This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this
material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this site.
Copyright 2011, The Johns Hopkins University and M.E. Hughes. All rights reserved. Use of these materials
permitted only in accordance with license rights granted. Materials provided “AS IS”; no representations or
warranties provided. User assumes all responsibility for use, and all liability related thereto, and must independently
review all materials for accuracy and efficacy. May contain materials owned by others. User is responsible for
obtaining permissions for use from third parties as needed.
Section D
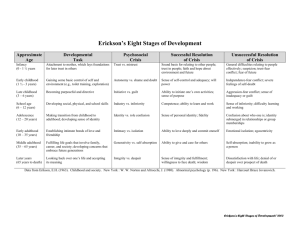
Determinants of Adult Health and Development
Determinants of Health Disparities
Disparities reflect groups’ relative social position which leads to
inequalities in access to resources of all types
This is called structured inequality—recall the Link and Phelan
(1995) we read for the third lecture
Unequal social positions expose people to “risk of risks” and so are a
fundamental cause of disease
3
Health Trajectories
Can conceptualize health trajectories: early experiences and health
influence later experiences and health
Risks accumulate over the life course
Key issue for public health is how to deflect or alter trajectories
4
Schematic Diagram of Health Trajectories
5
Early Influences on Adult Health
The effects we’ve discussed in the fetal period, infancy, childhood,
and adolescence carry over into adulthood
6
Early Influences on Health: Direct and Mediated
Fetal development (Barker)
Childhood adversity
Health behaviors learned in adolescence
Cognitive and social development in early childhood influence
school attainment, which influences adult occupational position and
social relationships
7
Relationship between Childhood Adversity and Chronic Disease
Childhood adversity increases odds of ischemic heart disease in
adulthood
8
Smoking in Adolescence and Beyond
Content for this slide to come
9
Child Development and Educational Attainment
Content for this slide to come
10
From Cognitive Development to Chronic Disease
Picture of pathway from cognitive development to chronic disease
via adult attainment
Content for this slide to come
11
Health Influences in Adulthood
Reflect continuation of earlier trajectories (previous slide)
Include new sources and types of risk (e.g., occupational hazards,
demands from social network)
May be exogenous (sudden job loss, natural disaster, displacement)
12
Two Key Domains of Adult Life
1. Work
2. Family life
13
Work Conditions and Cardiovascular Disease
Content for this slide to come
14
Marriage and Health
Content for this slide to come
15
Final Points
Health trajectories in adulthood set stage for later life—important
in aging societies
Social change due to economic development and Westernization
changes nature of adult life course and nature of health risks and
conditions
- Increasing age at marriage
Partly due to longer education
- Declines in fertility
- Differences in jobs
- Differences in gender roles
16