This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this
material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this site.
Copyright 2015, The Johns Hopkins University and Michael Trush. All rights reserved. Use of these materials
permitted only in accordance with license rights granted. Materials provided “AS IS”; no representations or
warranties provided. User assumes all responsibility for use, and all liability related thereto, and must independently
review all materials for accuracy and efficacy. May contain materials owned by others. User is responsible for
obtaining permissions for use from third parties as needed.
Section D
Strategies to Alter Aflatoxin Toxicokinetics
and Toxicodynamics in Humans
The material in this video is subject to the copyright of the owners of the material and is being provided for educational purposes under
rules of fair use for registered students in this course only. No additional copies of the copyrighted work may be made or distributed.
Risk Factors for Liver Cancer
! Chemicals and viruses
3
Liver Cancer Etiology: A Case-Control Study in Taiwan
Hepatitis B virus surface
antigen status
Relative risk for
liver cancer
HBV antigen
negative
1.0
HBV antigen
positive
98.4
Source: Beasley et al. (1981). Lancet, 2, 1129.
4
Age-Specific Male HCC Incidence Rates
! Age-specific male HCC incidence rates in populations with similar
incidence of HBV
10-fold difference
© Copyright - International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), 2015. All Rights Reserved.
5
Aflatoxin Ingestion and Liver Cancer
! Aflatoxin ingestion and liver cancer incidence in humans
6
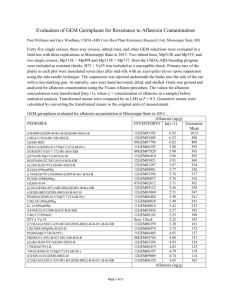
Study of Liver Cancer Risk Factors in Shanghai
! Nested case-control study of liver cancer risk factors in Shanghai
- 18,244 urine samples collected from healthy males (ages 45–64)
during 1986–1989
- 50 liver cancers developed in this group and cases were age
matched to 267 controls
- IAC/HPLC analysis was done on the coded samples for aflatoxin
urinary biomarkers
- Hepatitis virus B antigen status was determined
Sources: Ross et al. (1992). Lancet, 339, 943–946; Qian et al. (1994). Cancer Epi,
Biomarkers, and Prevention, 3, 3–10.
7
HBsAg and Urinary Aflatoxin Biomarker
! Combined effect of HBsAg and presence of urinary aflatoxin
biomarker on risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Shanghai
8
Liver Cancer (Male)
9
“Geographic Pathology”
10
“Geographic Pathology”
11
One in Ten Adults Develops HCC
12
Liver Cancer Incidence in Qidong
13
Liver Cancer Survival Rates in Qidong
14
Aflatoxin-Contaminated Staples in Qidong
! Dietary staples in Qidong consistently contaminated with aflatoxins
- Soy sauce
- Rice
- Peanuts
- Maize
15
Qidong Farm
16
Corn
17
Corn Storage
18
Corn Porridge
19
Peanuts
20
Peanuts
21
Strategies for Prevention
Primary
! Strategies for prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Immunization with HBV vaccine
- Reduced aflatoxin consumption
! Improve food storage; biocontrol
! Changes in dietary staples
22
Intervention Package in Kindia, Guinea
! Intervention villages
- Hand sorting: training in removal of groundnuts that were
visibly moldy or had the shells damaged
- Drying on mats: provision of locally produced natural fiber mats
for the sun drying process
- Sun drying: training in sun drying by shaking the kernels to
listen for the free movement of the dried nuts
- Storage in natural fiber bags: provision of natural fiber jute
bags to replace plastic or other synthetic bags
- Wooden pallets: provision of locally made wooden pallets on
which to store the bags
- Insecticide: provision of locally available insecticide (acetilite)
to sprinkle on the floor of the storage facility
! Control villages: farmers were left to follow their normal postharvest practices
23
Intervention
24
Primary Prevention
! Photos courtesy of Professor Chris Wild, University of Leeds
Improved groundnut storage in
Kindia, Guinea
25
Primary Intervention and Aflatoxin Biomarker Levels
26
Strategies for Prevention
Secondary
Primary
! Strategies for prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Immunization with HBV vaccine
- Reduced aflatoxin consumption
! Improve food storage; biocontrol
! Changes in dietary staples
- Chemopreventive interventions
! E.g., oltipraz, broccoli sprouts, chlorophyllin,
green tea
27
Cancer Chemoprevention
! Retardation, blockade, or reversal of the process of carcinogenesis
(before malignancy) by natural or synthetic agents, e.g., drugs,
foods, supplements
28
Cancer Chemoprevention
Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Assorted_Pills_3.JPG CC BY-SA
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ecologically_grown_vegetables.jpg CC BY-SA
29
Chlorophyllin
30
Chlorophyllin
! Semi-synthetic Na/Cu derivative of chlorophyll
! Non-prescription drug in the US
- Deodorizing activity (e.g., incontinent geriatric patients,
ileostomy/colostomy patients)
- Wound healing accelerant
! Food colorant
! Antioxidant, antimutagen and anticarcinogen in a variety of
experimental models
! Safe, inexpensive
31
Aflatoxin-Chlorophyllin Interaction
32
Chlorophyllin Intervention: Qidong
PE = physical exam
U = urine sample
S = serum sample
33
Chlorophyllin and Excretion of Aflatoxin-DNA Adducts
! Effect of three months of chlorophyllin on urinary excretion of
aflatoxin-DNA adducts
Source: Egner et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA). In press.
34
The Aflatoxin-DNA Adduct Is Excreted in Urine
! The aflatoxin-DNA adduct is unstable and is excreted in urine
35
Detoxication Enzymes from Vegetables
! Induction of detoxication enzymes by extracts from three families of
vegetables
36
Detoxication Enzymes from Vegetables
37
Broccoli Samples from Baltimore Area Markets
38
Protective Enzyme Inducer Potency
! Protective enzyme inducer potency: market stage broccoli versus
sprouts
39
Phase 2 Enzyme Induction Potency of Broccoli
40
Market-Stage Broccoli vs. Sprouts
41
Protection against Mammary Carcinogenesis in Rats
Source: Fahey et al. (1997). PNAS.
42
Broccoli Sprouts Intervention Trial
! Broccoli Sprouts Intervention Trial, He Zuo Township, Qidong, PRC
! Do broccoli sprouts modulate aflatoxin biomarkers?
43
Grew 200 kg Sprouts
44
Brewed 500 Liters of Sprouts Tea
! Dose = 125 ml (400 µmoles glucoraphanin)
45
Compliance Was 100%
46
Collected a “Truckload” of Urine
47
Glucosinolate Composition of Broccoli Sprouts “Tea”
48
Broccoli Sprouts Tea Intervention: He Zuo Township
! Urinary isothiocyanate/dithiocarbamate excretion
49
Urinary Excretions of Sulforaphane Metabolites
! Large INTER-individual variation in
urinary excretion of sulforaphane
metabolites
P < 0.001
50
Urinary Excretions of Sulforaphane Metabolites
! Small INTRA-individual differences in excretion of sulforaphane
metabolites in highest and lowest deciles
51
Measures of Exposure
52
Measures of Exposure
53
No Effect of Tea on Carcinogen Levels
! No effect of tea on urinary carcinogen biomarker levels based upon
“intent to treat”
AFB-N7-Guanine
fmol/mg creatinine
" Median (min, max)
Placebo
N=99
Tea
N=100
2.06 (0.12, 11.27)
1.88 (0.10, 7.75)
P-value
0.74
9%
Phenanthrene Tetraol
pmol/mg creatinine
" Median (min, max)
7.97 (0.45, 68.92)
7.20 (1.62, 28.53)
0.52
10%
Source: Kensler et al. (2005). CEBP.
54
Inverse Association
! Inverse association between urinary levels of sulforaphane
biomarker and aflatoxin-DNA adduct biomarker
55
Inverse Association
! Inverse association between urinary levels of sulforaphane
biomarker and phenanthrene tetraol (PheT) biomarker
56
The Public Health Significance of a 50% Reduction
! What might be the public health significance of a 50% reduction in
the burden of aflatoxin-DNA adducts ?
57
Age-Specific Incidence Rate of HCC
! Age-specific incidence rate of HCC: Qidong and Beijing
58
Age-Specific Incidence Rate of HCC
! Age-specific incidence rate of HCC: Qidong and Beijing
Public Health Benefit from
Intervention against Aflatoxin
Benefit from
HBV Vaccination
59
Lecture Evaluation
Please take a moment to evaluate
this lecture. Your feedback is very
important and will be used for future
revisions. The Evaluation link is
available on the lecture page.
60