ECE 411
advertisement

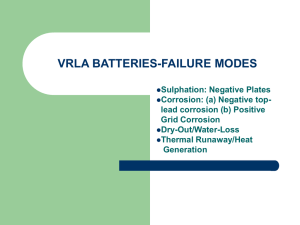
Course Syllabus ECE 411 – Electric Power Systems Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering 1. Course Number and Name: 2. Credit Units/Contact Hours: 3. Course Coordinator: ECE 411 – Electric Power Systems 3/3 Bruno Osorno 4. Text, References & Software Recommended Text: Textbook:”Power System Analysis” by Grainger and Stevenson, Published by McGraw-Hill, First Edition 1994. Additional References: IEEE power systems, journal Software: PSPICE, by ORCAD MicroSim Corporation, Matlab, Web browser such as explorer or Netscape, Microsoft Office (see Internet Resources below); Internet Resources: http://www.orcad.com/ (for downloading PSPICE) 5. Specific Course Information a. Course Description Review of single phase, three phase power and calculations of power using the “per-unit” method. Study of single line diagrams using reactance and impedance, three phase transformers as applied to power systems and synchronous machines. Discussion of series impedance, capacitance, voltage and current as related to power transmission lines. Modeling of admittance, impedance and network calculations are included. Flexible AC Transmission Systems (FACTS) and Automated Transmission Operations (ATO) are discussed as a consequence of the implementation of the smart grid. Also the effects of magnetic field in power transmission lines are discussed. Design and simulation projects are included. Students make presentations about their findings. PSPICE and Matlab are utilized. b. Pre-requisites by Topic Students should know the basic concepts of electromagnetism, such as inductance, capacitance and Maxwell’s laws. Also students should know basic DC and AC circuit analysis as well as vector and complex algebra (ECE240, MATH280). Calculus and differential equations need to be known and master their application. c. Elective Course 6. Specific Goals for the Course a. Specific Outcomes of Instructions – After completing this course the students should be able to: 1. Solve circuits with transformers 2. 3. 4. 5. Analyze synchronous generators Analyze and calculate series impedance and capacitance in transmission lines Analyze current voltage relations of a transmission line Analyze and design of a practical power transmission line b. Relationship to Student Outcomes This supports the achievement of the following student outcomes: a. An ability to apply knowledge of math, science, and engineering to the analysis of electrical engineering problems. b. An ability to design and conduct scientific and engineering experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. c. An ability to design systems which include hardware and/or software components within realistic constraints such as cost, manufacturability, safety and environmental concerns. e. An ability to identify, formulate, and solve electrical engineering problems. g. An ability to communicate effectively through written reports and oral presentations. i. A recognition of the need for and an ability to engage in life-long learning. k. An ability to use modern engineering techniques for analysis and design. m. An ability to analyze and design complex devices and/or systems containing hardware and/or software components. n. Knowledge of math including differential equations, linear algebra, complex variables and discrete math. 7. Topics Covered/Course Outline 1. Review of phasor, Single-Phase and Three-Phase Power. 2. Review of Basic Concepts of Transformers 3. Review of Basic Concepts of Synchronous Machines. 4. Series Impedance of Transmission Lines. 5. Capacitance of Transmission Lines. 6. Current and Voltage Relations on a Transmission Lines. 7. The Admittance Model and Network Calculations. 8. The Impedance Model and Network Calculations. Prepared by: Bruno Osorno, Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, November 2011 Ali Amini, Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, March 2013