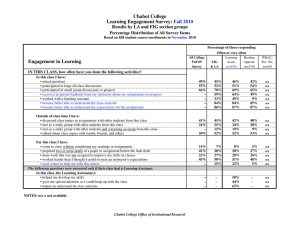
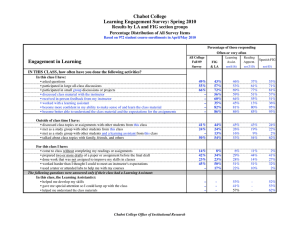
Chabot College Course Outline for Medical Assisting 70B
advertisement

Chabot College Fall 2001 Course Outline for Medical Assisting 70B CLINICAL SKILLS FOR THE MEDICAL ASSISTANT II Catalog Description: 70B- Clinical Skills For The Medical Assistant II 3 units Continuation of Medical Assisting 70A. Basic and advanced clinical skills common to medical offices and clinics. Use of advanced clinical skills while assisting the physician and performing direct patient care. Prerequisite: Medical Assisting 70A (completed with a grade of C or higher). 2 hours lecture, 3 hours laboratory. Prerequisite Skills: Before entering the course the student should be able to: 1. explain the role and scope of practice of the professional clinical Medical Assistant; 2. explain the need for patient confidentiality; 3. identify the fundamental concepts of infection control; 4. demonstrate the proper procedure for handwashing; 5. demonstrate the proper methods for obtaining and recording vital signs; 6. recognize the importance of reporting significant changes in patient's health status; 7. demonstrate how to assist the physician with a complete patient examination; 8. explain the psychology and sociology of patient care; 9. conduct a comprehensive patient interview; 10. describe the specific evaluation and treatment of the eye and the ear; 11. demonstrate safety measures for clients and other members of the health care team; 12. communicate effectively with clients and other members of the health care team; 13. demonstrate the promotion of tissue healing through the use of physical therapy; 14. demonstrate the proper procedures for sterilization and disinfection; 15. demonstrate the proper procedures involved in assisting the physician with all aspects of minor office surgery; 16. describe the role of laboratory tests in patient assessment; to include specific forms, collection of specimens, careful handling of specimens, and the interpretation of data; 17. demonstrate the proper procedure for performing a urinalysis; 18. describe the process of oxygen administration using various delivery systems. Expected Outcomes for Students Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to: 1. explain the principles underlying each step in the blood banking process; 2. demonstrate competency in the collection and interpretation of hematology, blood chemistry, immunology and microbiology tests; 3. perform venipunctures; 4. demonstrate the correct method for obtaining an electrocardiogram; 5. explain the preparation of the patient and purpose of specific radiological examinations, to include Scans, Ultrasound, and imaging techniques; 6. describe the components of the neurological examination; 7. state the specific procedure for conducting gynecological, prenatal, postnatal examinations; 8. assist with the various components of the health assessment of the pediatric patient; 9. state the preparation and purpose for proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy; 10. explain the role of the medical assistant as patient educator; 11. describe medical, legal, and ethical issues as they relate to the professional medical assistant's scope of practice; 12. explain pulmonary function testing; 13. demonstrate advanced orthopedic techniques; 14. demonstrate emergency procedures that may be utilized in the doctor's office or clinic; 15. describe the components of a balanced diet and diet modification. Chabot College MA 70B, Page 2 Fall 2001 Course Content 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Blood banking Hematological blood tests: a. Hematocrit b. Hemoglobin c. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate d. Blood cell counts e. Differential white blood cell count Blood chemistry tests a. Blood glucose b. Blood urea nitrogen c. Cholesterol d. Triglycerides Venipuncture Microbiology specimens a. Streptococcal testing b. Urine culture c. Wound culture d. Vaginal culture e. Gram staining f. Sensitivity testing Immunology a. Mononucleosis testing b. Streptococcal screening c. Rh factor d. Pregnancy tests Electrocardiography a. 12 lead EKG b. Rhythm strip c. Ambulatory monitoring devices Radiological, and other imaging examinations Pediatric examinations Gynecological examinations Prenatal and postnatal examinations Neurological examination Colon and rectal procedures Medical-legal issues Ethical issues Patient education Orthopedic care Pulmonary function tests Diet modification Emergency procedures Methods of Presentation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Lecture/discussion Skills demonstration Audio-visual materials Anatomical models and drawings Assignments and Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: 1. Typical Assignments Chabot College MA 70B, Page 3 Fall 2001 a. b. 2. Pediatric height and weight graphing Lab requisitions Methods of Evaluating Student Progress: a. Satisfactory completion of clinical competencies b. Quizzes c. Midterm and final examination Textbook(s) (typical) Clinical Skills for the Medical Assistant, Lindh, Pooler, Tamparo, Cerrato, Delmar 1998 The Medical Assistant Review Book, Palko, 1997 Special Student Materials: 1. 2. 3. Laboratory coat Watch with sweep second hand Student name badge revised 12-1-00