suddenly increases the head to 30.5 m. Compute the time for the head in the leaky confined aquifer to reach 30.45 m. *56. (Modified from exam 1, fall 2007) We will develop a detailed method of determining properties of aquifers from wells, but for now use a crude approximation. Suppose a well is pumped at 600 m3 /d for 1 day. The average drawdown (i.e., decline in head) is 4.1 m over a circular area of radius 200 m. Estimate the storativity.