Exam 1, Tuesday, February 18: Review Questions, Chapters 1- 5
advertisement

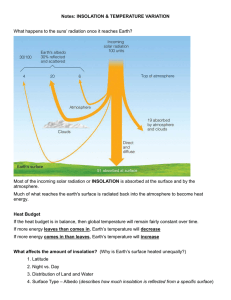
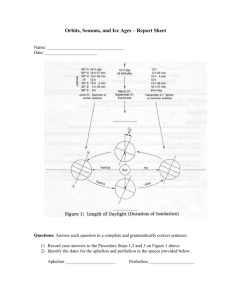
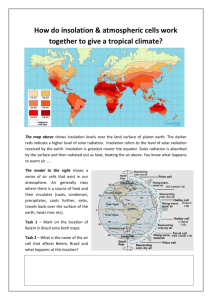
Exam 1, Tuesday, February 18: Review Questions, Chapters 1- 5 1. What is physical geography? 2. Name the four components of the earth system and give a definition of each sphere. 3. What is a great circle? What is Earth’s circumference (length of a Great Circle)? 4. Know the difference in the terms revolution and rotation. 5. What is shape of Earth’s orbit? What is perihelion and aphelion and in what month does each occur? 6. How many degrees is the earth's rotational axis tilted from a perpendicular to the Plane of the Ecliptic? 7. Understand how parallelism and tilt of the earth's axis cause the seasons. 8. Name the inner planets. List at least three things they have in common. 9. Name the outer planets. List at least three things they have in common. 10. Understand the system of latitude and longitude and the location of the Prime Meridian, International Dateline, North Pole, South Pole, and Equator. Be able to locate points on a map like the one I gave out in class. 11. What is the full name of the lines that measure the angular distance north or south of the Equator? 12. What is the full name of the lines that measure the angular distance east or west of the Prime Meridian? 13. Is one degree of latitude worth approximately the same number of miles anywhere on earth? Is one degree of longitude worth approximately the same number of miles anywhere on earth? Explain your answers. 14. How many time zones are there in the world? How many degrees in each idealized zone? If you go east, is the hour earlier or later? If you cross the dateline, how does the day change? What Meridian is Greenwich Mean Time centered upon? 15. What is the graticule? Know its 5 characteristics. 16. What are the 3 major map projections and how might you use the graticule to recognize each one? 17. Label these parallels of latitude. Know the latitude where the vertical rays of the sun strike on the June Solstice, the December Solstice, and the Equinoxes. 90N 66.5N 23.5N 0 23.5S 66.5S 90S 18. Define the map term "scale." What 3 ways can scale be expressed? Distinguish large scale from a small scale map. 19. What is an isoline? An isotherm? An isobar? What is the isoline interval? 20. What is the difference in meteorology and climatology? 21. What is insolation (use the three terms that the word is derived from)? 22. Total insolation depends on what 2 factors? 23. The intensity of insolation for any given location is a function of what 3 factors? 24. What two factors determine the duration of insolation? 25. Compare and contrast the seasonal (summer solstice, fall equinox, winter solstice, spring equinox) changes in insolation at the poles and at the equator. (That’s the chart we did in class) 26. Given a monthly insolation graph, be able to give the approximate latitude for that data. 27. What part of the earth has an energy surplus? an energy deficit?) 28. What is the troposphere? How does temperature change as you go up? Why does it change like that? 29. What component of the earth system created and now maintains our uniquely reactive atmosphere? 30. For ozone depletion and for global warming, understand the basics of how it works, problem, causes of the problem, consequences, and solutions (things you can do). 31. Define the term “albedo.” 32. Understand whether energy is taken from or released to the environment when water changes state. 33. Why does water heat and cool more slowly than land? What is continentality? 34. What is latent heat? 35. What is a temperature inversion? 36. How does atmospheric pressure vary with altitude? with temperature? with moisture content? 37. Know the relationships between seasonal insolation, temperature and pressure over land and water. 38. Relate air flow to the pressure gradient. 39. How are winds named? 40. Explain a land breeze and a sea breeze. 41. What is the Coriolis Force? Which way does it cause freely moving objects to go? 42. Know the direction that air circulates horizontally and vertically with a surface low and surface high in the northern hemisphere. 43. Know how air circulates in a low and high pressure cell in the northern and southern hemisphere.