QCC COURSE ASSESSMENT FORM Fall 2011 Date: May 31, 2012
advertisement
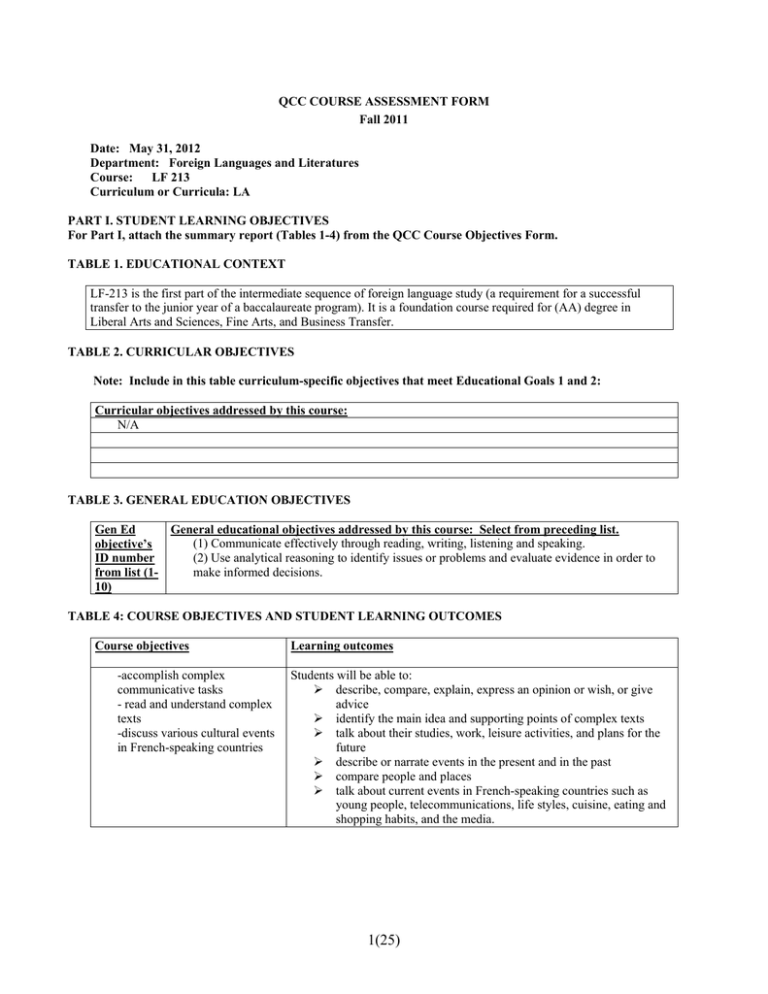
QCC COURSE ASSESSMENT FORM Fall 2011 Date: May 31, 2012 Department: Foreign Languages and Literatures Course: LF 213 Curriculum or Curricula: LA PART I. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES For Part I, attach the summary report (Tables 1-4) from the QCC Course Objectives Form. TABLE 1. EDUCATIONAL CONTEXT LF-213 is the first part of the intermediate sequence of foreign language study (a requirement for a successful transfer to the junior year of a baccalaureate program). It is a foundation course required for (AA) degree in Liberal Arts and Sciences, Fine Arts, and Business Transfer. TABLE 2. CURRICULAR OBJECTIVES Note: Include in this table curriculum-specific objectives that meet Educational Goals 1 and 2: Curricular objectives addressed by this course: N/A TABLE 3. GENERAL EDUCATION OBJECTIVES General educational objectives addressed by this course: Select from preceding list. Gen Ed (1) Communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening and speaking. objective’s (2) Use analytical reasoning to identify issues or problems and evaluate evidence in order to ID number make informed decisions. from list (110) TABLE 4: COURSE OBJECTIVES AND STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES Course objectives -accomplish complex communicative tasks - read and understand complex texts -discuss various cultural events in French-speaking countries Learning outcomes Students will be able to: describe, compare, explain, express an opinion or wish, or give advice identify the main idea and supporting points of complex texts talk about their studies, work, leisure activities, and plans for the future describe or narrate events in the present and in the past compare people and places talk about current events in French-speaking countries such as young people, telecommunications, life styles, cuisine, eating and shopping habits, and the media. 1(25) PART II. ASSIGNMENT DESIGN: ALIGNING OUTCOMES, ACTIVITIES, AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS For the assessment project, you will be designing one course assignment, which will address at least one general educational objective, one curricular objective (if applicable), and one or more of the course objectives. Please identify these in the following table: TABLE 5: OBJECTIVES ADDRESSED IN ASSESSMENT ASSIGNMENT Course Objective(s) selected for assessment: (select from Table 4) 1. Provide information in French on topics such young people, telecommunications, life styles, cuisine, eating and shopping habits, and the media 2. Demonstrate ability to accomplish communicative tasks such as comparing and contrasting people’s customs and beliefs, narrating in the present and past, describing events, people and objects in the past, analyzing past and present cultural practices, and talking about artistic expressions. Curricular Objective(s) selected for assessment: (select from Table 2) N/A General educational objectives addressed by this course: Select from preceding list. 1. Communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening and speaking. 2. Use analytical reasoning to identify issues or problems and evaluate evidence in order to make informed decisions In the first row of Table 6 that follows, describe the assignment that has been designed for this project. In writing the description, keep in mind the course objective(s), curricular objective(s) and the general education objective(s) identified above, The assignment should be conceived as an instructional unit to be completed in one class session (such as a lab) or over several class sessions. Since any one assignment is actually a complex activity, it is likely to require that students demonstrate several types of knowledge and/or thinking processes. Also in Table 6, please a) identify the three to four most important student learning outcomes (1-4) you expect from this assignment b) describe the types of activities (a – d) students will be involved with for the assignment, and c) list the type(s) of assessment tool(s) (A-D) you plan to use to evaluate each of the student outcomes. (Classroom assessment tools may include paper and pencil tests, performance assessments, oral questions, portfolios, and other options.) Note: Copies of the actual assignments (written as they will be presented to the students) should be gathered in an Assessment Portfolio for this course. 2(25) TABLE 6: ASSIGNMENT, OUTCOMES, ACTIVITIES, AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS Briefly describe the assignment that will be assessed: This project will assess students’ overall abilities. Conversational abilities Students’ conversational abilities will be assessed by engaging them in role-play activities where both they and the instructor play a specific role. Students may play the role of… - a person looking for a job at the Alliance Française in NYC, - a person talking with his/her best friend after participating in a study abroad program in France or - a student answering an ad and looking for a place to live. (See Appendix 1 for a description of the oral exam) Written abilities Their listening, reading and writing abilities as well as their knowledge of grammar and vocabulary will be assessed by a comprehensive final exam. See below for a description of the final exam. Listening comprehension abilities will be evaluated by asking the students to listen to… - a series of personalized questions - a passage in French (which is three voice messages left by three different people) Students will be then asked to complete a true or false section and a multiple-choice section. Reading abilities will be evaluated by asking the students to read two passages: one about the Versailles castle in France, and the other regarding children education in Tahiti. Students will be then asked to answer true/false questions in one instance, and multiple choice questions in the other. Vocabulary knowledge will be assessed by asking the students to complete a fill-in the blank exercise on the following lexical themes… - social problems (unemployment, poverty, criminality…) - technology (computers, TV, and phones) - food, shopping, departmental stores versus and small neighborhood stores - news, press, and media publications (daily newspapers, magazines, weekly newspapers, monthly newspapers, literary or scientific magazines, comic books…) Grammar accuracy will be assessed by asking the students to complete various sections (fill in the blanks and exercises based on vignettes). Students are asked to use the correct form of… - past tense (present perfect) - imperfect - difference between present perfect and imperfect - superlatives Writing abilities will be assessed by asking the students to describe their recent trip to France. They are encouraged to talk about what they have learned there, about the French culture, and include… - cuisine, shopping, stores, and malls - housing and housing conditions - life, sport, and leisure of young people - French TV and telecommunications. Desired student learning outcomes for the assignment (Students will…) List in parentheses the Curricular Objective(s) and/or Briefly describe the range of activities student will engage in for this assignment. Listening comprehension: listen 3(25) What assessment tools will be used to measure how well students have met each learning outcome? (Note: a single assessment tool may be used to measure multiple learning outcomes; some learning General Education Objective(s) (1-10) associated with these desired learning outcomes for the assignment. to one passage and a series of personalized questions followed by multiple choice and true/false answers. Gen-Ed objective (1) Communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening and speaking. Reading activity: read two passages followed by multiple choice and true/false answers. (2) Use analytical reasoning to identify issues or problems and evaluate evidence in order to make informed decisions. Curricular objectives N/A Vocabulary activity: complete various fill in the blank exercises. Grammar activities: complete various sections with verbs and superlative structures. Writing activities: write a composition about a recent trip to France. Speaking abilities. Students will engage in a role-play activity with his/her instructor. The activity is designed so that it can be completed in 7-10 minutes interaction, students will select at random one of three situations (see detailed description above). 4(25) outcomes may be measured using multiple assessment tools.) Students will be asked to listen to two conversations and answer questions. Students will be asked to read two paragraphs and answer questions. Students will be asked to provide the correct vocabulary in various exercises. Students will be asked to provide sentences using the correct verb morphology and mode. Students will be asked to describe in writing a recent trip that they had in France. Oral interview. Role-play activity: Students will be asked to complete a task where they need to look for a job at the Alliance Française in NYC - talk with their best friend after participating in a study abroad program in France or - answer an ad and look for a place to live. They will be assessed using the rubric for oral assessment designed by the department (See appendix 2 for a detailed description) PART III. ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (RUBRICS) Before the assignment is given, prepare a description of the standards by which students’ performance will be measured. This could be a checklist, a descriptive holistic scale, or another form. The rubric (or a version of it) may be given to the students with the assignment so they will know what the instructor’s expectations are for this assignment. Please note that while individual student performance is being measured, the assessment project is collecting performance data ONLY for the student groups as a whole. TABLE 7: ASSESSMENT STANDARDS (RUBRICS) Brief description of assignment: (Copy from Table 6 above) Conversational abilities This project will assess students’ speaking abilities at a intermediate low level as described in ACTFL 2006 guidelines. Their conversational abilities will be assessed by engaging them in role-play activities where both they and the instructor play a specific role. Students may play the role of… - a person looking for a job at the Alliance Française in NYC - a person talking with his/her best friend after participating in a study abroad program in France or - a student answering an ad and looking for a place to live. Written abilities Their listening, reading and writing abilities as well as their knowledge of grammar and vocabulary will be assessed by a comprehensive final exam. See below for a description of the final exam. Listening comprehension abilities will be evaluated by asking the students to listen to… - a series of personalized questions - a passage in French (which is three voice messages left by three different people) Students will be then asked to complete a true or false section and a multiple-choice section. Reading abilities will be evaluated by asking the students to read two passages: one about the Versailles castle in France, and the other regarding children education in Tahiti. Students will be then asked to answer true/false questions in one instance, and multiple choice questions in the other. Vocabulary knowledge will be assessed by asking the students to complete a fill-in the blank exercise on the following lexical themes… - social problems (unemployment, poverty, criminality…) - technology (computers, TV, and phones) - food, shopping, departmental stores versus and small neighborhood stores - news, press, and media publications (daily newspapers, magazines, weekly newspapers, monthly newspapers, literary or scientific magazines, comic books…) Grammar accuracy will be assessed by asking the students to complete various sections (fill in the blanks and exercises based on vignettes). Students are asked to use the correct form of… - past tense (present perfect) - imperfect - difference between present perfect and imperfect - superlatives Writing abilities will be assessed by asking the students to describe their recent trip to France. They are encouraged to talk about what they have learned there, about the French culture, and include… - cuisine, shopping, stores, and malls - housing and housing conditions 5(25) - life, sport, and leisure of young people - French TV and telecommunications. Desired student learning outcomes from the assignment: (Copy from Column 1, Table 6 above; include Curricular and /or General Education Objectives addressed) Assessment measures for each learning outcome: (Copy from Column 3,Table 6 above) Students will be asked to listen to two conversations and answer questions. Gen-Ed objectives (1) Communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening and speaking. Students will be asked to read two paragraphs and answer questions. 2) Use analytical reasoning to identify issues or problems and evaluate evidence in order to make informed decisions. Curricular objectives N/A Students will be asked to provide the correct vocabulary in various exercises. Students will be asked to provide sentences using the correct verb morphology and mode. Students will be asked to describe in writing a recent trip that they had in France. Oral interview. Role-play activity: Students will be asked to complete a task where they need to look for a job at the Alliance Française in NYC - talk with their best friend after participating in a study abroad program in France or - answer an ad and look for a place to live. They will be assessed using the rubric for oral assessment designed by the department (See appendix 2 for a detailed description) Standards for student performance: The parameters for measuring students’ speaking abilities will be to determine whether: (i) they understand the questions being asked by the interlocutor and they respond without probing, (ii) they speak continuously with few pauses or stumbling, (iii) they are understood by the interlocutor by using the correct intonation and pronunciation, (iv) they speak with some degree of fluidity, (v) they use correctly the required grammatical structures and (vi) they use the appropriate vocabulary Students’ listening comprehension ability will be determined by calculating their accuracy rates in providing the correct answers to the questions asked. 75 per cent of them are expected to meet the course standards (80% accuracy rate). Students’ reading comprehension ability will be determined by calculating their accuracy rates in providing the correct answers to the questions asked. 75 per cent of them are expected to meet the course standard (80% accuracy rate). Students’ vocabulary knowledge will be determined by calculating the accuracy rates in providing the correct words or phrases in a given situation. 75 per cent of them are expected to meet the course standard (80% accuracy rate). Students’ grammar knowledge will be determined by calculating their accuracy rates in providing the correct forms or structures. 75 per cent of them are expected to meet the course standards (80% accuracy rate). The parameters used to measure students’ writing abilities will be to determine whether: (i) they will provide all the information they have been asked, (ii) their writing displays a vocabulary appropriate to their proficiency level, (iii) they show an adequate control of the syntactic structures for a French beginning 6(25) level class, (iv)their sentences are fully developed, even though sporadically connected. 75% of the students tested are anticipated to meet the course’s expectations as described in the attached rubric. 7(25) PART IV. ASSESSMENT RESULTS TABLE 8: SUMMARY OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS Use the following table to report the student results on the assessment. If you prefer, you may report outcomes using the rubric(s), or other graphical representation. Include a comparison of the outcomes you expected (from Table 7, Column 3) with the actual results. NOTE: A number of the pilot assessments did not include expected success rates so there is no comparison of expected and actual outcomes in some of the examples below. However, projecting outcomes is an important part of the assessment process; comparison between expected and actual outcomes helps set benchmarks for student performance. TABLE 8: SUMMARY OF ASSESSMENT RESULTS Desired student learning outcomes: (Copy from, Column 1,Table 6 above; include Curricular and/or General Education Objectives addressed) Gen-Ed objectives Communicate effectively through reading, writing, listening and speaking. Student achievement: Describe the group achievement of each desired outcome and the knowledge and cognitive processes demonstrated. See Table 9 Curricular objectives N/A 8(25) TABLE 9. EVALUATION AND RESULTING ACTION PLAN In the table below, or in a separate attachment, interpret and evaluate the assessment results, and describe the actions to be taken as a result of the assessment. In the evaluation of achievement, take into account student success in demonstrating the types of knowledge and the cognitive processes identified in the Course Objectives. A. Analysis and interpretation of assessment results: 1. Speaking task. Oral interview: 12 students completed the speaking task in French, and their performance was rated according to five parameters: listening comprehension, fluidity, pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. Student performance was scored using the scoring rubric (Appendix II). The results are as follows: Table 1 Average Score in Each Category Listening comprehension Range Listening Comprehension 4 Fluidity Pronunciation Vocabulary Grammar Total 4 4 4 4 20 Average score 3.7 3.7 3.9 2.1 3.5 16.9 # of students 12 12 12 12 12 12 The total points a student could achieve (adding up all five parameters, each worth a maximum of four points) was 20. The scale agreed upon beforehand by the Assessment Committee defined the following ranges: 0-5 points= student performance does not meet expectations; 6 – 10 points= student performance almost meets expectations; 1115 points= student performance meets expectations; 16-20= student performance exceeds expectations. The results for percentage of students in each category are as follows: Table 2 Percentage of Students in Each Proficiency Level Range # of students Percentage Does not meet expectations 0-5 0 0% Almost meets expectations 6-10 0 0% Meets expectations 11-15 4 33.33% The overall student performance shows that all students (100%) met or exceeded expectations. 9(25) Exceed expectations 16-20 8 66.66% 2. Written Final Examination The data of 12 students who completed the written final exam in French was gathered. Their performance was rated according to five categories: listening comprehension, vocabulary, grammar, reading and writing. The results are as follows: Table 3 SCORING SHEET- LF General Performance in E ach Category Listening Vocabulary Grammar Reading Writing Total Range 0-16 0-16 0-36 0-16 0-16 0-100 Score 15.5 10.4 28.3 13.7 11.6 79.5 # of Students 12 12 12 12 12 12 The average score achieved was 79.5% The total points a student could achieve (adding up all five categories) was 100. The scale agreed upon beforehand by the Assessment Committee defined the following ranges: 0-60 points= student performance does not meet expectations; 61–73 points= student performance almost meets expectations; 74-89 points= student performance meets expectations; 90-100= student performance exceeds expectations. Table 4 OVERALL. Student performance … Does not meet Almost meets expectations expectations 0-60 61-73 Meets expectations 74-89 Exceeds expectations 90-100 # 0f Students 2 2 5 3 Percentage 16.66% 16.66% 41.66% 25% Range The overall student performance shows that only 66% of students met or exceeded expectations. The results for percentage of students in each category are as follows: Table 5 LISTENING. Student performance … Range # of Students Does not meet expectations 06 0 Almost meets expectations 6.59.5 0 Meets expectations 10-13.5 2 Exceeds expectations 1416 10 Percentage 0 0 16.7 83.3 Table 6 VOCABULARY. Student performance … Range # of Students Does not meet expectations 06 4 Almost meets expectations 6.59.5 6 10(25) Meets expectations 10-13.5 0 Exceeds expectations 1416 2 Table 7 Percentage 33.3 50 0 16.7 GRAMMAR. Student performance … Does not meet Almost meets Meets expectations expectations expectations 0-16 16.5-22.5 23-30.5 Exceeds expectations 31-36 # of Students 1 5 3 3 Percentage 8.3 41.7 25 25 Range Table 8 READING. Student performance … Does not meet Almost meets Meets expectations 0- expectations 6.5expectations 6 9.5 10-13.5 Exceeds expectations 1416 # of Students 0 4 3 5 Percentage 0 33.3 25 41.7 Range For rating student performance the writing the scoring rubric was used (Appendix IV). Table 9 WRITING. Student performance … Does not meet Almost meets expectations 0- expectations 6.56 9.5 Meets expectations 10-13.5 Exceeds expectations 1416 # of Students 3 4 3 2 Percentage 25 33.3 25 16.7 Range B. Evaluation of the assessment process: What do the results suggest about how well the assignment and the assessment process worked both to help students learn and to show what they have learned? Speaking test: The results of the oral interview: all students (100%) met or exceeded expectations. This is a very positive result. Written test: In the final written exam the overall performance results show the following percentages of students who met or exceeded expectations in the different categories: - 100 % in listening, - 16.7 % in vocabulary, - 50 % in grammar , - 66.7 % in reading comprehension, - 41 % in writing. B2) Evaluation of the assessment A formal evaluation of the assessment tools and assessment process has not been conducted, but informal reactions from students were positive overall. The majority of students seemed to have taken the speaking task assessment 11(25) seriously, and they seemed to have studied for it, even practicing with the tutors at the SLC. Faculty gave of their personal time to be able to complete the student oral assessments. The results obtained seem to indicate that the assessment tools used and the assessment process undertaken has been effective in determining our students’ strengths and weaknesses. C. Resulting action plan: Based on A and B, what changes, if any, do you anticipate making? The average achieved in the oral interview was satisfactory. However, the averages in other categories show weaknesses in… - vocabulary (speaking test) - vocabulary, grammar and writing (written test) This observation should be taken into consideration in our teaching in order to improve these results and students’ performance. Conclusion and Action Plan The acquisition scenario among the foreign languages evaluated (Italian, Spanish and French) lacks uniformity. As Table 1 shows, in the three languages, the number of students reaching the proficiency levels set up for an intermediate language course (LX213) ranges from 100% (Italian) to 67% (French), and 38% (Spanish). Members of the committee seem to have diverging opinions on the assessment tools and on the scoring scale used to achieve these results. Therefore, the committee will reconvene to discuss at length on the actions to take, the significance of the results, and the re-evaluation of the assessment tools and the scoring scales used. Table 1 LX213 Percentage of Students in Each Proficieny Level (except oral) 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 Italian Spanish French 0 35 17 Almost meets expectations (61‐73) 0 27 17 Meets expectations (74‐89) 62 27 42 Exceeds expectations (90‐100) 38 11 25 Does not meet expectations (0‐60) In fact, as shown in Table 2, the average score of Spanish students was 68.1% vs. 79.5% (French) and 85.3% (Italian), indicating that their overall performance was significantly below the course expectations (74 to 89). Interestingly, such discrepancies were also noticed in a previous assessment of beginners II during the academic year 2010-2011. Table 2 12(25) Spanish students scored lower than the Italian and French learners, even though all three language groups reported some weaknesses in the Vocabulary, Grammar and Writing areas. In other words, they showed a general lack of grammatical accuracy and poor assimilation of the vocabulary which has affected the quality of their written production. Table 3 Table 3 indicates the average score in each category: listening, vocabulary, grammar, reading and writing. Table 4 Table 3 indicates the average score in the overall oral assessment. The results in the oral assessment do not show the same discrepancies as in the overall written seen above. 13(25) In the oral assessment none of the students was in the “does not meet expectation” category (compared to 35% in the written assessment, see above). Aside from that, only 17 percent performed below the “Meets expectations level.” As Table 5 shows, students in all three languages performed better than in the written assessment. It shows that 83% of the students of Spanish met expectations, which is 8% above the 75 percent which is normally expected, while all students of Italian and students of French met or exceeded the expectations. Table 5 Despite the performance above the expected 75 percent of all students of the three languages, a closer look at the data reveals that there are divergences among the three language groups in all areas (see Table 6 below). For instance, the three groups of learners did not report visible difficulty in understanding the instructor, and using the target language with appropriate speed and pronunciation. However, similarly to the written test, their use of the vocabulary and their grammatical accuracy was not as native-like. The most affected were the Spanish learners followed by the French ones. 14(25) In Table 6 below the results of French in the oral assessment are not consistent with the results in the written assessment, especially in the vocabulary and grammar results. The students of French exceed the performance of students of Italian in the oral grammar category, which was not the case in the written assessment. In the vocabulary area, the students of French performed worse in the oral assessment than the students of Spanish, but in the written assessment they had exceeded the performance of the students of Spanish. Table 6 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 LX213 Oral Assessment Average Score in Each Category Listening Fluidity Pronunciation Vocabulary Grammar 4 4 4 4 4 Italian 3.6 3.6 3.6 3.1 3.1 Spanish 3.5 3 3.2 2.7 2.6 French 3.7 3.7 3.9 2.1 3.5 Maximum score In sum, data collected shows that, although students tend to do better in the oral task, they seem to encounter greater difficulties in properly acquiring the necessary lexical and syntactic expertise of the target language. The weaknesses in the oral assessment show that vocabulary and grammar needs improvement and in the written assessment the same two areas need more emphasis as well as writing. This situation needs to be addressed and discussed with all faculty members, and some changes in our teaching and assessment strategies need to be introduced. Students will continue to be encouraged to attend the College Learning Center where their acquisition problems may be individually addressed by the tutors. Furthermore, the educational staff of the Foreign Language Department should continue working with CETL (the Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning) to find more effective ways to tackle and solve this problem. 15(25) APPENDIX I SITUATIONS FOR ORAL ASSESSMENT IN FRENCH 213– FALL 2011 Oral assessment It is a conversation between teacher and student (about 10 minutes) Student selects AT RANDOM one of three situations (see following pages) Student should answer with complete sentences. English is not allowed. Listening comprehension, fluidity, pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar will be evaluated For top results: a. Listening comprehension: understand the questions and respond easily without probing b. Fluidity: speak continuously with few pauses or stumbling c. Pronunciation: pronounce properly d. Vocabulary: use the appropriate vocabulary. Don’t repeat the same words e. Grammar: use the necessary grammatical structures correctly Study guide: Practice the following situations and questions: a. in class b. with your classmates outside the classroom c. with a tutor at the Student Learning Center in the Library Building (L-125) d. with your French-speaking friends When practicing, always KEEP IN MIND the skills you will be tested on (see attached rubric) 16(25) SITUATION 1. UN(E) COLOCATAIRE You are looking for a roommate and student from France (played by your instructor) answers your ad. (S)he just moved to NY from France for a year at QCC. (S)he has several questions for you. This is an informal conversation (use « tu »). - Greet each other and exchange names Give personal information to warm-up Start the conversation with questions and answers, and finally… Wrap-up and goodbyes Questions possibles: A. Parle-moi de ton quartier. 1. Tu habites dans quel quartier? 2. Qu’est-ce que tu aimes dans ton quartier? Pourquoi ? 3. Qu’est-ce que tu n’aimes pas dans ton quartier? Pourquoi ? 4. Ton quartier est près du métro ? du train ? du bus ? de la fac ? 5. Quels sont les problèmes sociaux de ton quartier ? 6. Qu’est-ce que tu penses de ces problèmes ? 7. Quelle sorte de logements y a-t-il dans ton quartier ? Y a-t-il des HLM ? Peux-tu me les décrire ? 8. Qu’est-ce que tu penses des logements collectifs ? 9. Tu habitais où avant ? Cela te plaisait ? Pourquoi ? 10. Pourquoi est-ce que tu as changé de quartier? B. Décris-moi ton immeuble ou ta maison. 11. Tu peux me parler des locataires de ton immeuble ? 12. Quelle sorte de personnes habitent un immeuble comme le tien ? 13. Penses-tu que les conditions de logement y soient satisfaisantes ? Pourquoi ? 14. La surface moyenne d’un appartement te semble petite, normale ou grande ici? C. Parle-moi de ton appartement. 15. Tu peux me décrire ton appartement et tes colocataires? Ils sont sympas ? 16. Qu’est-ce que tu fais avec eux ? 17. Quel type de problèmes avez-vous? 18. Tu peux me décrire une situation de conflit que tu as vécue avec eux ? Comment est-ce que vous avez résolu le conflit ? 19. Dans quel appartement habitais-tu avant ? Cela te plaisait ? Pourquoi ? 20. Pourquoi est-ce que tu as changé d’appartement? D. Qu’est-ce que tu penses de la banlieue de NY? Qu’est-ce que tu penses de Manhattan? 21. Qu’est-ce que tu aimes dans la banlieue ? Qu’est-ce que tu n’aimes pas dans la banlieue ? Pourquoi ? 22. Qu’est-ce que tu aimes dans la ville ? Qu’est-ce que tu n’aimes pas dans la ville ? Pourquoi ? 23. Tu préfères la campagne ou la ville ? Pourquoi ? E. Tu peux me décrire ta routine typique ? 24. Quelle est ta routine? Qu’est-ce que tu fais pendant la journée ? 25. Tu te réveilles à quelle heure le matin ? Tu te couches à quelle heure le soir ? 26. Habites-tu seul(e) ou avec ta famille ou un(e) camarade de chambre ? 27. Tu fais la cuisine? Quand ? Qu’est-ce que tu sais préparer ? 28. Tu sors ? Quand ? Avec qui ? Tu vas où ? 29. Qui fait le ménage ? et quand ? 30. Quels cours suis-tu à la fac? G. Tu as des questions pour moi, n’est-ce pas ? 17(25) SITUATION 2: AU CAFÉ You meet with a friend of yours (played by your instructor) at the coffee shop. You just got back to the US after two years spent in France within a study abroad program. Your friend asks you questions about your experience abroad. What would you say, and how would you answer his/her questions? This is an informal conversation (use « tu »). - Greet each other Share your memories Festivities and traditions Wrap up and goodbyes Questions possibles: A. Alors, ton expérience en France? Cela s’est bien passé ? Qu’est-ce que tu peux me raconter ? 1. Où étais-tu en France ? 2. Tu y es resté(e) combien de temps? 3. Pourquoi as-tu choisi cette ville ? 4. Quelles autres villes as-tu visitées ? Pourquoi ? 5. Quand es-tu retourné(e) aux États-Unis ? 6. Qu’est-ce que tu as aimé le plus dans la ville où tu as habité en France ? Pourquoi ? 7. Qu’est-ce que tu n’as pas aimé ? Pourquoi ? 8. Qu’est-ce que tu as appris de la culture française quand tu étais en France? 9. Qu’est-ce que tu savais déjà de la culture française ? 10. Parle-moi des aspects culturels de la France et des Français que tu as observés. 11. De quelles célébrations, traditions, et fêtes te souviens-tu et as-tu célébrées en France ? B. Parle-moi de ta routine quotidienne en France. 1. Qu’est-ce que tu faisais pendant la journée ? 2. Tu te réveillais à quelle heure le matin ? 3. Tu te couchais à quelle heure le soir? 4. Tu faisais la cuisine? Quand ? Qu’est-ce que tu préparais ? 5. Tu sortais ? Quand ? Avec qui ? Où allais-tu ? 6. Quels jours de la semaine allais-tu à la fac ? C. Parle-moi de l’université où tu as étudié. 1. Où as-tu étudié ? 2. Qu’est-ce que tu y as étudié ? 3. Quels cours as-tu suivis ? 4. T’es-tu fait des copains ? Comment tes camarades étaient-ils ? 5. Qu’est-ce que tu as aimé le plus à l’université? Pourquoi ? 6. Qu’est-ce que tu n’as pas aimé à l’université? Pourquoi ? D. Parle-moi de ton quartier à Paris ou dans la ville où tu habitais. 1. Tu habitais dans quel quartier ? 2. Qu’est-ce que tu aimais dans ton quartier ? Pourquoi ? 3. Qu’est-ce que tu n’aimais pas dans ton quartier ? Pourquoi ? 4. Ton quartier était près du métro ? du train ? du bus ? de la fac ? 5. Quels étaient les problèmes sociaux de ton quartier ? 6. Qu’est-ce que tu penses de ces problèmes ? 7. Y avait-il des HLM dans ton quartier ? Tu peux me les décrire ? E. Parle-moi de ton appartement à Paris ou dans la ville où tu habitais. 1. Tu peux me décrire ton appartement ? 2. Parle-moi de tes colocataires. 18(25) 3. 4. 5. Qu’est-ce que tu faisais avec eux ? Quel type de problèmes aviez-vous? Tu peux me décrire une situation de conflit que tu as vécue avec eux ? Comment est-ce que vous avez résolu ce conflit? F. Parle-moi de la nourriture en France. 1. Où allais-tu faire les courses? 2. Qu’est-ce que tu achetais ? 3. Quels étaient tes restos favoris ? Pourquoi ? 4. Quels étaient tes plats favoris ? Pourquoi ? 5. Tu préférais les grandes surfaces ou les petites surfaces ? Pourquoi ? 6. Quels sont les petits commerces que tu avais l’habitude de fréquenter ? Pourquoi ? 7. Tu aimais les grands magasins ? Pourquoi ? 8. Quel était ton hypermarché préféré ? Pourquoi ? 9. Quel était ton épicerie préférée ? Pourquoi ? 10. Où achetais-tu les fruits et les légumes ? Pourquoi ? Tu as des questions pour moi, n’est-ce pas ? Qu’est-ce que tu veux savoir ? 19(25) SITUATION 3: ENTRETIEN A L’ALLIANCE FRANCAISE A NY You have applied for a job at the Alliance Française in NY, the French Institute in NY whose mission is to create and offer New Yorkers innovative and unique programs in education and the arts that promote the French culture. The director of the Alliance Française (played by your instructor) invited you for an interview. (S)he wants to know about your background and your knowledge of the French culture. What would you say, and how would you answer his/her questions. This is a formal conversation (use « vous »). - Greet each other and exchange names Give personal information Reasons to work with the Alliance Française in NY Questions about the language and the culture Wrap-up and goodbyes Questions possibles: A. Voulez-vous me parler de vous? 1. D’où êtes-vous ? 2. Quelles langues parlez-vous ? 3. Où est-ce que vous avez appris le français ? 4. Pendant combien d’années avez-vous étudié le français ? 5. Quels diplômes avez-vous reçus ? Quand ? De quelles institutions avez-vous reçu vos diplômes? 6. Dans quels pays avez-vous vécu ? Pendant combien de temps ? 7. Dans quels pays francophones avez-vous vécu ? Pendant combien de temps? 8. Cela a été une expérience positive ? Pourquoi ? Qu’est-ce que vous avez fait là-bas ? 9. Quelles sont vos expériences professionnelles ? 10. Pourquoi avez-vous posé votre candidature pour ce poste à l’Alliance Française ? B. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la culture française en général ? 1. Qu’est-ce que vous aimez le plus de la culture française, des Français et de la France? Pourquoi ? 2. Qu’est-ce que vous n’aimez pas trop de la culture française, des Français et de la France? Pourquoi ? 3. Quels aspects de la culture française vous semblent particulièrement intéressants ? Pourquoi ? C. Qu’est-ce que vous savez du commerce et de la consommation en France et en Europe ? 1. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la zone euro ? Qu’est-ce que vous pensez d’une monnaie commune en Europe? Quels sont les avantages ? Quels sont les désavantages? Quels sont les pays qui utilisent l’euro ? Quels sont les nouveaux pays membres de l’Union Européenne ? 2. Qu’est-ce que vous savez des petites et des grandes surfaces ? Pouvez-vous citer un exemple de petites et de grandes surfaces en France et ici aux États-Unis? 3. Quelle est l’importance historique de Carrefour ? 4. Quels sont les avantages et désavantages des petits commerces de proximité ? 5. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de l’histoire des grands magasins ? Pouvez-vous donner un exemple de grand magasin en France et dans votre pays ? 6. Préférez-vous les petites ou les grandes surfaces ? Pourquoi ? 7. Qu’est-ce que vous achetez et où ? D. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la situation du logement en France? 1. Quels problèmes sont liés aux conditions de logement en ville en France, et dont les Français se plaignent? 2. Quelles sortes de logements se trouvent dans les cités de banlieue en France ? Qui habitent ce type de logement ? Quels problèmes sociaux sont souvent liés aux cités de banlieue ? 3. Qu’est-ce que vous pensez de ces problèmes ? E. Qu’est-ce que vous savez du sport collectif et individuel en France? 1. Quel pourcentage de Français pratique un sport ? Pourquoi ? 2. Les Français préfèrent-ils les sports individuels ou collectifs ? Expliquez. 20(25) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Quels sports attirent les femmes en France ? Quels sports se pratiquent dans la rue en France ? Quels sont les sports les plus chers en France? Quelle es une différence entre la France et les États-Unis à propos des sports et des activités sportives ? Et une analogie entre la France et les États-Unis? Vous-même pratiquez-vous un sport ? Lequel ? Quand ? Avec qui ? F. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la télévision française ? 1. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la télévision française ? 2. Combien de chaînes gratuites de télé y a-t-il en France ? 3. Combien de chaînes payantes de télé y a-t-il en France ? 4. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la chaîne Canal + ? G. Qu’est-ce que vous savez de la bande dessinée ? 1. Depuis combien de temps y a-t-il des B.D. ? 2. Quels types d’artistes collaborent à la création des B.D.? 3. Donnez des exemples de genres de B.D. 4. Lisez-vous des B.D. ? Pourquoi ? Lesquelles ? Vous avez des questions pour moi? 21(25) APPENDIX II Speaking Task - Holistic Rubric Performance exceeds expectations Listening comprehension Student fully understands the examiner’s questions, without probing Fluidity Pronunciation Vocabulary Grammar Speech continuous with few pauses or stumbling. Cohesive devices appropriate for this level are frequently used 4 points Excellent pronunciation Student fully addresses the information requested and provides additional details using rich vocabulary Perfect control of the syntactic structures and grammar required. (Accuracy level 90% - 100%) 4 points 4 points Performance meets expectations Performance almost meets expectations 4 points Student fully understands the examiner’s questions, but needs occasional probing 3 points Student understands less than 60% of the examiner’s questions after probing Continuous speech with some pauses and stumbling. Cohesive devices are sporadically used 3 points Speech choppy and/or slow with frequent pauses. Rare use of cohesive devices 4 points Good pronunciation with a few imperfections 3 points Satisfactory pronunciation Student addresses the information requested without providing additional details using adequate vocabulary 3 points Adequate control of the syntactic structures. Some grammatical errors (Accuracy level 79% - 89%) 3 points Student addresses less than 60% of the examiner’s questions using inadequate vocabulary Emerging control of the syntactic structures. Several grammatical errors (Accuracy level 61% - 78%) 2 points 2 points 2 points Performance does not meet expectations 2 points Student understands less than 40% of the questions even after probing Speech halting and uneven with long pauses 2 points Unsatisfactory pronunciation 1 point 1 point 1 point Student addresses less than 40% of the examiner’s questions using inaccurate vocabulary. 1 point 22(25) Minimal control of the syntactic structures. Numerous grammatical errors (Accuracy level 0%- 60%) 1point APPENDIX III: Scoring scales Grammar task (Range: 0 to 36) GRAMMARSECTION ACCURATE USE OF THE GRAMMATICAL STRUCTURES LEARNED IN THE COURSE Performance exceeds expectations More than 90% completion of the task (31 – 36 points) Performance meets expectations Between 74% and 89% completion of the task (23 – 30.5 points) Performance almost meets expectations Between 61% and 73% completion of the task (16.5- 22.5 points) Performance does not meet expectations Between 0% to 60% completion of the task (0 – 16 points) Vocabulary task (Range: 0 to 16) VOCABULARY ACCURATE AND ADEQUATE USE OF THE VOCABULARY SECTION LEARNED IN THE COURSE Performance exceeds expectations More than 90% completion of the task (14 – 16 points) Performance meets expectations Between 74% and 89% completion of the task (10-13.5 points) Performance almost meets expectations Between 61% and 73% completion of the task (6.5-9.5 points) Performance does not meet expectations Between 0% to 60% completion of the task (0- 6 points) 23(25) Listening task (Range: 0 to 16) LISTENING SECTION UNDERSTAND RELATIVELY COMPLEX MESSAGES RELATED TO THE TOPICS COVERED IN THE COURSE Performance exceeds More than 90% completion of the task expectations (14 – 16 points) Performance Between 74% and 89% completion of the task meets (10- 13.5 points) expectations Performance almost meets expectations Performance does not meet expectations Between 61% and 73% completion of the task (6.5 – 9.5 points) Between 0% to 60% completion of the task (0 to 6points) Reading task Holistic Rubric (Range: 0 to 16) READING SECTION UNDERSTAND RELATIVELY COMPLEX MESSAGES RELATED TO THE TOPICS COVERED IN THE COURSE Performance exceeds More than 90% completion of the task expectations (14– 16 points) Performance Between 74% and 89% completion of the task meets (10- 13.5 points) expectations Performance Between 61% and 73% completion of the task almost (6.5 – 9.5 points) meets expectations Performance Between 0% to 60% completion of the task does not (0 to 6 points) meet expectations 24(25) APPENDIX IV Writing Task Holistic Rubric Task Completion Exceeds expectations Meets expectations Almost meets expectations Does not meet expectations Superior completion of the task. Student fully addresses the information requested, and provides additional details 4 POINTS Completion of task. Student fully addresses the information provided, but does not provide additional details 3 POINTS Level of Discourse Sentences are fully developed and interconnected with cohesive devices appropriate for this level Vocab. Grammar Rich use of vocabulary Perfect control of the syntactic structures required. (Accuracy level 90% - 100%) 4 POINTS Sentences are fully developed. Cohesive devices are sporadically used 4 POINTS Adequate and accurate use of vocabulary 4 POINTS 3 POINTS Adequate control of the syntactic structures. Some grammatical errors (Accuracy level 79% - 89%) 3 POINTS 3 POINTS Partial completion of task. Student completes no more than 60% of the information requested Sentences are somewhat complete. Rare use of cohesive devices Somewhat inadequate and/or inaccurate use of vocabulary 2 POINTS Minimal completion of task. Student completes less than 40% of the information requested. 2 POINTS Sentences are mostly incomplete. No use of cohesive devices 2 POINTS Inadequate and/or inaccurate use of vocabulary Emerging control of the syntactic structures Several grammatical errors (Accuracy level 61% - 78%) 2 POINTS Minimal control of the syntactic structures. Numerous grammatical errors (Accuracy level 0%60%) 1 POINT 1 POINT 1 POINT 25(25) 1 POINT






