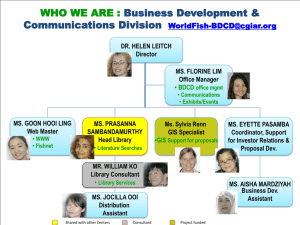
Financial Report 2012
advertisement

Financial Report 2012 This detailed report on the financial performance of the CGIAR Centers in 2012 is based on their audited financial statements Financial Report 2012 Contents Executive summary ....................................................................................................................................... 2 Financial highlights ........................................................................................................................................ 3 Accounting standards and audit .................................................................................................................... 6 Overall financial outcome .............................................................................................................................. 7 The CGIAR Fund and donor contributions .................................................................................................... 7 CGIAR Research Program financial summary ............................................................................................ 14 Centers’ financial summary ......................................................................................................................... 15 CGIAR expenditure over 40 years............................................................................................................... 20 CGIAR system financial position ................................................................................................................. 21 Center financial performance indicators ...................................................................................................... 23 Long-term financial stability ..................................................................................................................... 24 Liquidity .................................................................................................................................................... 26 Indirect cost ratio ...................................................................................................................................... 26 Annex tables ................................................................................................................................................ 28 Glossary of terms ........................................................................................................................................ 74 www.cgiar.org 1 Financial Report 2012 Executive summary The political, financial, technological, and environmental context of CGIAR’s research continues to evolve. So as to make the most of new opportunities to reduce rural poverty, increase food security, improve human health and nutrition, and ensure more sustainable management of natural resources, CGIAR launched a reform process in 2009. In 2012 the initial changes proposed by the reform were fully implemented. CGIAR Research Programs are now the main organizational mechanism for planning and conducting research. The 16 CGIAR Research Programs represent a new program-based approach to doing research, thereby aligning the research activities of the CGIAR Research Centers and their partners into efficient, coherent, multidisciplinary programs that tackle cross-cutting issues in agricultural development across the globe. This research is aligned with the Strategy and Results Framework developed by the members of the CGIAR Consortium, and endorsed by the Funders Forum to establish common goals, objectives, and results for the whole CGIAR partnership. The first two CGIAR Research Programs were launched in January 2011: 1. CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security 2. CGIAR Research Program on Rice. The next three Programs were launched in mid-2011: 3. CGIAR Research Program on Aquatic Agricultural Systems 4. CGIAR Research Program on Maize 5. CGIAR Research Program on Forests, Trees and Agroforestry. The beginning of 2012 saw the inception of eight Programs: 6. CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems 1 7. CGIAR Research Program on Policies, Institutions and Markets 8. CGIAR Research Program on Wheat 9. CGIAR Research Program on Roots, Tubers and Bananas 10. CGIAR Research Program on Livestock and Fish 11. CGIAR Research Program on Agriculture for Nutrition and Health 12. CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems 1 The inception phase of the CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems was approved in 2012 and the full Program was approved in early 2013 www.cgiar.org 2 Financial Report 2012 13. CGIAR Research Program on Managing and Sustaining Crop Collections. The transition was completed when the final three CGIAR Research Programs were approved in October 2012 (retro-active to July 1, 2012): 14. CGIAR Research Program on Integrated Systems for the Humid Tropics 15. CGIAR Research Program on Grain Legumes 16. CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Cereals. As CGIAR Research Programs represent a new way of working, they need a new system of funding. The CGIAR Fund (the Fund) is a multi-donor, multi-year mechanism that provides strategic financing for agricultural research. By contributing directly to the Fund, donors now have the option of supporting the work of CGIAR as a whole. Fund contributors may designate their resources to three funding “windows”: Window 1: Contributions are received without donor restrictions. The Fund Council sets overall priorities and makes specific decisions about the use of Window 1 funds, such as allocation to CGIAR Research Programs, payment of system costs and any other use required to achieve the CGIAR mission Window 2: Contributions are designated by Fund donors to one or more specific CGIAR Research Programs. Once the funds are allocated to a given CGIAR Research Program, they flow to the Lead Center net of the 2% system costs Window 3: Contributions consist of funds that donors wish to allocate to specific Centers. Neither the Consortium nor the Fund Council makes decisions about the use of Window 3 funds. Centers receive the funds net of the 2% system costs. The continuing use of Window 3 funding is currently under review. Financial highlights In order to capitalize upon the vast potential of CGIAR’s ambitious research, which was specifically developed to tackle major global challenges for the benefit of the poor, a serious commitment from donors is required. Strong evidence of that commitment is witnessed by the significant increase in CGIAR funding and, consequently, activity. In the decade prior to reform (1998–2007) the average growth rate in funding was 5%. From 2008 to 2011, the annual growth rate averaged 12%. In 2012, the total system revenue was US$887 million (including Center-generated income of US$27 million), a 21% increase of US$152 million above 2011 revenues of US$735 million. This level of growth is of particular note when it is placed in the context of the continuing fiscal difficulties experienced by many of the donor nations. Total grant income in 2012 was US$860 million, an increase of US$147 million (21%) above 2011 revenues. It contributes to the goal of reaching US$1 billion in 2013 to strengthen the suite of CGIAR Research Programs. Since 2008, total grant income has increased by US$329 million (62%), an average annual increase of 15%. This increased financial commitment by donors reflects their confidence in key elements of the reform, including a results-oriented approach to research. www.cgiar.org 3 Financial Report 2012 Figure 1: Total grant income 2008–2012 1000 950 900 860 US$ million 850 800 750 713 673 700 650 606 600 550 531 500 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 The CGIAR Fund aims to provide reliable and predictable multi-year funding and thereby enable: research planning over the long term resource allocation based on agreed priorities timely and predictable disbursement of funds. As of December 2012, the following donors had made multi-year commitments to the CGIAR Fund: Australia, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Denmark, the International Development Research Centre (IDRC), Luxembourg, Netherlands, Russia, Spain, and the United Kingdom. Donors are increasingly beginning to channel their funding through the Fund: contributions increased by 33% from 2011 to 2012, growing from US$384 million to US$512 million. The total of US$512 million received by the Fund in 2012, together with US$127 million carried over from 2011, gave a total of US$639 million available for distribution. Amounts of US$458 million were disbursed during 2012, leaving a balance of US$181 million remaining in the Fund at the end of 2012. The high balance at the year end was because many grants were received by the Fund late in 2012. Of the total of US$458 disbursed in 2012, US$325 million was Window 1 and 2 funding and US$133 million from Window 3. Of the US$325 million of Window 1 and 2 funding disbursed, US$29.9 million related to 2011 activities that had been pre-funded by Centers, and the remainder of US$295.6 million was used to fund CGIAR Research Program activities. The Fund was the major donor to the system in 2012, financing US$316 million (45%) of total CGIAR Research Program activities during the year (2011: 45%). This comprised Window 1 and 2 funding of www.cgiar.org 4 Financial Report 2012 US$260 million and Window 3 of US$56 million. Bilateral funded grant income accounted for US$384 million (55%) of CGIAR Research Program activities. Total expenditure in 2012 was US$876 million, an increase of US$169 million (24%) over 2011 expenditures of US$707 million. CGIAR Research Program expenditures amounted to US$700 million (80% of the total of US$876 million) compared to US$221 million (31%) in 2011. This change reflects the significant shift from Center-based to system-wide research through the CGIAR Research Programs. Expenditures in sub-Saharan Africa increased from an average of 43% during the period 1972–2008 to 53% in 2012. During the same period investment in Asia decreased from 31% to 27%, in Latin America from 15% to 13%, and in the Central and West Asia and North Africa (CWANA) region from 11% to 7%. Personnel costs as a percentage of total costs decreased from 43% in 2011 to 36% in 2012 while supplies and services increased from 30% to 35%, and partnership expenditures from 16% to 17%. The increase of 17% in partnership expenditures was noticeably up from a historical average of 4%, and clearly demonstrated a change in the modus operandi of Centers. System costs came down from more than 3% of total in 2009 to less than 2% in 2012. The 2012 financial data confirmed that, as was the case in previous years, CGIAR as a whole remains in a stable financial position. Cash and cash equivalents totaled US$834 million at the end of 2012, an increase of US$83 million compared to US$751 million at the end of 2011. Property, plant, and equipment net of depreciation amounted to US$110 million, up from US$84 million at the end of 2011. This represents an increase of US$26 million of new investments in fixed assets. The Centers’ total net assets at the end of the year were US$356 million (2011: US$343 million). These assets are made up of US$242 million (2011: US$257 million) in unrestricted net assets (excluding investments in fixed assets), investments in fixed assets of US$110 million (2011: US$84 million), and restricted assets of US$4 million (2011: US$2 million). Unrestricted net assets by Center are set out in Figure 8. Unrestricted net assets of US$242 million represent 106 days (2011: 117 days) of operating reserves. The short-term solvency or liquidity ratio for CGIAR as a whole amounted to 152 days (2011: 176 days). The reduction in both of these indicators clearly shows that as total funding to the system increases, it impacts negatively on both the reserve and liquidity days and demonstrates the need to carefully monitor these indicators going forward. Cash and cash equivalents of US$834 million were held at the year end. However, of this amount US$150 million was held by Bioversity on behalf of the Global Crop Diversity Trust. Excluding this amount the net cash position represented 285 days of operating expenditures. In conclusion, the 2012 finances confirm the strong continuing donor commitment to the CGIAR system with an increasing amount of support being channeled through the Fund and targeted at CGIAR Research Programs. The system remains well on course to meet its target of US$1 billion in funding by 2013. www.cgiar.org 5 Financial Report 2012 Accounting standards and audit Externally audited financial statements, from each Center, form the basis for this Financial Report. They were reviewed and aggregated according to fiduciary management and reporting standards approved by CGIAR to guide the Centers in these areas. In conformity with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), Center financial statements have been prepared on the accruals basis. To ensure that Center financial statements are prepared in accordance with international GAAP, the CGIAR Financial Guideline No. 2: “Accounting Policies and Reporting Practices Manual” is currently being updated to bring it into compliance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Additional information on financial compliance is in Box 1, and Center external auditors are listed in Box 2. Box 1: Compliance with financial guidelines (FGs) To ensure transparency and consistency in financial practices and the presentation of financial information, the 15 Centers of CGIAR are required to follow financial guidelines issued by the Consortium. Developed with input from Center finance personnel and external experts, these guidelines bring CGIAR’s fiduciary practices into conformity with relevant international standards. As part of the annual review of substantive financial performance, a peer group of Centers’ finance and internal audit professionals reviewed the Centers’ externally audited 2012 financial statements to assess their compliance with CGIAR accounting policies and reporting guidelines, as well as to validate the analysis underpinning the CGIAR Financial Report. The Peer Review found that all of the Center’s financial statements had been prepared in accordance with CGIAR Financial Guideline No 2: Accounting Policies and Reporting Practices Manual. Box 2: Center auditors AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish Consortium Office 2011 Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers KPMG Ernst & Young Ernst & Young KPMG McGladrey& Pullen Ernst & Young KPMG KPMG Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers Grant Thornton PricewaterhouseCoopers 2012 Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers KPMG Ernst & Young Ernst & Young KPMG KPMG Ernst & Young Ernst & Young KPMG Ernst & Young PricewaterhouseCoopers Grant Thornton PricewaterhouseCoopers www.cgiar.org 6 Financial Report 2012 All of the Centers and the Consortium Office received an unqualified audit opinion from their external auditors. Overall financial outcome Total system revenues in 2012 amounted to US$887 million, an increase of US$152 million (21%) in comparison to US$735 million in 2011. Expenditures in 2012 were US$876 million, an increase of US$169 million (24%) over 2011 expenditures of US$707 million. The overall net result was a surplus of US$11 million, which was taken to reserves. Table 1 sets out the total revenues and expenditures for 2012 compared to 2011. Table 1: CGIAR financial results US$ million Revenue CGIAR Fund Window 1&2 CGIAR Fund Window 3 Bilateral Sub-total funding Center own income Total revenue Expenditure CRPs Center own programs System entities Total expenditure Net result Total 284 78 498 860 27 887 2012 CRPs Non-CRPs 260 24 56 22 384 114 700 160 Total 187 16 510 713 22 735 700 162 14 876 221 477 9 707 11 28 2011 CRPs 95 2 124 221 Non-CRPs 92 14 386 492 The CGIAR Fund and donor contributions In order to capitalize upon the vast potential of CGIAR’s ambitious research, which was specifically developed to tackle major global challenges for the benefit of the poor, a serious commitment from donors is required. That commitment has been demonstrated by the recent growth rate of the CGIAR Fund (the Fund), which has grown twice as fast as it did previously. From 2008 to 2011, the annual growth rate averaged about 12%. This can be compared to an average growth rate in funding of 5% in the decade prior to the reform (1998–2007). In 2012, total funding to CGIAR was US$860 million, indicating steady progress towards the goal of reaching US$1 billion in 2013 to support the suite of CGIAR Research Programs. This increased financial commitment by donors reflects strong confidence in key elements of the reform, including a results-oriented approach to research. Figure 1 shows the growth in grant income from 2008 to 2012 and Figure 2 illustrates the changing modalities of funding. www.cgiar.org 7 Financial Report 2012 Figure 1: Total grant income 2008–2012 1000 950 900 860 US$ million 850 800 750 713 700 673 650 606 600 550 531 500 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 Figure 2: Modalities of funding 900 US$ million 800 284 700 187 600 16 78 CGIAR Fund W1/2 500 CGIAR Fund W3 400 Bilateral and own funds 300 532 525 200 100 0 2011 2012 www.cgiar.org 8 Financial Report 2012 Donors can flow their contributions either through the Fund or through bilateral grants made directly to Centers. Contributions channeled through the Fund increased by 33% from 2011 to 2012, growing from US$384 million to US$512 million. Recognizing that agricultural research requires funding stability that stretches well beyond political budget cycles, CGIAR’s multi-donor trust fund aims to provide reliable and predictable multi-year funding and thereby enable research planning over the long term, resource allocation based on agreed priorities, and the timely and predictable disbursement of funds. As of December 2012, the following donors had made multi-year commitments to the CGIAR Fund: Australia, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Denmark, IDRC, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Russia, Spain, and the United Kingdom. The total of US$512 million received by the Fund in 2012, together with US$127 million carried over from 2011, gave a total of US$639 million available for distribution. Amounts of US$458 million were disbursed during 2012, leaving a balance of US$181 million remaining in the Fund at the end of 2012. The amount of US$181 million remaining in the Fund at the year end was high because, as is shown in Figures 3 and 4, many grants were received by the Fund late in 2012 and could not be disbursed before the year end. Figure 3: Cumulative Fund inflows for CY2012 600 498 500 409 US$ million 400 374 390 390 407 420 435 511 515 512 455 10 505 149 330 300 268 200 104 159 100 134 - Received Confirmed Projected inflows 2012 www.cgiar.org 9 Financial Report 2012 Figure 4: Balance in the Fund at each month end 200.0 171 180.0 160.0 US$ million 140.0 133 142 127 137 180 131 120.0 100.0 80.0 63 71 82 70 71 59 60.0 40.0 20.0 0.0 Inflows Disbursements Balance Of the total of US$458 disbursed in 2012, US$325 million was Window 1 and 2 funding and US$133 million from Window 3. Of the US$325 million of Window 1 and 2 funding disbursed, US$30 million related to 2011 activities that had been pre-funded by Centers, and the remainder of US$295 million was used to fund CGIAR Research Program activities. Tables 2 and 3 shows donor contributions received by the CGIAR Fund. This being a co-mingled Fund, the disbursements are shown in Table 4, detailed for Windows 1 and 2 by activity/Program and broken down by donors for Window 3. A provisional amount of US$20 million had been received from four donors but not allocated at the year end. This was because the Fund was awaiting instructions from the respective donors as to which Programs they wished to fund. Note also that, in accordance with good financial management practices, the Fund has set a target of not less than US$30 million in Window 1 funding at the year end. This is to ensure that the Fund has resources available in case of emergency. www.cgiar.org 10 Financial Report 2012 Table 2: CGIAR Fund Statement of receipts, disbursements and Fund balance as of December 31, 2012 US$ million Balance b/f from 2011 2011 contributions received in 2012 2012 contributions received in 20121 Cost sharing percentage Window 1 Window 2 Window 3 Provisional Total CGIAR Fund 93 21 1 12 127 1 2 3 184 116 185 6 20 1 505 1 Sub-total receipts in 2012 186 118 188 20 512 Total available in 2012 279 139 189 32 639 8 3 (5) (6) 0 219 106 133 0 458 68 36 52 25 181 Transfers Less: disbursements2 Fund balance 1See Table 3 2See Table 4 www.cgiar.org 11 Financial Report 2012 Table 3: CGIAR Fund 2012 donor contributions US$ million Receipts Australia Bangladesh** Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Canada China Denmark European Commission Finland France IDRC IFAD India Iran Ireland Japan Korea Luxembourg Mexico Netherlands New Zealand Nigeria Norway Portugal Russia Spain Sweden Switzerland Thailand Turkey United Kingdom United States of America World Bank Sub-total 2012 receipts Belgium* Nigeria* Iran* Window 1 Window 2 Window 3 8.8 20.5 11.3 0.1 1.5 24.3 15.6 0.1 2.7 3.1 3.0 21.0 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.2 8.0 2.6 0.7 0.5 1.8 0.5 1.9 3.4 0.1 0.7 1.0 0.3 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.5 5.8 30.0 2.0 2.0 0.1 0.1 18.5 0.6 0.5 17.6 6.5 51.4 0.5 50.0 183.7 0.5 20.6 6.7 Provisional 0.1 3.8 21.0 1.9 0.1 0.5 22.6 85.5 16.1 116.3 184.6 20.0 7.1 1.3 0.5 Total CGIAR Fund 40.6 0.1 25.8 15.6 2.8 6.1 21.0 3.9 1.2 8.0 2.6 3.1 0.5 5.3 1.8 0.3 0.6 1.0 37.8 2.0 0.1 18.5 0.6 3.8 0.5 38.2 15.0 0.1 0.5 74.1 123.1 50.0 504.5 8.4 0.5 0.5 Total 2012 contributions 184.2 123.4 186.4 20.0 514.0 *Contributions which are supported by signed contribution agreement but the money was not yet received by Dec 31, 2012 **Includes contributions which have been received but the contribution agreement is still in process www.cgiar.org 12 Financial Report 2012 Table 4: CGIAR Fund Schedule of disbursements as of December 31, 2012 US$ million Window 1 & 2 (by Program) Dryland Systems Humidtropics AAS PIM WHEAT MAIZE GRiSP RTB Grain Legumes Dryland Cereals Livestock and Fish A4NH WLE Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS Genebanks Funding stability/Transitional financing System offices Sub-total 14 13 25 27 44 15 30 17 325 Window 3 (by donor) Australia Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation China European Commission Finland India Iran Ireland Japan Luxembourg Mexico Netherlands Nigeria Portugal South Africa Spain Switzerland Thailand Turkey United Kingdom United States of America Sub-total 8 24 1 11 3 2 0 3 1 0 0 2 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 6 67 133 Total 458 9 7 27 13 15 38 31 www.cgiar.org 13 Financial Report 2012 CGIAR Research Program financial summary Total CGIAR Research Program expenditures in 2012 were US$700 million. These accounted for 80% of the total expenditures of US$876 million expended by Centers (see Table 6). The breakdown of CGIAR Research Program funding by source is shown in Table 5. As can be seen in Table 5, Windows 1 and 2 (W1/2) funding of US$260 million accounted for 37% of CGIAR Research Program funding, Window 3 (W3) for US$56 million (8%) and bilateral for US$384 million (55%). Table 5: Summary of CGIAR Research Program funding 2012 US$ million From financial statements of individual Centers Dryland Systems Humidtropics AAS PIM WHEAT MAIZE GRiSP RTB Grain Legumes Dryland Cereals Livestock and Fish A4NH WLE Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS Genebanks Total % of individual CRP funding W1/2 9.1 7.2 7.5 15.2 11.4 13.5 35.4 22.3 7.5 3.2 7.7 9.1 22.4 W3 2.8 2.9 1.0 9.5 2.3 9.2 12.7 2.6 3.8 0.1 0.3 1.2 5.1 Bilateral 18.6 9.9 11.6 50.4 27.0 51.5 50.9 26.3 11.1 4.1 7.9 27.1 28.4 Total 30.5 20.0 20.1 75.1 40.7 74.2 99.0 51.2 22.4 7.4 15.9 37.4 55.9 W1/2 30% 36% 36% 21% 28% 18% 35% 44% 33% 43% 47% 24% 38% W3 9% 11% 5% 13% 5% 12% 13% 7% 19% 2% 2% 3% 10% Bilateral 61% 53% 59% 66% 67% 69% 52% 49% 47% 55% 51% 73% 51% Total (% of Total) 4% 3% 3% 11% 6% 11% 14% 7% 3% 1% 2% 5% 8% 29.4 1.3 40.5 71.2 41% 1% 58% 10% 46.4 12.6 0.5 - 16.0 3.3 62.9 15.9 73% 79% 1% 0% 26% 21% 9% 2% 260 56 384 700 37% 8% 55% 100% Figure 5 sets out Center revenue by source of funding. The International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI), International Center for Tropical Agriculture (CIAT) and International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) have the largest amounts of non-CGIAR Research Program funding. In ILRI’s case this is explained by the BecA-ILRI Hub in Nairobi. CIAT has a large national program with the Government of Colombia. www.cgiar.org 14 Financial Report 2012 Figure 5: Center revenue by CRP and non-CRP 120.0 US$ million 100.0 80.0 60.0 CRP 40.0 20.0 Non-CRP Other - Centers’ financial summary Total funding to Centers, including Challenge Program Partners and system-level activities, in 2012, amounted to US$887 million, an increase of US$152 million (21%) over 2011 revenue of US$735 million. Total expenditures were US$876 million against US$707 million in 2011, an increase of US$169 million (24%). The net accumulated surplus was US$11 million, which is added to accumulated reserves. From an individual Center perspective it is worth noting that the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) finished the year with a deficit of US$12.2 million due to the write-off of its failed investment. The International Center for Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) recorded a deficit of US$5.7 million due to the write-off of assets at its headquarters in Aleppo and the costs of moving staff out of Syria. The Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) recorded an operating surplus of US$7.2 million primarily as a result of bringing an unspent allocation to reserves that the institute will draw down for program activities in 2013 and 2014. www.cgiar.org 15 Financial Report 2012 Table 6: 2012 financial results by Center US$ million Center AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI ICRAF WorldFish Sub-total System-level activities CRP 20.7 30.4 51.9 34.0 108.5 39.4 32.7 39.6 80.6 47.5 30.0 77.3 37.2 45.4 25.9 700.4 700.4 Challenge Program Partners Revenue Non-CRP Other 1.8 0.2 5.2 1.7 17.4 4.3 6.8 0.3 6.4 1.1 3.9 0.8 5.8 1.5 15.7 4.8 3.1 0.4 14.7 1.0 20.6 5.2 7.3 2.0 2.2 1.4 5.6 1.7 0.7 0.7 117.0 27.1 13.9 130.9 27.1 Total 22.7 37.3 73.5 41.1 116.0 44.0 39.9 60.1 84.0 63.2 55.7 86.5 40.7 52.7 27.3 844.4 13.9 858.3 Expenditure CRP Non-CRP 20.7 1.5 30.4 6.3 51.9 16.2 34.0 (0.1) 108.5 1.6 39.4 4.4 32.7 12.9 39.6 16.8 80.6 3.7 47.5 27.9 30.0 24.1 77.3 7.9 37.2 2.4 45.4 7.1 25.9 0.9 700.4 133.6 13.9 700.4 147.5 Surplus/ (Deficit) Total 22.2 36.7 68.1 33.8 110.1 43.8 45.6 56.3 84.3 75.4 54.0 85.1 39.6 52.5 26.8 833.4 13.9 847.3 29.1 29.1 29.1 29.1 700 160 27 887 700 177 876 In 2012 results, inter-Center activities have already been eliminated from reported results 0.5 0.6 5.5 7.2 5.9 0.2 (5.7) 3.8 (0.2) (12.2) 1.7 1.4 1.1 0.2 0.5 10.5 0.0 10.5 0.0 11 www.cgiar.org 16 Financial Report 2012 Table 7: CGIAR revenue and expenditure US$ million 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 CRP revenues Dryland Systems 9 Humidtropics 7 AAS 3 8 PIM 15 WHEAT 11 MAIZE 3 14 GRiSP 34 35 RTB 22 Grain Legumes 7 Dryland Cereals 3 Livestock and Fish 8 A4NH 9 WLE 22 Forests, Trees and Agroforestry 11 29 CCAFS 32 46 Genebanks 12 13 95 260 126 56 CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 Bilateral Total CRP revenue 384 - - - 221 700 Restricted 355 420 460 356 111 Unrestricted 171 181 208 127 35 9 14 Total non-CRP revenue 526 601 668 492 160 Total grant income 526 601 668 714 860 22 23 23 22 27 548 624 691 735 887 Non-CRP System offices Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure - - - 221 700 Restricted non-CRP expenditure 341 402 435 350 110 Unrestricted 181 177 192 127 30 - - - - 22 9 14 542 603 657 707 876 6 21 34 28 11 Extraordinary expenditure System offices Total expenditure Results of operations www.cgiar.org 17 Financial Report 2012 Table 8: Summary of Challenge Programs US$ million HarvestPlus Receipts Receipts from donors Australia Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation European Commission IFAD Pioneer Foundation Sweden Switzerland Syngenta United Kingdom United States of America Zinc Project Group Consortium – Stability/Transition Consortium – Water, Land and Ecosystems Others Sub-total donors Other Interest Total receipts Disbursements Disbursements to CGIAR Centers in 2012 AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI WAF WorldFish Sub-total CGIAR Others Research - Other partners Program management Administration fees Total disbursements Generation Water and Food 1 9 5 0 0 1 1 2 0 5 0 6 3 0 0 1 2 6 Totals 1 14 3 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 0 13 18 11 13 6 0 42 0 0 ` 11 0 0 13 42 18 6 1 2 0 0 1 5 1 0 1 4 0 0 7 0 2 0 0 2 5 1 0 2 2 0 1 22 6 2 0 12 22 7 1 52 0 1 1 0 0 0 16 2 9 3 1 29 7 2 11 0 1 2 www.cgiar.org 18 Financial Report 2012 Cumulative cash reserves Opening level 1/1/2012 58 10 5 73 2012 receipts (as above) 18 11 13 42 Contingency Fund - now reported here 3 3 2012 disbursements -29 -11 -12 -52 Closing level 31/12/2012 47 13 6 66 Notes 1 Funding received by the CGIAR Centers from the Challenge Programs is eliminated from system-level reports. 2 HarvestPlus received US$5m from Window 1 in 2012 in respect of 2011 stability funding. 3 Generation Challenge Programme (GCP) received US$785k from Window 1 in 2012, re 2011 stability funding. Closing balance of Generation Challenge Programme (GCP) includes US$4.532k A/R amount from EC. 4 The sub-Saharan Africa Challenge Program is not reported from 2012 onwards. It is considered part of CRP Program in Integrated Systems for the Humid Tropics, and funds were transferred from IITA to FARA in 2012 under this CRP. That fund transfer was reported as CRP expenditure by IITA so is already captured. EC also provided funding to FARA for the Challenge Program in 2012, but that is considered external to the CGIAR. www.cgiar.org 19 Financial Report 2012 CGIAR expenditure over 40 years Annex Table A5.1 shows expenditure cumulated for the last 40 years by Center, region, and object of expense. Annex Table A3.1 sets out expenditure by Center for the period 2008–2012. Annex Table 3.2 shows expenditure by geographic region. Of note is that expenditures in sub-Saharan Africa have increased from an average of 43% of total during the period 1972–2008 to 53% in 2012. During the same period investment in Asia has decreased from 31% to 27%; in Latin America from 15% to 13%; and in the CWANA region from 11% to 7%. Figure 6: 2012 expenditure by region 7% 13% 53% 27% Sub-Saharan Africa Asia Latin America CWANA Annex Table A3.3 provides detailed Center-level information on object of expenditure. Expenditures on personnel have decreased as a percentage of the total from 50% during the period 1972–2008 to 36% in 2012. During the same period expenditures on supplies and services have increased from 32% to 35%; on partnerships from 4% to 17%; travel has remained constant at 7%, and depreciation has dropped from 7% to 5%. The increase in partnership expenditures to 17% is a noticeable rise from a historical average of 4%, and clearly demonstrates a change in the modus operandi of Centers. www.cgiar.org 20 Financial Report 2012 Figure 7: Expenditure by cost category in 2012 Depreciation 5% Travel 7% Personnel costs 36% Collaboration and partnerships 17% Supplies and services 35% Annex Table A3.4 presents data on CGIAR staffing from 2008 to 2012. CGIAR system financial position The aggregations of 2007–2012 Center data, shown in Table 9 and elaborated below, reflect the financial position of the CGIAR system as a whole. Annex Table A4.1 provides details by Center as of December 31, 2012. The 2012 financial data confirmed that, as was the case in previous years, CGIAR as a whole remains in a stable financial position. Cash and cash equivalents totaled US$834 million at the end of 2012, an increase of US$83 million up from US$751 million at the end of 2011. This figure includes US$143 million (2011: US$125 million) disclosed under non-current assets. At the end of 2012, US$132 million (2011: US$115 million), equivalent to 15% of the total funding, was outstanding as accounts receivable from donors. However, Centers were also holding US$351 million (2011: US$261 million) in grants received in advance. Property, plant, and equipment net of depreciation amounted to US$110 million, up from US$84 million at the end of 2011. This represents an increase of US$26 million of new investments in fixed assets. It includes an increase of US$23 million made by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) at their headquarters in Mexico. During 2012 ICARDA wrote off US$3.5 million in fixed assets at its headquarters in Aleppo. www.cgiar.org 21 Financial Report 2012 Total net assets at the end of the year were US$356 million (2011: US$343 million). These assets are made up of US$242 million (2011: US$257 million) in unrestricted net assets (excluding investments in fixed assets), investments in fixed assets of US$110 million (2011: US$84 million), and restricted assets of US$4 million (2011: US$2 million). Net assets by Center are set out in Figure 8. Unrestricted net assets of US$242 million represent 106 days (2011: 117 days) of operating reserves. These are set out by Center in Figure 9. The short-term solvency or liquidity ratio is computed by taking current assets plus long-term investment minus current liabilities and dividing by per-day operating expenses excluding depreciation. For CGIAR as a whole this amounted to 152 days (2011: 176 days). These are set out in Figure 10. The reduction in both of these indicators clearly shows that as total funding to the system increases it negatively impacts on both the reserve and liquidity days and demonstrates the need to monitor carefully these indicators going forward. Cash and cash equivalents of US$834 million were held at the year end. However, of this amount US$150 million was held by Bioversity on behalf of the Global Crop Diversity Trust. Excluding this amount the net cash position represented 285 days of operating expenditures. www.cgiar.org 22 Financial Report 2012 Table 9: CGIAR system financial position US$ million 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 360 480 558 626 691 80 3 28 6 4 2 483 69 4 31 5 4 2 595 126 4 27 5 6 3 728 115 4 37 5 5 4 797 132 4 55 5 13 2 902 79 61 2 142 625 76 80 4 160 755 81 93 3 177 905 84 125 5 214 1,011 110 143 8 261 1,163 197 18 86 33 334 231 20 135 40 426 212 19 263 39 533 261 19 288 43 611 351 23 315 63 752 46 52 56 57 55 380 478 589 668 807 164 79 243 2 245 199 76 275 2 277 233 81 314 2 316 257 84 341 2 343 242 110 352 4 356 Total liabilities and net assets 625 755 905 *Includes US$150k held in trust by Bioversity for the Global Crop Diversity Trust 1,011 1,163 Assets Current assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable Donors Employees Others Inventories Pre-paid expenses Other current assets Total current assets Non-current assets Net property, plant, and equipment Investments Others assets Total non-current assets Total assets Liabilities and net assets Current liabilities Accounts payable Donors Employees Others* Accruals and provisions Total current liabilities Long-term liabilities Total liabilities Net assets Unrestricted Unrestricted net assets excl. fixed assets Fixed assets Unrestricted net assets Restricted Total net assets Center financial performance indicators Traditionally, CGIAR uses five financial indicators to monitor the financial health of Centers, and the Consortium Office is continuing with these indicators. These are the long-term financial stability ratio, which aims to measure the adequacy of an organization’s reserves; the short-term solvency ratio, which aims to monitor the liquidity of a Center and its ability to operate in the short term; the indirect cost ratio, www.cgiar.org 23 Financial Report 2012 which aims to measure the efficiency of a Center’s support functions; the management of donor receivable/payable ratio, which measures cash flow from donors; and the external audit opinion. Set out below are the indicators and how individual Centers measure up. As noted on page 7 all of the centers received an unqualified audit opinion. The donor receivable/payable ratio is 0.38. Long-term financial stability The measure of the long-term financial stability of a Center is computed as unrestricted net assets minus net fixed assets, divided by per-day operating expenses. The minimum recommended acceptable range is 75 to 90 days, and trends may be used to evaluate how a Center is performing over a period of time. Set out in Figures 8 and 9 are the absolute level of reserves held by Centers and the number of reserve days per Center. Figure 8: Unrestricted net assets excluding fixed assets by Center 35 30 US$ million 25 20 15 10 5 0 www.cgiar.org 24 Financial Report 2012 Figure 9: Available reserves expressed in days 250 200 150 237 215 178 164 155 147 142 136 104 100 100 91 106 78 72 45 50 31 0 Figure 10: Liquidity expressed in days 300 250 200 150 100 2011 2012 50 0 www.cgiar.org 25 Financial Report 2012 Liquidity Liquidity is an organization’s ability to meet its short-term spending requirements. Two primary indicators of liquidity are current ratio and working capital. Current ratio is current assets divided by current liabilities, represented as a number. This liquidity measure is comparable across organizations, regardless of their size, because it is a relative figure. Working capital expressed in terms of future spending requirements is useful for such purposes. The Centers’ liquidity levels hinge to some extent on the pattern of members’ disbursements, which occur throughout the calendar year. Figure 11: Current ratio by Center for 2012 3.0 2.5 2.5 2.0 2.0 1.5 1.0 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.0 0.5 - Indirect cost ratio The indirect cost ratio indicator is the ratio of indirect costs to direct costs (indirect costs divided by direct costs). In 2012, CGIAR’s indirect cost ratio is an average of 15%, one percentage point lower than 2011. www.cgiar.org 26 Financial Report 2012 Figure 12: Indirect cost ratio by Center 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 2012 2011 0% www.cgiar.org 27 Financial Report 2012 Annex tables Table A1.1: CGIAR grant income for the approved research agenda CGIAR Fund (Window 1 & 2) Challenge Programs Window 3 and bilateral contributions by group of donor Europe Austria Belgium Denmark European Commission Finland France Germany Ireland Italy Luxembourg Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain Sweden Switzerland United Kingdom Sub-total North America Canada United States of America Sub-total Pacific Rim Australia Japan Korea, Republic of New Zealand Sub-total Developing countries China Colombia Egypt, Arab Republic of India Iran, Islamic Republic of Libya Malaysia Mexico Morocco Nigeria Peru Philippines Turkey Uganda Sub-total Foundations Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Ford Foundation IDRC Kellogg Foundation Rockefeller Foundation Syngenta Foundation Sub-total 1972-2008 2009 2010 2011 187 60 2012 284 61 Total 471 121 36 137 192 490 52 125 394 48 148 10 320 205 3 30 247 371 510 3,316 2 11 6 41 5 5 24 10 6 1 15 16 0 3 15 20 42 220 2 12 6 43 4 5 21 11 4 1 15 22 1 2 12 22 49 233 3 14 20 2 1 21 6 1 1 7 6 0 1 4 12 3 103 2 6 0 22 3 1 20 7 1 0 7 5 0 0 11 11 10 107 46 179 204 615 66 137 480 81 160 13 363 254 5 36 289 436 614 3,979 501 1,396 1,897 42 79 121 40 86 127 7 59 67 9 90 99 601 1,710 2,311 182 615 19 12 827 13 16 2 2 33 22 16 2 2 42 29 13 2 0 44 24 14 2 40 271 674 25 16 986 16 26 11 37 21 0 17 3 30 5 9 3 3 182 3 1 1 7 1 4 1 1 9 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 16 0 4 0 1 1 1 0 1 23 3 2 1 10 1 1 0 16 2 0 1 1 1 38 4 2 0 8 1 0 0 31 0 3 0 1 0 0 52 31 31 13 72 23 1 1 69 3 36 7 13 5 5 311 66 59 7 109 6 247 1 4 0 2 2 9 71 0 3 0 1 3 80 71 0 3 0 1 4 79 70 0 1 0 1 73 213 68 69 8 115 15 487 www.cgiar.org 28 Financial Report 2012 International and regional organizations ADB AfDB Arab Fund FAO Gulf Cooperation Council IDB IFAD OPEC Fund UNDP UNEP World Bank Sub-total Total Others (analysis for 2012 available in Annex Table 2.3) 60 20 25 18 2 174 121 18 163 43 1,146 1,789 8,258 452 Total 8710 *From 2012 onwards, all inter-Center activities have been eliminated at Center level 3 1 1 6 1 2 9 1 2 5 50 80 478 128 2 1 2 5 0 1 11 1 1 3 50 77 582 91 3 1 2 5 1 0 22 2 5 41 618 95 3 4 2 2 0 1 15 1 2 3 34 747 113 72 27 33 35 4 178 177 20 166 55 1,254 2,021 10,684 725 606 673 713 860 11,301 www.cgiar.org 29 Financial Report 2012 Table A1.2: CGIAR grant income for the approved research agenda by Center US$ million Centers AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI ISNAR IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish Less inter-Center activities* 1972–2008 210 467 890 201 906 533 620 794 481 869 828 857 157 242 377 192 -49 2009 22 36 48 24 49 33 32 48 63 49 55 48 2010 22 40 56 27 59 34 39 60 71 51 41 57 2011 22 36 60 30 80 33 36 63 81 47 39 76 2012 23 36 69 41 115 43 38 55 84 62 51 85 28 34 17 -20 30 40 17 -18 34 42 17 -21 39 51 26 626 675 818 11,257 17 643 30 673 9 684 29 713 14 832 29 861 134 11,391 174 11,564 Total 8,575 564 System-level System-level activities 75 18 Total funding to the agreed agenda 8,650 582 plus Challenge Program Partners 62 24 Total CGIAR Program 8,712 606 *As from 2012, all inter-Center activities have been eliminated at Center level Total 299 614 1,123 323 1,209 676 764 1,020 780 1,078 1,013 1,123 157 374 543 269 -108 www.cgiar.org 30 Financial Report 2012 Table A2.1: Funding to the agreed research agenda by donor group by Center, 2012 US$ million Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI ICRAF WorldFish Total Window 3 and bilateral contributions by group of donor Europe Austria Belgium Denmark European Commission Finland France Germany Ireland Italy Luxembourg Netherlands Norway Portugal Spain Sweden Switzerland United Kingdom Sub-total North America Canada United States of America Sub-total Pacific Rim Australia Japan Korea, Republic of New Zealand Sub-total AfricaRice Members CGIAR Fund (Window 1 & 2) Total Window 1 & 2 Funding less payments to other CGIAR Centers Net funding from W1/2 to CRPs Challenge Program 10 20 64 (35) 30 (15) 29 (4) 30 (13) 18 (5) 25 (6) 27 (13) 19 (3) 20 (3) 38 (13) 29 (10) 20 10 (0) 388 (120) 10 1 20 28 10 15 26 3 17 13 20 2 14 7 16 18 1 25 3 19 5 20 9 270 32 0 3 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 2 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 2 2 0 1 2 0 0 0 2 1 7 0 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 4 1 0 1 0 0 3 0 1 9 4 0 6 19 1 - 3 1 4 3 3 1 8 8 0 6 6 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 8 1 0 4 4 1 1 2 8 0 2 1 1 2 1 0 3 0 0 0 1 7 5 7 4 12 12 3 3 6 0 9 9 0 2 2 1 4 5 6 6 9 90 99 1 0 4 7 1 1 0 1 0 2 0 1 12 1 1 2 0 1 0 1 1 2 1 1 4 7 5 0 6 2 10 4 4 0 6 6 27 27 5 1 0 0 1 6 1 1 0 2 3 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 2 0 0 3 0 2 6 6 (0) 1 11 2 6 0 22 3 1 20 7 1 0 7 5 0 0 11 11 10 107 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 2 1 0 24 14 2 40 www.cgiar.org 31 Financial Report 2012 Developing countries China Colombia Egypt, Arab Republic of India Iran, Islamic Republic of Libya Malaysia Mexico Morocco Nigeria Peru Philippines Turkey Uganda Sub-total Foundations Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Ford Foundation IDRC Kellogg Foundation Rockefeller Foundation Syngenta Foundation Sub-total International and regional organizations ADB AfDB Arab Fund FAO Gulf Cooperation Council IDB IFAD OPEC Fund UNDP UNEP World Bank Sub-total Others (analysis in Table A2.3) Center only total 1 0 2 1 0 1 0 0 0 31 0 0 - 0 1 0 0 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 1 2 - 4 0 32 1 15 7 2 6 0 3 0 4 0 0 12 5 7 0 0 16 2 2 0 0 0 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 0 15 1 7 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 5 22 1 0 3 3 36 0 0 2 14 69 0 1 2 41 0 2 17 115 2 3 43 - 12 6 0 0 1 2 0 0 0 7 0 3 0 0 1 0 17 2 2 0 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 6 4 38 0 1 3 56 2 4 17 86 0 3 17 65 1 1 1 0 2 10 50 3 4 83 1 0 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 2 2 39 0 3 11 49 0 1 1 25 4 2 0 8 1 0 0 31 0 3 0 1 0 0 52 70 0 1 0 1 73 3 4 2 2 0 1 15 1 2 3 34 113 818 www.cgiar.org 32 Financial Report 2012 Table A2.2: W3 and bilateral donors >US$3m in 2012 Donor AfDB ADB Australia Belgium Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Canada China CFC European Commission Finland Germany IFAD India Ireland Japan Mexico Netherlands Nigeria Norway Sweden Switzerland United Kingdom United States of America Wageningen University World Bank Others <US$2m Total CRP Non-CRP Total Window 3 2.6 78.4 Bilateral 4.1 3.3 21.0 5.8 47.5 9.6 1.8 3.2 16.8 1.0 20.9 12.7 7.2 4.5 7.9 30.9 6.7 2.9 5.5 11.0 10.9 3.4 64.0 5.8 3.8 185.9 498.0 Total 4.1 3.3 23.6 5.8 70.2 9.6 3.7 3.2 22.1 3.2 20.9 12.7 7.6 6.5 14.3 30.9 6.7 2.9 5.5 11.0 11.1 9.6 90.0 5.8 3.8 188.4 576.4 56.8 21.6 78.4 383.0 115.0 498.0 439.8 136.6 576.4 2.7 22.7 1.9 5.3 2.2 0.4 2.0 6.4 0.1 6.2 26.0 www.cgiar.org 33 Financial Report 2012 Table A2.3: Breakdown of other donors 2012 US$ million Total System entities WorldFish ICRAF IWMI IRRI ILRI IITA IFPRI ICRISAT ICARDA CIP CIMMYT CIFOR CIAT Bioversity AfricaRice Members CGIAR Fund legacy programs Developing countries other Europe other Pacific Rim other Foundations other International and regional organizations Multi donor projects Universities and other academic institutions Private sector Other small donations Total other 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 7 1 1 2 0 5 0 0 0 2 1 1 3 2 1 1 1 3 1 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 6 4 0 0 5 1 7 0 0 2 5 7 1 0 1 1 14 1 1 17 1 0 0 4 6 1 2 1 0 17 1 0 10 1 1 4 0 2 0 3 3 0 0 3 17 4 0 0 2 5 0 0 22 1 19 1 13 1 0 28 6 0 0 1 18 7 113 11 - www.cgiar.org 34 Financial Report 2012 Table A3.1: CGIAR expenditure by Center US$ million 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 AfricaRice 11 20 20 21 22 Bioversity 38 36 39 36 37 CIAT 47 47 56 61 68 CIFOR 21 23 25 28 34 CIMMYT 42 44 56 73 110 CIP 28 32 33 34 44 ICARDA 32 33 38 37 46 ICRISAT 48 50 61 65 56 IFPRI 48 58 67 80 84 IITA 51 51 52 47 75 ILRI 43 57 43 43 54 IRRI 41 50 57 74 84 IWMI 25 26 27 32 40 World Agroforestry 28 35 37 42 53 WorldFish 21 18 16 17 27 524 580 627 690 835 16 19 17 9 14 (16) (20) (18) (21) 0 (1) (0) (12) 14 524 579 627 678 849 18 25 30 29 29 542 603 657 707 878 Agreed agenda System level System-level activities less inter-Center activities* Sub-total system level Total plus Challenge Program Partners Total CGIAR Program *As from 2012, inter-Center activities have been eliminated at Center level www.cgiar.org 35 Financial Report 2012 Table A3.2: Centers' research agenda expenditure by region, 2012 US$ million and percentages Expenditure Sub-Saharan Asia Latin America CWANA* US$ % US$ % US$ % US$ % US$ AfricaRice 22 100% 22 0% 0 0% 0 0% 0 Bioversity 37 36% 13 29% 4 22% 8 12% 4 CIAT 68 43% 29 14% 10 43% 29 0% 0 CIFOR 34 37% 13 34% 11 29% 10 0% 0 110 51% 56 25% 28 18% 20 6% 7 CIP 44 63% 28 19% 8 18% 8 0% 0 ICARDA 46 13% 6 8% 4 2% 1 77% 35 ICRISAT 56 49% 28 51% 29 0% 0 0% 0 IFPRI 84 50% 42 33% 28 13% 11 4% 3 IITA 75 100% 75 0% 0 0% 0 0% 0 ILRI 54 61% 33 22% 12 9% 5 8% 4 IRRI 84 29% 24 62% 52 9% 8 1% 0 IWMI 40 56% 27 34% 13 5% 2 5% 2 World Agroforestry 53 62% 33 31% 16 7% 4 0% 0 WorldFish 27 47% 13 44% 12 1% 0 8% 2 833 52.9% 441 27.1% 226 12.6% 105 7.0% 58 CIMMYT Sub-total System level System level Challenge Program Partners 14 29 Total CGIAR Program 876 *Central and West Asia and North Africa www.cgiar.org 36 Financial Report 2012 Table A3.3: Centers' research agenda expenditure by object, 2012 US$ million AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish Sub-total System level System offices Challenge Program Partners Total CGIAR Program AfricaRice Bioversity CIAT CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish Total Center level Total 22 37 68 34 110 44 46 56 84 75 54 84 40 53 27 833 Personnel 9 16 29 14 33 19 15 23 27 23 18 28 16 20 14 303 Supplies 7 12 16 12 32 13 19 23 30 39 22 30 14 16 7 290 Collaboration 3 7 16 5 25 6 6 4 21 4 8 17 7 7 3 139 Travel 2 1 5 3 5 4 4 4 5 4 4 4 3 7 3 58 Depreciation 2 0 2 1 15 2 2 3 1 5 1 6 1 3 0 43 Total 22 37 68 34 110 44 46 56 84 75 54 84 40 53 27 Personnel 38% 44% 43% 41% 30% 43% 32% 40% 32% 31% 34% 33% 40% 38% 51% Supplies 31% 32% 23% 35% 29% 30% 41% 41% 35% 51% 40% 35% 35% 31% 27% Collaboration 14% 18% 25% 15% 23% 14% 14% 6% 25% 6% 16% 20% 17% 13% 12% Travel 9% 3% 7% 8% 5% 8% 9% 7% 6% 6% 7% 5% 7% 14% 10% Depreciation 8% 1% 3% 2% 13% 5% 4% 6% 1% 6% 2% 7% 2% 5% 0% 833 36% 35% 17% 7% 5% 14 29 876 www.cgiar.org 37 Financial Report 2012 Table A3.4: Centers’ staffing 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 International Other International Other International Other International Other International Other AfricaRice 47 237 56 249 58 270 59 255 51 224 Bioversity 71 187 70 180 60 156 60 198 62 148 CIAT 82 645 92 643 95 692 90 700 88 744 CIFOR 43 138 40 131 52 131 72 125 73 133 CIMMYT 77 521 85 521 101 542 119 679 191 811 CIP 59 456 64 483 62 520 90 700 79 620 ICARDA 93 426 93 432 91 515 93 525 89 324 ICRISAT 64 1,099 73 1,031 82 1,108 73 1,146 76 1,162 IFPRI 107 125 118 228 132 245 146 316 149 328 IITA 103 968 97 882 100 857 102 881 116 958 ILRI 83 617 110 573 102 546 103 482 108 485 IRRI 149 827 134 921 131 998 133 1,080 129 1,127 IWMI 86 178 91 174 97 185 106 196 113 202 World Agroforestry 50 259 72 259 78 307 77 317 60 393 WorldFish 49 221 43 215 37 209 42 201 53 290 1,163 6,904 1,238 6,922 1,278 7,281 1,365 7,801 1,437 7,949 Total www.cgiar.org 38 Financial Report 2012 Table A4.1: Centers' financial position, December 31, 2012 US$ million ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish Total 25 20 691 17 13 1 2 1 0 8 0 1 1 4 9 1 2 0 0 3 0 2 0 0 11 0 3 0 1 4 0 1 132 4 55 5 13 1 0 1 ICARDA 40 CIP 50 CIMMYT 73 CIFOR 19 CIAT 59 Bioversity Total assets 12 AfricaRice Assets Current assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable Donors Employees Others Inventories Prepaid expenses Other current assets Total current assets Non-current assets Net property, plant, and equipment Investments Other assets Total noncurrent assets 8 179 40 38 72 32 22 10 0 0 0 0 13 15 1 2 1 0 3 1 5 13 3 0 7 0 4 10 0 4 18 0 5 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 2 20 193 59 47 88 47 36 38 76 35 88 63 46 41 25 902 0 1 7 20 0 2 41 6 0 2 6 55 5 4 29 12 7 2 6 15 0 0 12 24 - 110 143 8 3 0 1 28 5 41 6 2 66 33 12 7 36 2 20 0 261 20 195 86 52 129 53 38 104 110 47 96 99 48 61 25 1,163 www.cgiar.org 39 Financial Report 2012 Liabilities and net assets Current liabilities Accounts payable Donors In-trust accounts Employees Others Accruals and provisions Total current liabilities Long-term liabilities Long-term loan Others Total long-term liabilities Total liabilities Net assets Unrestricted Unrestricted net assets excluding fixed assets Fixed assets Unrestricted net assets Restricted Total net assets Total liabilities and net assets 3 1 1 9 2 163 20 16 46 16 10 31 68 15 49 30 12 17 10 351 0 33 1 4 0 21 4 6 2 21 7 19 5 10 2 4 17 2 12 1 2 2 23 315 4 2 5 2 1 0 6 4 11 0 6 8 1 8 3 63 8 175 58 23 66 37 26 58 85 30 61 56 26 29 15 752 - 7 3 5 10 2 3 13 - - 4 - 3 6 - 8 7 183 3 61 5 28 10 76 2 39 3 29 13 71 85 30 4 65 56 3 29 6 34 15 55 807 12 0 10 1 18 7 21 2 12 41 8 6 8 2 23 6 20 4 5 12 23 7 30 12 17 2 21 6 10 0 242 110 13 13 12 12 25 25 24 24 53 53 14 14 10 10 29 4 33 24 24 18 18 31 31 43 43 19 19 27 27 10 10 352 4 356 20 195 86 52 129 53 38 104 110 47 96 99 48 61 25 1,163 55 www.cgiar.org 40 Financial Report 2012 Table A4.2: Additions to property, plant, and equipment by Center US$ million 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 AfricaRice 0.6 0.3 1.2 1.2 0.1 1.7 Bioversity 0.3 0.5 0.3 0.5 0.3 0.4 CIAT 1.0 2.7 2.6 2.6 2.9 3.7 CIFOR 0.6 0.4 0.7 0.7 1.1 0.7 CIMMYT 1.4 2.0 4.6 4.9 5.7 37.9 CIP 0.9 1.0 2.0 2.2 1.6 3.7 ICARDA 0.5 0.7 1.5 1.3 1.5 1.7 ICRISAT 1.0 1.1 3.1 2.8 2.3 3.8 IFPRI 2.5 0.4 1.2 0.6 1.2 0.7 IITA 1.0 1.3 2.3 5.3 0.6 3.5 ILRI 4.3 7.4 6.7 2.5 2.4 1.7 IRRI 3.6 2.0 3.2 4.6 5.2 6.6 IWMI 0.2 0.3 0.5 0.4 1.0 0.9 World Agroforestry 0.5 0.8 1.0 0.9 1.7 2.2 WorldFish 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 18.7 21.2 30.9 30.4 27.6 69.1 Total www.cgiar.org 41 Financial Report 2012 Table A5.1: CGIAR expenditure1 US$ million 1972-2008 US$ % 2009 US$ % 2010 US$ % 2011 US$ % 2012 US$ % Center AfricaRice 254 3% 20 3% 20 3% 21 3% 22 3% Bioversity 486 5% 36 6% 39 6% 36 5% 37 4% CIAT 990 10% 47 8% 56 9% 61 9% 68 8% CIFOR 198 2% 23 4% 25 4% 28 4% 34 4% CIMMYT 1,017 10% 44 8% 56 9% 73 11% 110 13% CIP 591 6% 32 5% 33 5% 34 5% 44 5% ICARDA 691 7% 33 6% 38 6% 37 5% 46 5% ICRISAT 897 9% 50 9% 61 10% 65 9% 56 7% IFPRI 512 5% 58 10% 67 11% 80 12% 84 10% IITA 1,089 11% 51 9% 52 8% 47 7% 75 9% ILRI 896 9% 57 10% 43 7% 43 6% 54 6% IRRI 1,063 11% 50 9% 57 9% 74 11% 84 10% ISNAR2 193 2% 0 0% 0 0% 0% 0% IWMI 255 3% 26 4% 27 4% 32 5% 40 5% World Agroforestry 384 4% 35 6% 37 6% 42 6% 53 6% WorldFish 201 2% 18 3% 16 3% 17 2% 27 3% Total 9,717 100% 580 100% 627 100% 688 100% 834 100% Region Sub-Saharan Africa 4,199 43% 294 51% 313 50% 323 48% 441 53% Asia 2,974 31% 165 29% 181 30% 229 33% 226 27% Latin America and the Caribbean 1,492 15% 75 13% 82 13% 84 12% 105 13% Central and West Asia and North Africa 1,052 11% 47 7% 51 7% 52 7% 61 7% Total 9,717 100% 580 100% 627 100% 688 100% 834 100% Object Personnel 4,890 50% 245 42% 268 43% 296 43% 303 36% Collaboration and partnership costs Others 397 4% 105 18% 112 18% 110 16% 139 17% Supplies and services 3,084 32% 156 27% 173 27% 206 30% 291 35% Travel 691 7% 41 7% 48 8% 48 7% 58 7% Depreciation 655 7% 33 6% 26 4% 28 4% 43 5% Total 9,717 100% 580 100% 627 100% 688 100% 834 100% 1This data is aggregated at the Center level 2The International Service for National Agricultural Research (ISNAR) was subsumed in part under IFPRI after 2004 Total US$ % 338 634 1,222 307 1,300 733 844 1,129 801 1,315 1,093 1,329 193 380 550 279 12,447 3% 5% 10% 2% 10% 6% 7% 9% 6% 11% 9% 11% 2% 3% 4% 2% 100% 5,570 3,775 45% 30% 1,838 15% 1,264 12,447 10% 100% 6,002 48% 863 7% 3,910 886 784 12,446 31% 7% 6% 100% www.cgiar.org 42 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.1: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Australia IFAD India AFESD Others <US$1 m Dryland Systems ICARDA 3 years July 2012* CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 10.0 10.0 Center own 4.0 0.5 0.4 0.4 1.8 1.0 0.4 0.7 9.1 2.8 2.8 2.5 0.2 0.1 2.8 Total 2011 Total 34.5 44.5 44.5 2.6 2.6 2.0 1.4 10.0 18.6 9.1 2.6 2.6 2.0 1.4 13.1 30.8 - 9.1 2.6 2.6 2.0 1.4 13.1 30.8 - 16.4 0.6 0.6 0.6 5.8 3.5 1.0 2.2 30.8 9.1 9.1 By participant ICARDA Bioversity CIAT CIP ICRISAT ILRI IWMI World Agroforestry 2012 Bilateral 9.9 0.2 0.0 0.1 4.1 2.4 0.6 1.2 18.6 0.3 0.3 0.3 16.4 0.6 0.6 0.6 5.8 3.5 1.0 2.2 30.8 *Inception phase www.cgiar.org 43 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.2: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 USAID Sweden Nigeria Others <US$1 m Integrated Systems for the Humid Tropics IITA 3 years July 2012 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 11.8 7.3 Center own 2.2 4.3 0.2 0.5 0.4 1.3 0.3 0.2 7.2 0.7 2.9 2.1 0.0 0.1 0.5 0.3 2.9 Total 2011 Total 12.2 24.0 24.0 0.7 2.2 1.1 5.9 9.9 0.2 0.2 7.2 2.9 2.2 1.1 6.8 20.2 - 7.2 2.9 2.2 1.1 6.8 20.2 0.2 0.2 13.6 0.2 1.9 1.6 1.8 0.3 0.7 20.2 - 13.6 0.2 1.9 1.6 1.8 0.3 0.7 20.2 7.2 7.2 By participant IITA Bioversity CIAT CIP ILRI IWMI World Agroforestry 2012 Bilateral 7.2 1.3 0.7 0.2 0.0 0.3 9.9 www.cgiar.org 44 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.3: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 USAID Australia Sweden Others <US$1 m By participant WorldFish Bioversity IWMI Aquatic Agricultural Systems WorldFish 3 years July 2011 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 9.7 9.7 2012 Bilateral Center own Total 2011 Total 8.8 18.5 8.7 4.4 27.2 - 7.5 6.2 1.5 1.4 3.5 20.1 2.6 5.2 1.5 1.4 3.5 11.6 10.1 6.2 1.5 1.4 7.0 26.1 - 19.3 0.3 0.5 20.1 7.5 1.0 7.5 1.0 7.1 0.2 0.2 7.5 1.0 1.0 11.2 0.1 0.3 11.6 3.5 6.0 6.0 6.0 25.3 0.3 0.5 26.1 www.cgiar.org 45 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.4: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 USAID/World Bank USAID Bill &Melinda Gates Foundation GTZ European Commission World Bank IFAD SIDA Others <US$1 m Policies, Institutions and Markets IFPRI 3 years January 2012 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 30.3 27.0 50.7 Center own Total 1.0 81.9 81.9 15.2 17.5 7.9 15.2 15.2 By participant IFPRI Bioversity CIAT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IITA ILRI World Agroforestry WorldFish 2012 Bilateral 8.8 1.0 0.7 0.7 0.0 1.6 0.5 1.1 0.6 0.1 15.2 2011 Total 7.5 10.0 7.9 15.2 17.5 7.9 1.7 4.1 5.8 5.8 3.3 3.3 3.3 1.8 1.8 1.8 1.5 1.5 1.0 19.3 50.4 1.5 1.5 1.0 19.8 75.3 - 1.5 1.5 1.0 19.8 75.3 - 58.6 2.0 1.8 2.7 0.0 5.3 1.8 1.5 0.9 0.7 75.3 0.3 9.5 9.5 9.5 0.2 0.2 40.3 1.0 1.1 2.0 3.7 1.3 0.4 0.1 0.6 50.4 0.2 0.2 58.6 2.0 1.8 2.7 0.0 5.3 1.8 1.5 0.9 0.7 75.3 www.cgiar.org 46 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.5: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Wheat CIMMYT 3 years January 2012 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 13.6 13.0 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Mexico USDA Cornell IRRI GRDC Others <US$1 m By participant CIMMYT ICARDA 2012 Bilateral Center own Total 2011 Total 38.4 52.0 52.0 11.4 9.7 2.9 4.1 2.2 1.4 9.2 40.7 - 11.4 9.7 2.9 4.1 2.2 1.4 9.2 40.7 34.0 6.7 40.7 - 34.0 6.7 40.7 11.4 11.4 2.3 2.3 9.7 2.9 4.1 2.2 1.4 6.8 27.0 9.7 1.7 11.4 1.0 1.3 2.3 23.3 3.7 27.0 www.cgiar.org 47 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.6: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Maize CIMMYT 3 years July 2011 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 14.9 14.5 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 SAGARPA (Mexico) Gates Foundation ACIAR (Australia) SDC (Switzerland) USAID AATF IRRI HarvestPlus IFAD SFSA Others <US$1 m By participant CIMMYT IITA 2012 Bilateral Total 2011 Total 41.8 56.7 25.7 7.1 82.4 13.5 19.5 16.7 6.7 3.0 2.9 1.9 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.3 4.8 74.2 3.4 25.5 28.9 16.9 19.5 16.7 6.7 3.0 2.9 1.9 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.3 30.2 103.1 67.6 6.5 74.2 25.3 3.5 28.9 93.0 10.1 103.1 13.5 13.5 9.2 19.5 7.5 6.7 3.0 2.9 1.9 1.4 1.3 1.3 1.3 4.8 51.5 11.8 1.7 13.5 7.3 1.9 9.2 48.5 3.0 51.5 9.2 Center own www.cgiar.org 48 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.7: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Gates Foundation Japan USA European Commission Australia Switzerland CGIAR Centers IRRI ADB Germany IFAD India Chinese Academy of Agriculture HarvestPlus Canada FLAR Korea Others <US$1 m Rice IRRI 5 years January 2011 Center own Total 2011 Total 27.4 1.2 89.0 85.8 34.9 174.9 5.4 5.2 35.4 15.7 9.3 5.6 34.3 15.7 3.9 0.4 69.7 15.7 9.3 5.6 1.5 2.0 3.5 3.5 0.3 2.8 2.1 1.8 1.8 1.5 1.5 1.1 2.8 2.1 1.8 1.8 1.5 1.5 1.3 2.8 2.1 1.8 1.8 1.5 1.5 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.3 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.0 10.8 50.9 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.0 11.0 99.1 62.9 97.2 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.0 73.8 196.3 8.7 2.4 39.9 50.9 19.0 6.4 73.7 99.1 20.4 6.5 70.3 97.2 39.3 12.9 144.0 196.3 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 60.4 34.9 35.4 0.2 35.4 By participant AfricaRice CIAT IRRI 2012 Bilateral 8.7 4.0 22.7 35.4 0.2 12.7 1.6 11.1 12.7 - www.cgiar.org 49 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.8: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Roots, Tubers and Bananas CIP 3 years January 2012 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 38.3 33.7 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Gates Foundation USAID Belgium AFDB Nigeria Others <US$1m By participant CIP Bioversity CIAT IITA 22.3 2.6 2012 Bilateral Center own Total 19.1 0.9 58.3 58.3 22.3 6.9 6.4 1.4 1.3 1.0 11.9 51.2 - 22.3 6.9 6.4 1.4 1.3 1.0 11.9 51.2 26.1 9.3 4.6 11.2 51.2 - 26.1 9.5 4.6 11.2 51.3 22.3 2.6 4.3 6.4 1.4 1.3 1.0 11.9 26.3 9.1 5.8 2.9 4.5 22.3 1.0 0.1 0.1 1.4 2.6 16.0 3.4 1.6 5.3 26.3 - 2011 Total www.cgiar.org 50 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.9: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Gates Foundation USAID CIDA India GCP Others <US$1 m By participant ICRISAT CIAT ICARDA IITA Grain Legumes ICRISAT 3 years July 2012 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 10.1 10.1 2012 Bilateral Center own Total 2011 Total 9.3 19.4 19.4 7.5 4.4 1.8 1.7 1.7 1.0 4.4 22.5 - 7.5 4.4 1.8 1.7 1.7 1.0 4.4 22.5 10.6 4.8 2.2 4.9 22.5 - 10.6 4.8 2.2 4.9 22.5 7.5 4.4 7.5 4.4 1.8 1.7 1.7 1.0 4.4 10.6 3.0 1.4 1.2 1.8 7.5 2.6 0.8 0.3 0.8 4.4 5.0 2.6 0.7 2.3 10.6 - www.cgiar.org 51 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.10: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Gates Foundation Others <US$1 m By participant ICRISAT ICARDA Dryland Cereals ICRISAT 3 years July 2012 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 5.3 5.3 2012 Bilateral Center own 2.4 0.9 3.2 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 2011 Total 6.6 11.9 11.9 2.1 2.0 4.1 3.2 2.1 2.2 7.4 - 3.2 2.1 2.2 7.4 3.7 0.4 4.1 6.2 1.3 7.4 - 6.2 1.3 7.4 3.2 3.2 Total - www.cgiar.org 52 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.11: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start Date: Approved budget Approved financing By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Switzerland Others <US$1 m By participant ILRI CIAT ICARDA WorldFish Livestock and Fish ILRI 3 years January 2012 CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 11.9 15.2 2012 Bilateral 5.0 1.2 0.4 1.1 7.7 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 Total Total 1.9 33.8 33.8 1.3 6.7 7.9 7.7 1.3 7.0 16.0 - 7.7 1.3 7.0 16.0 4.5 1.5 0.1 1.9 7.9 9.8 2.7 0.5 3.0 16.0 - 9.8 2.7 0.5 3.0 16.0 20.0 7.7 7.7 2011 Center own - www.cgiar.org 53 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.12: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Agriculture for Nutrition and Health IFPRI 3 years January 2012 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 32.8 17.2 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Family Health Inc. Gates Foundation USAID IDRC DFID European Commission Others <US$1 m Center own Total 30.2 0.4 63.4 63.4 4.4 3.0 2.1 1.7 1.5 9.2 4.4 3.0 2.1 1.7 1.5 9.2 4.4 3.0 2.1 1.7 1.5 1.0 0.4 1.4 1.4 0.1 1.2 14.1 27.1 14.2 37.4 1.0 0.1 15.6 1.1 1.2 1.6 1.2 3.0 3.1 0.2 0.2 27.1 19.3 2.7 1.8 1.9 2.1 4.0 5.0 0.5 0.2 37.4 9.2 9.2 By participant IFPRI Bioversity CIAT CIP ICRISAT IITA ILRI World Agroforestry WorldFish 2012 Bilateral 2.7 1.6 0.6 0.3 0.9 1.0 1.8 0.3 0.0 9.2 0.1 1.2 - 2011 Total - 14.2 37.4 - 19.3 2.7 1.8 1.9 2.1 4.0 5.0 0.5 0.2 37.4 www.cgiar.org 54 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.13: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Water, Land and Ecosystems IWMI 3 years January 2012 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 55.4 29.0 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Gates Foundation Wageningen University Switzerland IFAD AusAid AGRA ACIAR Others <US$1 m By participant IWMI Bioversity CIAT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI World Agroforestry WorldFish 2012 Bilateral Center own Total 27.3 0.7 83.4 83.4 0.1 0.1 22.4 6.7 4.3 4.0 3.7 1.8 1.1 1.0 11.0 56.1 - 22.4 6.7 4.3 4.0 3.7 1.8 1.1 1.0 11.0 56.1 - 29.7 2.5 9.1 0.4 2.6 2.3 1.0 3.2 1.9 3.1 0.2 56.0 22.4 1.4 1.4 1.4 22.4 14.7 1.9 1.1 0.4 0.8 1.0 0.5 0.2 0.2 1.5 0.1 22.4 0.9 5.1 5.3 4.3 2.7 2.2 1.8 1.1 1.0 10.0 28.4 3.4 11.7 0.6 7.9 0.3 1.6 1.3 0.5 1.6 1.6 1.5 0.1 28.4 1.4 0.1 5.1 0.1 0.1 29.7 2.5 9.1 0.4 2.6 2.3 1.0 3.2 1.9 3.1 0.2 56.0 2011 Total www.cgiar.org 55 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.14: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CIFOR 3 years July 2011 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 25.7 27.9 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 European Commission Multi donor (MARS Inc.) Norway USAID IFAD African Development Bank GIZ/BMZ CIDA ACIAR Belgium Others <US$1 m Total 2011 Total 47.9 78.4 33.9 12.7 112.3 2.1 2.1 29.4 6.7 5.8 4.7 3.5 1.7 1.6 1.4 1.3 1.1 1.1 15.1 73.3 11.1 6.7 5.8 4.7 3.2 1.7 1.6 1.4 1.3 1.1 1.1 11.9 40.5 17.6 28.7 40.5 6.7 5.8 4.7 3.5 1.7 1.6 1.4 1.3 1.1 1.1 32.7 102.0 2.1 2.1 33.0 6.1 1.4 32.8 73.3 13.3 4.1 0.1 11.2 28.7 46.3 10.3 1.5 44.0 102.0 Center own 29.4 0.3 29.4 By participant CIFOR Bioversity CIAT World Agroforestry 2012 Bilateral 14.3 3.9 0.3 10.9 29.4 1.0 1.3 1.1 0.3 1.3 17.6 1.9 1.2 19.7 40.5 www.cgiar.org 56 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.15: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security CIAT 5 years January 2011 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 56.1 41.4 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 USAID ACIAR Challenge Others <US$1 m Center own Total 2011 Total 11.4 3.6 71.1 63.2 41.4 134.3 46.4 1.6 1.4 1.3 12.2 63.0 31.7 1.5 1.4 1.3 11.8 16.0 25.1 56.8 78.1 1.6 1.4 1.3 37.4 119.7 2.8 0.6 1.4 0.4 1.5 0.4 0.4 1.3 1.0 0.3 0.4 0.3 1.1 2.8 1.4 16.0 14.1 1.3 5.7 1.0 4.7 2.4 1.9 5.2 3.3 1.3 5.9 1.4 4.7 8.1 1.9 63.0 11.8 0.3 6.2 0.1 5.6 1.9 2.1 3.9 2.7 1.1 6.9 0.5 3.6 7.9 2.1 56.8 26.0 1.6 11.9 1.1 10.3 4.3 4.0 9.2 6.0 2.4 12.8 1.8 8.4 16.0 3.9 119.7 46.4 0.1 46.4 By participant CIAT AfricaRice Bioversity CIFOR CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IFPRI IITA ILRI IRRI IWMI World Agroforestry WorldFish 2012 Bilateral 11.3 0.7 4.1 0.6 3.2 2.0 1.4 3.9 2.3 1.0 5.5 1.1 3.6 5.3 0.5 46.4 0.4 0.5 0.0 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.0 0.5 - www.cgiar.org 57 Financial Report 2012 Table A6.16: CRP highlights US$ million CRP: Lead Center: Duration: Start date: Managing and Sustaining Crop Collections (Genebanks) Global Crop Diversity Trust 3 years January 2012 Approved budget Approved financing CGIAR Fund Window 1/2 Window 3 18.2 18.2 By major donor CGIAR Window 1/2 Others <US$1 m Total 2011 Total 2.6 20.8 21.0 13.1 41.8 3.3 3.3 12.6 3.3 15.9 12.0 2.0 14.0 24.6 5.3 29.9 1.0 0.4 2.6 2.1 3.8 0.9 2.1 1.0 0.6 1.5 15.9 0.8 0.3 2.5 2.4 2.8 1.0 2.2 0.9 1.8 0.7 5.1 4.5 6.6 1.9 4.3 1.9 0.6 2.6 29.9 Center own 12.6 12.6 By participant Bioversity AfricaRice CIAT CIMMYT CIP ICARDA ICRISAT IITA ILRI IRRI 2012 Bilateral 0.9 0.4 2.3 0.9 3.4 0.5 1.7 0.8 0.6 1.2 12.6 - 0.1 0.3 1.2 0.4 0.3 0.4 0.2 - 0.3 3.3 - 1.1 14.0 www.cgiar.org 58 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.1: AfricaRice US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue GRiSP CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 Bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 8.5 9.8 8.5 8.2 0.0 0.3 8.5 11.7 9.8 8.7 0.7 0.4 9.8 1.6 9.2 20.7 0.3 1.5 1.8 22.4 0.2 22.7 0.0 5.8 6.8 12.6 12.6 0.3 12.9 0.0 16.7 5.6 22.3 22.3 0.1 22.4 0.0 14.0 8.3 22.3 22.3 0.1 22.4 20.2 0.3 1.8 2.1 22.3 0.1 22.4 5.8 5.1 16.7 3.1 14.0 6.3 20.2 0.3 0.7 10.9 2.0 19.8 2.6 20.3 2.1 21.2 1.2 20.7 0.3 1.2 0.0 22.1 0.5 47 237 284 56 249 305 58 270 328 59 255 314 51 224 275 181 2.0 181 152 1.8 152 195 2.5 195 221 2.4 221 215 2.5 215 0.3 53% 29% 1.2 119% 15% 1.2 101% 16% 2.3 100% 14% 1.7 101% 15% www.cgiar.org 59 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.2: Bioversity US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics AAS PIM RTB A4NH WLE Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 Bilateral Total CRP Window 1/2 revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP Window 1/2 revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 6.3 0.0 21.0 16.4 37.4 37.4 1.1 38.5 0.0 21.5 14.3 35.8 35.8 0.1 35.9 0.0 21.8 16.3 38.1 38.1 0.0 38.1 6.3 19.7 10.0 29.7 36.0 0.9 36.9 20.2 (0.2) 20.0 0.5 0.2 0.2 1.0 5.8 1.6 1.9 3.9 4.1 0.9 20.0 0.6 9.8 30.4 3.4 1.8 5.2 35.5 1.7 37.3 21.0 17.3 21.5 14.9 21.8 15.3 6.3 19.7 10.2 30.4 3.4 2.9 38.3 0.2 36.4 (0.5) 37.1 1.0 36.2 0.7 36.7 0.6 71 187 258 70 180 250 60 156 216 60 198 258 62 148 210 121 1.2 81 126 1.2 82 137 1.1 90 164 1.1 99 180 1.1 105 0.5 87% 19% 0.3 56% 20% 0.5 93% 17% 0.3 48% 18% 0.4 75% 18% 6.3 1.9 3.6 0.8 6.3 www.cgiar.org 60 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.3: CIAT US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics PIM GRiSP RTB Grain Legumes Livestock and Fish A4NH WLE Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 38.1 (25.6) 12.5 0.0 33.8 12.5 46.3 46.3 1.9 48.2 0.0 34.1 13.9 48.0 48.0 1.2 49.2 0.0 39.8 16.3 56.1 56.1 6.1 62.2 8.3 20.8 32.8 6.1 38.8 59.6 2.8 62.4 61.7 (34.9) 26.8 0.4 0.5 0.7 4.0 2.9 1.4 1.2 0.6 1.1 0.3 11.3 2.3 26.8 0.4 24.7 51.9 15.6 1.8 17.4 69.3 4.3 73.6 33.8 13.5 34.1 12.9 39.8 16.3 20.8 32.8 7.4 51.9 15.6 0.7 47.3 0.9 47.0 2.2 56.1 6.1 61.0 1.4 68.2 5.4 82 645 727 92 643 735 95 692 787 90 700 790 88 744 832 31 1.1 39 69 1.3 56 95 1.4 84 97 1.3 83 113 1.4 99 2.7 135% 18% 2.6 114% 12% 2.6 140% 12% 3.0 134% 15% 3.7 192% 16% 4.3 0.0 6.0 2.1 12.5 www.cgiar.org 61 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.4: CIFOR US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 11.2 (6.5) 4.7 4.6 0.2 4.8 8.3 0.0 11.7 9.6 21.3 21.3 0.6 21.9 0.0 13.9 9.7 23.6 23.6 0.3 23.9 0.0 15.4 11.6 27.0 27.0 0.1 27.1 13.1 10.4 6.4 16.8 29.9 0.1 30.0 30.0 (15.1) 14.8 14.3 0.6 14.8 1.1 18.0 34.0 0.0 6.8 6.8 40.8 0.3 41.1 11.7 8.9 13.9 8.8 15.4 9.5 13.1 10.4 4.5 34.0 0.0 (0.1) 20.6 1.3 22.7 1.2 24.9 2.2 28.0 2.0 33.8 7.2 43 138 181 40 131 171 52 131 183 72 125 197 73 133 206 213 2.5 176 216 1.7 175 236 2.1 190 235 3.0 190 275 2.0 237 0.4 129% 20% 0.7 121% 29% 0.7 129% 28% 1.1 161% 19% 0.7 106% 20% www.cgiar.org 62 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.5: CIMMYT US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue WHEAT MAIZE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.7 0.0 29.8 11.0 40.8 40.8 2.3 43.1 0.0 38.1 10.7 48.8 48.8 1.6 50.4 0.0 43.5 15.3 58.8 58.8 2.0 60.8 33.2 40.5 6.2 46.7 79.9 1.7 81.6 29.4 (3.9) 25.5 9.7 11.8 3.2 0.9 25.5 8.8 74.1 108.5 6.3 0.1 6.4 114.9 1.1 116.0 29.8 11.9 38.1 6.2 43.5 12.5 33.2 40.5 (0.9) 108.5 6.3 (4.7) 41.7 1.4 44.3 6.1 56.0 4.8 72.8 8.8 110.1 5.9 77 521 598 85 521 606 101 542 643 119 679 798 191 811 1,002 165 1.9 106 217 1.6 153 192 1.7 141 197 1.8 157 82 1.3 45 2.0 98% 19% 4.6 154% 14% 4.9 150% 16% 5.7 118% 10% 37.9 262% 7% 2.7 2.7 4.2 0.8 7.7 25.5 www.cgiar.org 63 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.6: CIP US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics PIM RTB A4NH WLE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 3.7 0.0 3.7 0.0 19.0 8.5 27.5 27.5 0.5 28.0 0.0 20.6 12.1 32.7 32.7 0.6 33.3 0.0 21.4 12.1 33.5 33.5 0.6 34.1 3.7 20.3 9.2 29.5 33.2 0.6 33.8 29.9 (13.2) 16.7 0.4 0.4 0.7 9.1 0.3 0.4 2.0 3.4 16.7 1.5 21.2 39.4 2.7 1.1 3.9 43.3 0.8 44.1 19.0 8.6 20.6 11.2 21.4 11.6 3.7 20.3 9.7 39.4 2.7 1.7 27.6 0.4 31.8 1.5 33.0 1.1 33.7 0.1 43.9 0.2 59 456 515 64 483 547 62 520 582 71 518 589 79 620 699 92 1.4 84 104 1.4 90 120 1.5 100 113 1.5 92 89.8 1.3 72 1.0 134% 13% 2.0 131% 14% 2.2 121% 21% 1.6 104% 21% 3.1 131% 17% 0.9 2.8 3.7 www.cgiar.org 64 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.7: ICARDA US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems PIM WHEAT Grain Legumes Dryland Cereals Livestock and Fish WLE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.5 0.0 2.5 16.0 (5.1) 10.9 4.0 0.0 1.7 1.2 0.9 0.4 0.8 1.4 0.5 10.9 4.5 17.3 32.7 2.1 3.7 5.8 38.5 1.5 39.9 1.5 1.0 2.5 0.0 19.3 10.8 30.1 30.1 1.8 31.9 0.0 19.4 12.4 31.8 31.8 1.3 33.1 0.0 25.9 12.8 38.7 38.7 0.7 39.4 2.5 23.9 9.5 33.4 35.9 1.5 37.4 19.3 12.7 19.4 13.1 25.9 12.4 2.5 23.9 10.6 32.0 (0.1) 32.5 0.6 38.3 1.1 37.0 0.4 32.7 2.1 4.2 6.7 45.6 (5.6) 93 426 519 93 432 525 91 515 606 93 525 618 89 324 413 205 1.9 124 163 1.6 121 151 1.6 114 178 1.7 108 104 1.4 78 0.7 50% 21% 1.5 113% 18% 1.3 53% 18% 2.7 157% 17% 1.7 91% 15% www.cgiar.org 65 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.8: ICRISAT US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems PIM Grain Legumes Dryland Cereals A4NH WLE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.1 0.0 2.1 0.0 34.1 13.9 48.0 48.0 2.6 50.6 0.0 33.5 14.3 47.8 47.8 4.2 52.0 0.0 43.7 16.2 59.9 59.9 4.8 64.7 6.0 46.1 10.4 56.5 62.5 4.5 67.0 21.6 (5.6) 15.9 1.8 1.6 3.0 2.4 0.9 1.0 3.9 1.7 16.2 2.9 20.4 39.6 10.8 4.9 15.7 55.4 4.8 60.2 34.1 13.8 33.5 16.4 43.7 17.5 6.0 46.1 13.2 39.6 10.8 6.0 47.9 2.7 49.9 2.1 61.2 3.5 65.3 1.7 56.4 3.8 64 1,099 1,163 73 1,031 1,104 82 1,108 1,190 73 1,146 1,219 76 1,162 1,238 170 1.9 127 169 1.6 132 205 1.8 130 190 1.7 118 227 1.6 147 1.1 51% 23% 3.1 138% 23% 2.8 98% 23% 2.8 127% 18% 3.8 114% 15% 2.1 2.1 4.2 1.8 www.cgiar.org 66 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.9: IFPRI US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue PIM A4NH WLE CCAFS CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.1 0.0 2.1 0.0 35.8 14.3 50.1 50.1 0.4 50.5 0.0 46.9 15.5 62.4 62.4 0.6 63.0 0.0 53.2 17.2 70.4 70.4 (0.4) 70.0 2.6 62.3 16.6 78.9 81.5 0.3 81.8 27.1 (13.2) 13.9 8.8 2.6 0.5 2.3 14.2 10.5 55.9 80.6 1.2 1.9 3.1 83.7 0.4 84.1 35.8 12.7 46.9 11.4 53.2 12.9 2.6 62.3 14.6 80.6 1.2 2.5 48.5 2.0 58.3 4.7 66.1 3.9 79.5 2.3 84.3 (0.2) 107 125 232 118 228 346 132 245 377 146 316 462 149 328 477 114 1.4 94 128 1.4 108 137 1.4 116 125 1.4 103 118 1.0 91 0.4 52% 16% 0.5 67% 17% 0.6 75% 16% 1.6 175% 15% 2.0 163% 16% 0.5 0.5 2.1 www.cgiar.org 67 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.10: IITA US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Humidtropics PIM MAIZE RTB Grain Legumes A4NH WLE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 1.5 0.0 1.5 18.7 (2.9) 15.8 4.3 0.5 1.7 4.5 1.8 1.0 0.2 1.0 0.8 15.8 7.6 24.1 47.5 9.9 4.7 14.7 62.2 1.0 63.1 0.7 0.8 0.0 1.5 0.0 36.0 12.2 48.2 48.2 2.9 51.1 0.0 34.4 14.0 48.4 48.4 3.8 52.2 0.0 36.4 16.0 52.4 52.4 0.8 53.2 3.1 1.5 31.5 13.8 45.3 46.8 0.6 47.4 36.0 14.8 34.4 16.4 36.4 16.6 1.5 31.5 13.7 50.8 0.3 50.8 1.4 53.0 0.2 46.7 0.7 47.5 9.9 3.2 14.8 75.4 (12.3) 103 968 1,071 97 882 979 100 857 957 102 881 983 116 958 1,074 158 2.0 158 161 1.8 161 135 1.9 135 159 1.6 159 31 1.2 31 1.3 102% 20% 2.3 168% 20% 5.3 268% 17% 1.5 96% 16% 3.5 247% 15% www.cgiar.org 68 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.11: ILRI US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics PIM Livestock and Fish A4NH WLE CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 4.2 0.0 4.2 0.0 25.1 14.8 39.9 39.9 4.2 44.1 0.0 37.7 17.0 54.7 54.7 3.8 58.5 0.0 23.5 17.7 41.2 41.2 3.3 44.5 6.0 19.1 14.4 33.5 39.5 4.1 43.6 19.3 (2.7) 16.6 1.0 1.4 1.1 5.0 1.8 0.2 5.5 0.6 16.6 0.8 12.6 30.0 18.0 2.6 20.6 50.6 5.2 55.8 25.1 17.5 37.7 19.6 23.5 19.8 6.0 19.1 17.6 30.0 18.0 5.9 42.6 1.5 57.3 1.2 43.3 1.2 42.7 0.9 53.5 2.2 83 617 700 110 573 683 102 546 648 103 482 585 108 485 593 116 1.5 78 179 2.1 146 210 2.0 170 212 1.5 144 189 1.4 164 7.4 455% 16% 6.7 50% 14% 2.5 74% 23% 2.4 152% 23% 0.8 68% 20% 4.2 4.2 1.8 www.cgiar.org 69 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.12: IRRI US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue GRiSP CCAFS Genebanks CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP revenue Other Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 35.7 (12.3) 23.3 22.0 0.2 1.0 23.2 48.4 0.0 23.9 13.5 37.4 37.4 0.3 37.7 0.0 33.7 14.4 48.1 48.1 1.8 49.9 0.0 40.8 15.9 56.7 56.7 1.7 58.4 71.6 1.2 2.9 4.1 75.7 1.8 77.5 37.7 (12.7) 25.0 22.7 1.1 1.2 25.0 11.9 40.4 77.3 5.4 1.8 7.3 84.5 2.0 86.5 23.9 17.5 33.7 16.4 40.8 16.4 71.6 1.2 1.2 77.3 5.4 1.6 41.4 (3.7) 50.1 (0.2) 57.2 1.2 74.0 3.5 84.3 2.2 149 827 976 134 921 1,055 131 998 1,129 133 1,080 1,213 129 1,127 1,256 260 1.8 260 206 1.6 206 181 1.6 181 161 1.0 161 142 1.1 142 2.0 81% 17% 3.2 103% 12% 4.6 131% 13% 5.2 97% 11% 6.6 112% 12% www.cgiar.org 70 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.13: IWMI US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics AAS WLE CCAFS CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP grant revenue Total grant revenue Other income Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.3 0.0 2.3 0.0 17.1 7.4 24.5 24.5 0.7 25.2 0.0 20.0 8.2 28.2 28.2 0.5 28.7 0.0 20.7 10.2 30.9 30.9 0.6 31.5 3.4 21.2 9.5 30.7 34.1 1.0 35.1 26.9 (7.7) 19.2 0.4 0.3 0.2 14.7 3.6 19.2 4.3 13.7 37.2 1.7 0.4 2.2 39.3 1.4 40.7 17.1 6.5 20.0 5.7 20.7 6.9 3.4 21.2 7.8 37.2 1.7 0.7 23.6 1.6 25.7 3.0 27.6 3.9 32.4 2.7 39.6 1.1 86 178 264 91 174 265 97 185 282 106 196 302 113 202 315 132 1.7 104 170 1.6 140 219 2.0 188 218 2.2 187 187 1.8 161 0.3 64% 26% 0.5 91% 21% 0.4 57% 21% 1.0 143% 17% 0.9 121% 14% 0.1 2.2 2.3 1.1 www.cgiar.org 71 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.14: World Agroforestry US$ million Revenues CRP Win 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue Dryland Systems Humidtropics PIM A4NH WLE Forests, Trees and Agroforestry CCAFS CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP grant revenue Total grant revenue Other income Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 9.4 0.0 9.4 0.0 17.6 11.7 29.3 29.3 2.0 31.3 0.0 21.1 12.4 33.5 33.5 3.0 36.5 0.0 26.0 14.0 40.0 40.0 2.1 42.1 18.5 17.7 5.7 23.4 41.9 1.2 43.1 19.8 (0.4) 19.4 0.7 0.2 0.6 0.3 1.4 10.9 5.3 19.4 0.0 26.0 45.4 4.1 1.5 5.6 50.9 1.7 52.6 17.6 10.7 21.1 13.8 26.0 10.9 18.5 17.7 5.7 45.4 4.1 3.4 28.3 3.0 34.9 1.6 36.9 5.2 41.9 1.2 52.9 (0.2) 50 259 309 72 259 331 78 307 385 77 317 394 60 393 453 229 2.3 178 221 1.9 165 253 2.3 199 242 2.2 194 195 1.4 155 0.8 84% 21% 1.0 129% 21% 0.9 95% 19% 1.8 107% 15% 2.9 112% 15% 4.6 4.8 9.4 9.1 www.cgiar.org 72 Financial Report 2012 Table A7.15: WorldFish US$ million Revenues CRP Window 1/2 Lead Center CRP income less collaboration CGIAR should equal total CRP revenue AAS PIM Livestock and Fish A4NH WLE CCAFS CRP Window 1/2 CRP Window 3 CRP bilateral Total CRP revenue Non-CRP restricted Unrestricted Total non-CRP grant revenue Total grant revenue Other income Total revenue Expenditure Restricted CRP expenditure Restricted non-CRP expenditure Unrestricted Extraordinary expenditure Total expenditure Results of operations Staffing Internationally recruited Nationally recruited Total Indicators Liquidity ratio Current ratio Reserves expressed in days Fixed assets Capital expenditure US$ million Capital expenditure/depreciation Indirect/direct cost ratio 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2.6 (0.1) 2.5 2.5 0.0 11.0 7.6 18.6 18.6 0.7 19.3 0.0 10.6 6.7 17.3 17.3 0.4 17.7 0.0 9.1 8.1 17.2 17.2 0.5 17.7 8.0 4.3 4.9 9.2 17.2 0.6 17.8 9.5 (0.4) 9.1 7.1 0.1 1.1 0.0 0.2 0.5 9.1 1.0 15.9 25.9 0.2 0.5 0.7 26.6 0.7 27.3 11.0 9.8 10.6 7.3 9.1 7.1 8.0 4.3 5.1 25.9 0.2 0.8 20.8 (2.2) 17.9 (0.6) 16.2 1.0 17.4 0.4 26.8 0.5 49 221 270 43 215 258 37 209 246 42 201 243 53 290 343 119 1.9 119 118 1.5 118 178 2.5 178 200 2.1 172 136 1.7 136 0.3 112% 19% 0.1 41% 19% 27% 17% 0 32% 18% 0 41% 16% 0.4 2.9 5.1 www.cgiar.org 73 Financial Report 2012 Glossary of terms CGIAR Research Programs (operating names) CGIAR Research Program on Agriculture for Nutrition and Health (A4NH) CGIAR Research Program on Aquatic Agricultural Systems (AAS) CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS) CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Cereals (Dryland Cereals) CGIAR Research Program on Dryland Systems (Dryland Systems) CGIAR Research Program on Forests, Trees and Agroforestry (Forests, Trees and Agroforestry) CGIAR Research Program on Grain Legumes (Grain Legumes) CGIAR Research Program on Integrated Systems for the Humid Tropics (Humidtropics) CGIAR Research Program on Livestock and Fish (Livestock and Fish) CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE) CGIAR Research Program on Managing and Sustaining Crop Collections (Genebanks) CGIAR Research Program on Policies, Institutions and Markets (PIM) CGIAR Research Program on Rice (Global Rice Science Partnership [GRiSP]) CGIAR Research Program on Roots, Tubers and Bananas (RTB) CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE) CGIAR Research Program on Wheat (WHEAT) CGIAR Centers Africa Rice Center (AfricaRice) Bioversity International (Bioversity) Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT; International Center for Tropical Agriculture) Centro Internacional de Mejoramiento de Maíz y Trigo (CIMMYT; International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center) Centro Internacional de la Papa (CIP; International Potato Center) International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) International Water Management Institute (IWMI) World Agroforestry Centre (World Agroforestry; also known as ICRAF) WorldFish (also known as ICLARM) Challenge Programs Challenge Program on Water and Food (CPWF) Generation Challenge Programme (GCP) HarvestPlus Sub-Saharan Africa Challenge Program (SSA CP) www.cgiar.org 74 Financial Report 2012 Terminology CGIAR The partnership of Centers, donors and Fund Office, Partners, Independent Science and Partnerships Council and other participants working together to implement the Strategy and Results Framework. Note that “CGIAR” is no longer an acronym, but has been adopted as a name. CGIAR Fund The multi-donor trust fund administered by the World Bank, as Trustee, and governed by the Fund Council. CGIAR Research Program Research program for coordinated implementation among CGIAR Centers of the Strategy and Results Framework. CGIAR Research Program Lead Center The Center assigned by the Consortium to coordinate the implementation of activities and physically receive fund transfers from the CGIAR Fund with respect to a CGIAR Research Program under a governing Program Implementation Agreement. Bilateral grants Grants that are received by Centers direct from donors; these can be unrestricted or restricted. Cash management of restricted operation A ratio that measures the ability of a Center to manage restricted project operations with the amount of cash advances received and reimbursements expected from donors. It is computed as restricted donors’ accounts receivable divided by restricted donors’ accounts payable. The desirable benchmark for the ratio is less than 1. Center CGIAR Research Center – one of the 15 Research Centers that belong to the Consortium, all of which are separate legal entities. Consortium Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centers – the partnership of 15 CGIAR Centers, led by the Consortium Board and supported by the Consortium Office. Cost sharing percentage The cost-sharing percentage determined by the Fund Office and designed to cover system costs, which is chargeable to all funding contributions. Direct costs Operating costs incurred by a Center that can be traced directly to a project or discrete research activity. Common examples of direct costs include the cost of staff assigned to a specific project, or the cost of supplies or equipment consumed by the project. www.cgiar.org 75 Financial Report 2012 Indirect costs General and management costs that are not directly attributable to research activities, so need to be allocated indirectly. They are also often referred to as overheads, institutional costs, or governance costs. Indirect cost rate Ratio of indirect costs to direct costs expressed as a percentage. Liquidity An organization’s ability to meet its short-term obligations. Technically, it is the difference between current assets and current liabilities. Liquidity can be in terms of a ratio (called current ratio) or number of days of operating expenditure. Liquidity is also referred to as “working capital”. Long-term financial stability (adequacy of reserve indicator)Indicator that measures the number of days of operation that a Center can support from its own resources (i.e. reserves). It is computed as unrestricted net assets minus net fixed assets, divided by per-day operating expenses (defined below) excluding depreciation. Net assets The total of what is owned by a Center after deducting what is owed (the equivalent of retained earnings or owner’s equity in a commercial business). Net assets are the accumulated surpluses (excess of revenue over expenses) over the years. Net fixed assets The cost of fixed assets (property and equipment) net of the depreciation charge. It is also referred to as the “book value” of property, plant, and equipment. Partner Any institution engaged in research activities for implementation of the CGIAR Research Programs. This term does not include CGIAR Centers. Per-day operating expenses Total operating expenses of a Center less depreciation divided by 365 days. This indicator measures the daily cash requirement of a Center in the course of normal operations. Program Implementation Agreement (PIA) Contract between the Consortium and the CGIAR Research Program Lead Center to implement a CGIAR Research Program. Quick ratio A more restricted measure of liquidity because it takes into account only those current assets that are cash or easily convertible into cash to pay for the current liabilities. Restricted grants Restricted grants are those donations that have a particular purpose or that fund a specific project. Restricted funds are time bound, have budget restrictions and are linked to particular deliverables or outputs. www.cgiar.org 76 Financial Report 2012 Short-term solvency (liquidity indicator) Working capital, as defined below, divided by per-day operating expenses, excluding depreciation. This indicator measures the ability of a Center to sustain current levels of operation in the event of donor delays in grant remittance. Strategy and Results Framework (SRF) The document setting forth common goals (in terms of development impacts), strategic objectives and results (in terms of outputs and outcomes) to be jointly achieved by the CGIAR participants. System costs System costs are for the components of the CGIAR structure that provide support services for the overall CGIAR. The costs are primarily for the operations of the Fund Office, Trustee, Consortium Board and Office, Independent Science and Partnership Council, and Independent Evaluation Arrangement. Unrestricted grants Unrestricted grants are provided to a Center by a donor, without restrictions, for the general objectives of that Center. Working capital Current assets minus current liabilities. Windows Donors to the Fund may designate their contributions to one or more of three funding windows: Contributions to Window 1 are the least restricted. The Fund Council makes decisions on how these funds are used, such as allocation to CGIAR Research Programs, payment of system costs or otherwise applied to achieving the CGIAR mission. Contributions to Window 2 are designated by Fund donors to specific CGIAR Research Programs. Contributions to Window 3 are allocated by Fund donors to specific CGIAR Centers. Acronyms ADB Asian Development Bank AfDB African Development Bank ARI Advanced research institutions CGIAR With the reforms, “CGIAR” has now been adopted as a name. It is derived from the acronym for the former Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research CIARC Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centers CRP CGIAR Research Program CSP Cost-sharing percentage EC European Commission www.cgiar.org 77 Financial Report 2012 FAO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations GNI Gross national income IBRD International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (usually known as The World Bank) IDB Inter-American Development Bank IDRC International Development Research Centre IFAD International Fund for Agricultural Development ISPC Independent Science and Partnership Council MDTF Multi-donor trust fund NARS National agricultural research system(s) NGO Non-governmental organization OPEC Fund Fund of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries PIA Program Implementation Agreement SRF Strategy and Results Framework UNDP United Nations Development Programme UNEP United Nations Environment Programme www.cgiar.org 78