Introduction • Computer = person • Rate of Advance - computing technology
advertisement
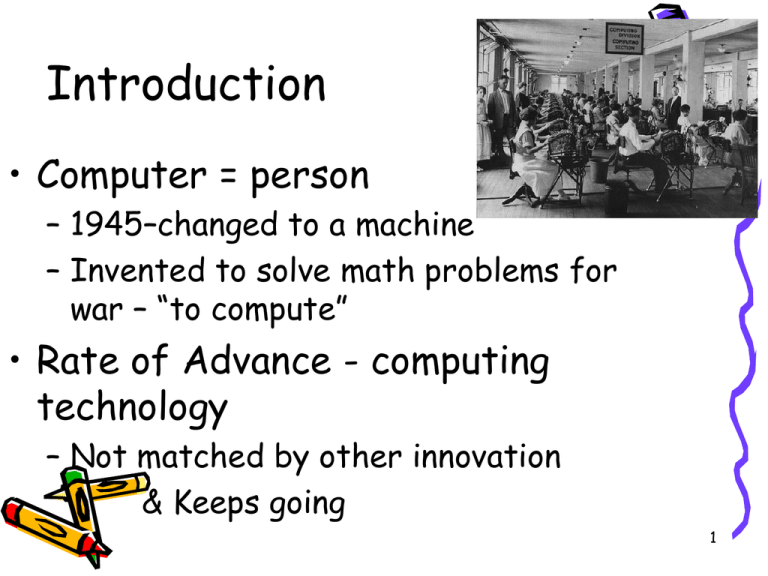
Introduction • Computer = person – 1945–changed to a machine – Invented to solve math problems for war – “to compute” • Rate of Advance - computing technology – Not matched by other innovation & Keeps going 1 e.g. Automobile • • • • • Ubiquitous Costs more - less gas mileage Luxurious, new technology BUT… Automobile = transportation Computer Many things, Everywhere, In everything, Intrusive, Cheaper yet Better 2 Approach – Driving Forces • • • • • Inventions – many, not just one Political – Governments, NASA Technological view Economic view – Post WWII Social view – “Us” – “Flat World” – How did “we” drive the development 3 Book Chronological • Don’t memorize a bunch of trivia • Turning Points – Defining Moments – 1940’s – science to commercial – 1960’s – small systems – 1970’s – personal computing – 1985+ – networking – 1990’s – Internet & WWW – * What since?? What next ??? 4 Major Themes - Ideas • von Neumann Architecture – 3 Generations • • • • Role of the government & military Established vs. Start-up Companies Software (1990’s) vs. Hardware Information in a Democratic Society 5 Three Generations Vacuum Tubes – Transistor – Integrated Circuit 6 Focus of Study • Mostly U.S. • England – Colossus @Bletchley Park – Alan Turing • Western Europe • Japan • Soviet Union – Post Cold War – - Reverse Engineering 7 * Recent History * The World is Flat A Brief History of the Twenty-First Century By Thomas L. Friedman 8