– Transformers Lesson 29 and Reflected Impedance
advertisement

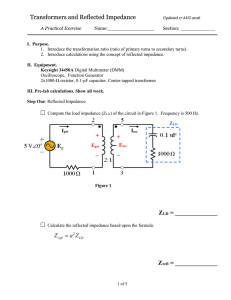
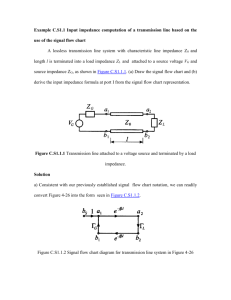
Lesson 29 – Transformers and Reflected Impedance Learning Objectives Predict the reflected impedance and derive an equivalent circuit using the reflected impedance. Calculate the transformation ratio to deliver maximum power to a load. Determine safe operation parameters from power transformer ratings. Explain how the transformer acts as an isolation device. List and explain several practical applications of transformers. REVIEW Winding direction The polarity of ac voltages can easily be changed by changing the direction of the windings. 0º phase shift 180º phase shift Transformation ratio The transformation ratio (or turns ratio) is given by the symbol a. a REVIEW E pri Esec I sec N pri I pri Nsec Because we are considering an ideal transformer, power in equals power out. Sin Sout E pri I pri Esec I sec Reflected Impedance Transformers make load impedances “look” bigger or smaller depending on their turns ratio “a”. Zpri-reflected is the impedance that “appears” at the primary windings. The term a2Zsec is referred to as the load’s reflected impedance. pri reflected E pri I pri aEsec 2 E sec a a 2 Zsec I sec I sec a Reflected Impedance Example Problem 1 a E pri Esec I sec N pri I pri Nsec pri reflected a 2 Zsec Use the reflected impedance concept to solve for the total impedance ZT. Determine Ig and ILD. NOTE: You must use the “reflected impedance” method any time there are line impedances in the primary circuit! Power Supply Transformers Power supply transformers are used to convert incoming 120 Vac to dc voltages of various levels necessary for different circuits. Impedance Matching Transformers are used to raise or lower the apparent impedance in order to achieve maximum power transfer. Example Problem 2 An amplifier is modeled with a Thèvenin equivalent impedance of 36-54j . a. b. What load impedance must be chosen to ensure maximum power transfer occurs? What is the transformer load (VA) for this value of ZLD? Example Problem 3 An amplifier is modeled with a Thèvenin equivalent impedance of 320-160j . A transformer is used to impedance match the load to the source to ensure max power transfer. a. b. What turns ratio should be chosen for the transformer, and what value of load resistance should be chosen to ensure max power transfer? What is the real and reactive power of the load? What is the real and reactive power delivered by the source?