Intro to Hypervisors
advertisement

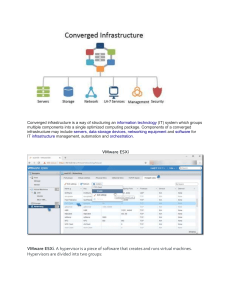
Intro to Hypervisors Big Picture: “It’s like VMWare Player, except you can build an entire network in it.” Multiple machines Switches Routers Multiple subnets Hypervisor/Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM) HOST MACHINE – runs the hypervisor software Our is carol.cs.usna.edu GUEST MACHINE – any VM running on the host The host: Runs multiple guest VMs (much like VMware Player) Connects the hosts with virtual switches May allow the hosts to access physical hardware such as network cards or Wireless AccessPoints Hosts can either: 1. 2. be sandboxed in a virtual network (unable to access Internet) access the outside world like any other server (e.g. webster) Physical layout for Hypervisors Type-1 (Native) hypervisors Type-2 (hosted) hypervisors e.g. VMware ESXi e.g. VMware Workstation VM VM Hypervisor VM VM VM Hypervisor OS Hardware Hardware VM Examples of servers running inside a hypervisor: rona – SI110 linux server nuzee – faculty linux server Semester project We will spend the semester building a complete network in a virtual environment (ESXi on carol) Add ESXi skills to your resume Hypervisors are your present and future 4x student subnets + instructor subnet 5x servers / subnet 2x routers / subnet 2x switches / subnet Total of 45+ devices replaced by a single rack-mounted server Other names you will see vSphere – suite of tools to manage networks on an ESXi server vCenter – centralized platform for managing multiple vSphere environments vCOPS – “vCenter Operations Manager”: a VM that runs inside carol to manage its own ESXi server gertie.cs.usna.edu (vCenter server) carol.cs.usna.edu (ESXi server) (VCOPS) Win 2008 (manages carol & peggy) peggy.cs.usna.edu (ESXi server) Software for accessing virtual network VMware vSphere Client VMware vCenter Converter Access any VM in the Copy VMs from local hypervisor machine to hypervisor Tour vSphere Client Home We will mostly be concenred with “Inventory” section Inventory → VMs and Templates Inventory → Datastores and Datastore Clusters Inventory → Networking