environmental concerns reasons for concern Ketil Hylland
advertisement
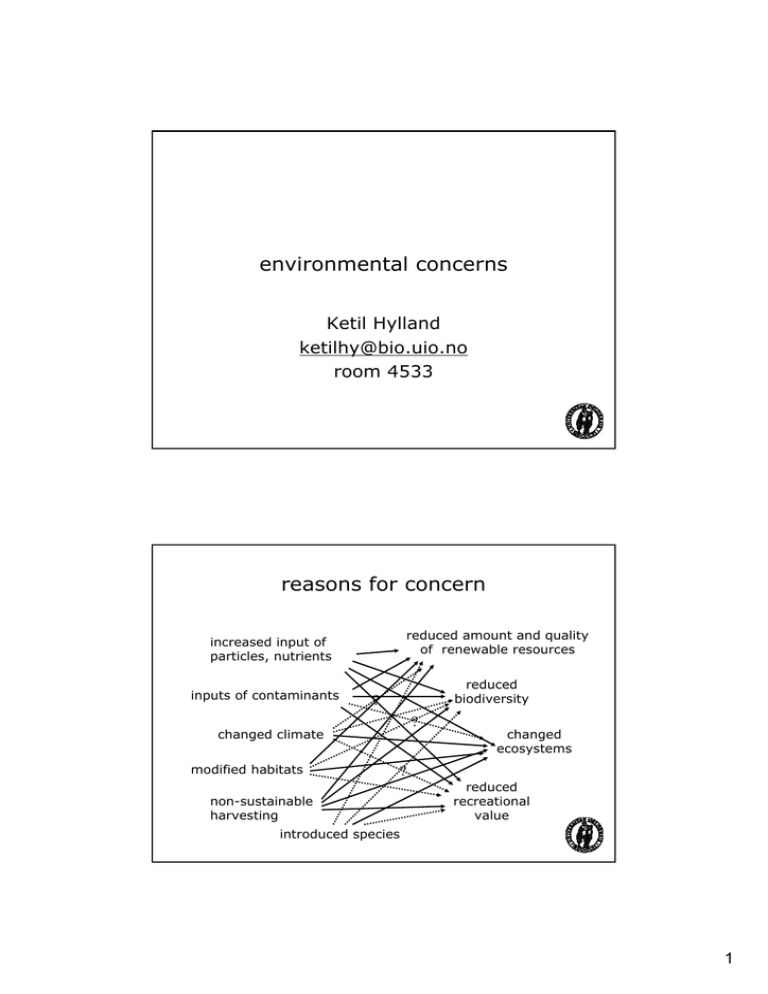
environmental concerns Ketil Hylland ketilhy@bio.uio.no room 4533 reasons for concern reduced amount and quality of renewable resources increased input of particles, nutrients inputs of contaminants reduced biodiversity ? ? changed climate modified habitats changed ecosystems ? non-sustainable harvesting reduced recreational value introduced species 1 mortality spawning population (mill ton) non-sustainable harvesting detecting anthropogenic influence contaminants molecule homeostasis cell disease tissue/organ individual overfishing eutrophication ”noise” population community reproduction growth survival behaviour species plasticity predation competition ecosystem habitat destruction 2 two main challenges • identify and separate effects from different impacts • identify and separate/correct for natural processes (natural variability) pollution? disturbance or introduction into the oceans of substances or energy that cause a change in marine ecosystems 3 OSPAR QSR 2000 overview • eutrophication • oil • contaminants – – – – industrial chemicals pesticides, biocides sewage, waste endocrine disruptors, pharmaceuticals • water framework directive • marine strategy framework directive 4 eutrophication • organic matter in water column (and subsequently sediment) • two sources: – added nutrients (autochtonous) – supplied organic material (allochtonous) • relationship between enrichment and water exchange eutrophication algal production/high levels organic material sedimentation of organic material (dead algae, etc) Dennis Sarson (University of Western Austrialia) increased bacterial biomass high oxygen consumption limited exchange of bottom waters hypoxia (low concentrations of oxygen) dead bottom fauna 5 concepts • • • • • biological oxygen demand (BOD) chemical oxygen demand (COD) primary dilution anoxia, hypoxia redoxcline, Eh oil • many sources – – – – production transport refineries consumption • complex mixture: alkanes, PAH, alkylated phenols, .. • natural degradation • most obvious impacts on the surface – birds – fish larvae/embryos • difference acute - chronic 6 offshore oil and gas production • different phases – drilling: mainly benthic – production: mainly pelagic • decreased environmental impact of drilling fluids following benthic monitoring (change in use of chemicals) • natural (metals, alkylphenols, PAHs) and additional (biocides, complexing agents, etc) substances in produced water • continuous efforts to decrease use of persistent and/or toxic substances • technically possible to reduce 7 offshore pelagic monitoring 8 blue mussel • histopathology • micronucleus in hemocytes • lysosomal stability 9 clean-up of spills • mechanical – pumps – shovels, etc – hosing, heat/pressure www.chemgapedia.de • chemical – surfactants www.soundtruth.info 10 contaminants - why worry? • human health • marine resources • environmental impacts production of new chemicals 11 unexpected impacts - birds of prey unexpected impacts - imposex VDSI 0-2 >2 - 4 >4 - 6 12 how contaminant? • • • • • • • persistent toxic (one way or another) fat-soluble (Kow) molecular size solubility, volatility similarity with natural substances presence, levels, transport contaminants? • metals – organic/inorganic • halogenated substances • • • • – chlorinated: PCB, dioxins/dibenzofurans, many pesticides (toksafen, DDT, HCH) – brominated: PBDE, PBB, HCBD – fluorinated: PFOS, PFOA polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) organophosphates organotins (TBT) endocrine disrupting substances 13 concepts - contaminants • Kow • hydrophobic, hydrophilic, lipophilic, lipophobic • BCF, BAF, TSF, .. • bioavailability, bioaccumulation, biomagnification bioavailability ”the fraction of a substance available for interaction with tissues” ionestyrke Kow hydrofil TOC Pow Koc 14 bioaccumulation = uptake (excretion + metabolism) biomagnification BMF = CB/CD CB = in predator CD = in prey Ruus et al., 1999 1. Cod/Sandeel Σ PCB: 3.2 Σ DDT: 3.7 Σ CHL: 3.2 HCB: 2.1 2. 4. Harbour seal/Cod Σ PCB: 8.7 Σ DDT: 9.9 Σ CHL: 10.3 Σ HCH: 2.5 HCB: 0.3 5. Harbour seal/Sandeel Σ PCB: 28.0 Σ DDT: 36.9 Σ CHL: 33.5 Σ HCH: 2.1 Grey seal/Cod Σ PCB: 10.0 Σ DDT: 9.5 Σ CHL: 10.8 3. Grey seal/Sandeel Σ PCB: 32.2 Σ DDT: 35.4 Σ CHL: 35.0 HCB: 2.7 15 toxicity • • • • • LC50, LD50, EC50 dose-response sublethal effect tolerance essential – non-essential do PAHs cause cancer? cancer DNA adducts bile metabolites CYP1A induction and metabolism PAH in sediment studies by NOAA (US) by T.K.Collier, J. Stein, M.S.Myers, L.L.Johnson, J.T.Landahl, M.M.Krahn and others 16 neoplasia external diseases lymphocystis epidermal papilloma 17 sedimentation and radioactivity • sedimentation – mining – regulation – glaciers • radioactivity – – – – detectable at very low concentrations global distribution limited (known) environmental effects released in produced water (offshore) risk assessment • • • • hazard assessment effect assessment exposure assessment risk characterisation 18 water framework directive • classification • ecological assessment - based on biodiversity • EQS - ecological quality standards; mainly chemical • currently under implementation in EU (and Norway) • extends from freshwater into the sea classification • deviation from ”natural state” acceptable state high good small natural communitie deviations from natural s communitie s unacceptable state moderate low bad moderate deviations from natural communitie s 19 WFD - parameters • biological: phytoplankton, macrophytes and benthic algae, benthic organisms, fish • physical: hydrology, temperature, salinity, oxygen • chemistry: nutrients, pH, ANC, contaminants marine strategy framework directive • currently under development • will regulate coastal and oceanic waters • expected to be less risk-oriented than WFD 20 regulating pollution impacts • international agreements – long-range transport – marine (OSPAR) – EU WFD, MSFD • costal zone management – – – – – industrial inputs vs edibility harbour development vs fisheries/recreation oil exploration vs fisheries swimming vs sewage/eutrophication ... why worry? - Lomborg revisited • does it matter if local or regional biodiversity is decreased? • is bioaccumulation of contaminants a problem (below levels affecting human consumption)? • is there really evidence of large-scale impact of contaminants or eutrophication? • will future changes of the climate really affect marine ecosystems? • is there a difference between fertilisation and eutrophication? 21 questions • what is pollution? • what is eutrophication? • what are important sources of oil pollution and what are the main components of crude oil • describe the most important contaminants and their properties • provide two examples of how contaminants may cause ecosystem impacts 22