Network Topology How topology decisions affect speed/availability/security/cost/etc.
advertisement

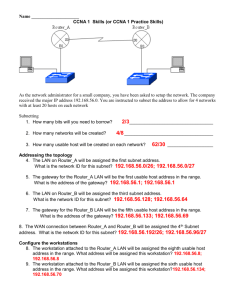
Network Topology How topology decisions affect speed/availability/security/cost/etc. Metrics for judging network design Cost $$$ Bandwidth Maintenance hours Clock cycles Electricity Space Cooling requirements Others ... Security Confidentiality Integrity Availability Authenticity Non-repudiation Biggest design trade-off: Availability vs. Confidentiality Dynamic vs. static addressing * Recommended settings: All workstations dynamic, all servers static. Workstation Dynamic Workstation Dynamic Workstation Dynamic Gateway Router Static DHCP server Static DNS server Static Dynamic addresses: • Allow machines to be easily added and removed • Simplifies management, reduces errors Static addresses: • Must/should be used for some servers • Reduces traffic for other servers (e.g. arp queries, DNS lookups) • Can be set in /etc/network/interfaces file Fileserver Either (Static recommended. Dynamic possible with discovery/DNS.) Webserver Either (Static recommended. Dynamic possible with DNS.) Mailserver Either (Static recommended. Dynamic possible with DNS.) Network “Attack Surface” * Each available port is theoretically open to attack IP: 5.5.5.5 ISP/Internet Router w/o NAT Switch IP: 5.5.5.5 ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Webserver IP: 5.5.5.100 Ports: 1-65535 DNS server IP: 5.5.5.101 Ports: 1-65535 Workstation IP: 5.5.5.102 Ports: 1-65535 Webserver IP: 5.5.5.100 Ports: 80, 443 DNS server IP: 5.5.5.101 Port: 53 Workstation IP: 5.5.5.102 Ports: None Basic Network Attacks “Front door” vs. “Back door” Webserver ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Fileserver Workstation • “Front door” attack originates from outside the network. Assume that the only open port on the router is 80, which goes to webserver Attacker finds an exploitable bug in the webserver. Attacker sends a packet that contains code that creates a shell between attacker and webserver 3. Attacker uses the shell to “pivot” to the workstation and fileserver * “Pivot” – to attack a device and gain a foothold (e.g. a shell) then use that 1. 2. foothold to attack other visible devices (ssh/telnet/metasploit/etc.). Basic Network Attacks “Front door” vs. “Back door” Webserver ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Fileserver Workstation • “Back door” attack originates from inside the network. Attacker sends an email with a malicious attachment 2. A workstation user clicks the attachment and runs the code 3. The code opens a connection to the hacker 4. The hacker now has a shell on the workstation and can install more software or pivot to other machines 1. Most basic topology * All servers & workstations in the ISP’s subnet * All IPs are visible to Internet Workstation Workstation ISP/Internet Router w/o NAT Switch PRO: • All IPs are easily accessible from anywhere in the world (Maximum Availability) • Low hardware costs CON: • All IPs are easily accessible from anywhere in the world (Minimum Confidentiality) • Can access every port on every IP remotely • Very large attack surface • Cost of buying one IP address for each device Workstation Webserver Fileserver WAP* * (WAP)Wireless Access Point Adding NAT * All servers & workstations in a single private subnet * Subnet IPs are hidden from Internet * The subnet appears as a single IP address for the router Workstation Workstation ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Workstation Webserver Fileserver WAP PRO: • Much smaller attack surface than previous slide • Only a few IP/port pairs are accessible through router CON: • All IPs are in the same subnet. An attacker who pwns one box can pivot to the others. Multiple isolated networks * Public servers are in blue subnet * Private servers & workstations are in green subnet Webserver Router w/ NAT Switch Router w/ NAT Router w/ NAT Switch WAP ISP/Internet PRO: • An attack against one network will not grant access to the other CON: • Extra Internet IP address is required • Extra routers, switches, licenses, etc. are required • Maintenance-intensive • Difficult to give special priviliges on bluenet from greennet machines Fileserver Workstation Workstation Workstation One network with a DMZ * Public servers are in blue subnet * Private servers & workstations are in green subnet Webserver ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Router w/ NAT WAP PRO: • An attack against the public webserver will not grant access to workstations or the private fileserver CON: • An extra router is required • “Double-NATing” of green subnet • Complexity increases chance of misconfigurations • Fileserver no longer available from outside LAN • WAP is a big target for attacks – will allow attacker to pivot to fileserver or workstations Switch Fileserver Workstation Workstation Workstation Moving WAP to DMZ * Wireless devices can now only connect to the public (blue) subnet WAP Webserver ISP/Internet Router w/ NAT Switch Router w/ NAT Switch Fileserver Workstation PRO: • An attacker can no longer access the private fileserver after attacking the WAP (Confidentiality UP) CON: • Mobile users no longer have access to the private fileserver (Availability DOWN) • Attacker can still pivot from WAP to webserver Workstation Workstation Single router with multiple subnets * WAP is moved to its own (purple) subnet Webserver ISP/Internet WAP Router w/ NAT Switch Fileserver Workstation PRO: • Increased separation of devices makes it difficult for attacker to pivot • Fewer routers CON: • More complex & expensive router required • Router rules are more complex, easier to misconfigure Workstation Workstation How many server applications per Webserver physical server? Fileserver Webserver, Fileserver, DNS, DHCP, FTP PRO: • Fewer physical servers to buy & maintain • Reduced cost, space, electrical req. • Security: • Only one box to patch • Fewer passwords to forget DNS DHCP FTP PRO: • Can buy smaller servers for each task • Can put servers in different subnets • Security: • Only 2-3 ports open per machine • Much easier to find attacks in logfiles & create firewall rules • A successful attack against one service does not grant control over all services Initial plan for class networks Webserver * Each group of 4 will build the following: Email server SI455 internet Router w/ NAT Switch DNS Router w/ NAT FTP Authentication Server DHCP Switch Bluenet: • Public – services available to other groups Greennet: • Private – services available only to user workstations Fileserver Workstation Workstation Workstation Workstation