Driver Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
advertisement
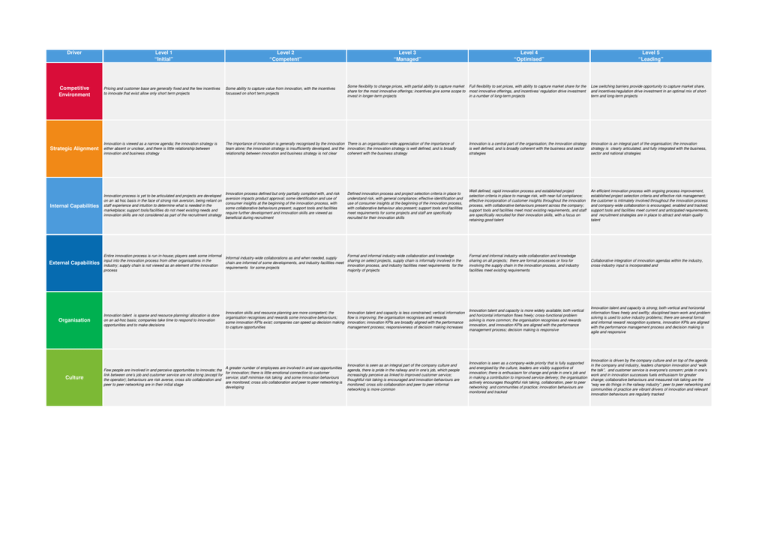
Driver Competitive Environment Level 1 “Initial” Level 2 “Competent” Level 3 “Managed” Level 4 “Optimised” Some flexibility to change prices, with partial ability to capture market Full flexibility to set prices, with ability to capture market share for the share for the most innovative offerings; incentives give some scope to most innovative offerings, and incentives/ regulation drive investment invest in longer-term projects in a number of long-term projects Level 5 “Leading” Low switching barriers provide opportunity to capture market share, and incentives/regulation drive investment in an optimal mix of shortterm and long-term projects Pricing and customer base are generally fixed and the few incentives to innovate that exist allow only short term projects Some ability to capture value from innovation, with the incentives focussed on short term projects Strategic Alignment Innovation is viewed as a narrow agenda; the innovation strategy is either absent or unclear, and there is little relationship between innovation and business strategy The importance of innovation is generally recognised by the innovation There is an organisation-wide appreciation of the importance of team alone; the innovation strategy is insufficiently developed, and the innovation; the innovation strategy is well defined, and is broadly relationship between innovation and business strategy is not clear coherent with the business strategy Innovation is a central part of the organisation; the innovation strategy is well defined, and is broadly coherent with the business and sector strategies Innovation is an integral part of the organisation; the innovation strategy is clearly articulated, and fully integrated with the business, sector and national strategies Internal Capabilities Innovation process is yet to be articulated and projects are developed on an ad hoc basis in the face of strong risk aversion, being reliant on staff experience and intuition to determine what is needed in the marketplace; support tools/facilities do not meet existing needs and innovation skills are not considered as part of the recruitment strategy Innovation process defined but only partially complied with, and risk aversion impacts product approval; some identification and use of consumer insights at the beginning of the innovation process, with some collaborative behaviours present; support tools and facilities require further development and innovation skills are viewed as beneficial during recruitment Well defined, rapid innovation process and established project selection criteria in place to manage risk, with near-full compliance; effective incorporation of customer insights throughout the innovation process, with collaborative behaviours present across the company; support tools and facilities meet most existing requirements, and staff are specifically recruited for their innovation skills, with a focus on retaining good talent An efficient innovation process with ongoing process improvement, established project selection criteria and effective risk management; the customer is intimately involved throughout the innovation process and company-wide collaboration is encouraged, enabled and tracked; support tools and facilities meet current and anticipated requirements, and recruitment strategies are in place to attract and retain quality talent External Capabilities Entire innovation process is run in-house; players seek some informal input into the innovation process from other organisations in the industry; supply chain is not viewed as an element of the innovation process Formal and informal industry-wide collaboration and knowledge Informal industry-wide collaborations as and when needed, supply sharing on select projects, supply chain is informally involved in the chain are informed of some developments, and industry facilities meet innovation process, and industry facilities meet requirements for the requirements for some projects majority of projects Formal and informal industry-wide collaboration and knowledge sharing on all projects; there are formal processes or fora for involving the supply chain in the innovation process, and industry facilities meet existing requirements Collaborative integration of innovation agendas within the industry, cross-industry input is incorporated and Organisation Innovation talent is sparse and resource planning/ allocation is done on an ad-hoc basis; companies take time to respond to innovation opportunities and to make decisions Innovation skills and resource planning are more competent; the organisation recognises and rewards some innovative behaviours; some innovation KPIs exist; companies can speed up decision making to capture opportunities Innovation talent and capacity is less constrained; vertical information flow is improving; the organisation recognises and rewards innovation; innovation KPIs are broadly aligned with the performance management process; responsiveness of decision making increases Innovation talent and capacity is more widely available; both vertical and horizontal information flows freely; cross-functional problem solving is more common; the organisation recognises and rewards innovation, and innovation KPIs are aligned with the performance management process; decision making is responsive Innovation talent and capacity is strong; both vertical and horizontal information flows freely and swiftly; disciplined team-work and problem solving is used to solve industry problems; there are several formal and informal reward/ recognition systems, innovation KPIs are aligned with the performance management process and decision making is agile and responsive Innovation is seen as an integral part of the company culture and agenda, there is pride in the railway and in one’s job, which people increasingly perceive as linked to improved customer service; thoughtful risk taking is encouraged and innovation behaviours are monitored; cross silo collaboration and peer to peer informal networking is more common Innovation is seen as a company-wide priority that is fully supported and energised by the culture, leaders are visibly supportive of innovation; there is enthusiasm for change and pride in one’s job and in making a contribution to improved service delivery; the organisation actively encourages thoughtful risk taking, collaboration, peer to peer networking and communities of practice; innovation behaviours are monitored and tracked Innovation is driven by the company culture and on top of the agenda in the company and industry, leaders champion innovation and “walk the talk”, and customer service is everyone's concern; pride in one’s work and in innovation successes fuels enthusiasm for greater change; collaborative behaviours and measured risk taking are the “way we do things in the railway industry”; peer to peer networking and communities of practice are vibrant drivers of innovation and relevant innovation behaviours are regularly tracked Culture A greater number of employees are involved in and see opportunities Few people are involved in and perceive opportunities to innovate; the for innovation; there is little emotional connection to customer link between one’s job and customer service are not strong (except for service; staff minimise risk taking and some innovation behaviours the operator); behaviours are risk averse, cross silo collaboration and are monitored; cross silo collaboration and peer to peer networking is peer to peer networking are in their initial stage developing Defined innovation process and project selection criteria in place to understand risk, with general compliance; effective identification and use of consumer insights at the beginning of the innovation process, with collaborative behaviour also present; support tools and facilities meet requirements for some projects and staff are specifically recruited for their innovation skills