( ) )( )( )
advertisement

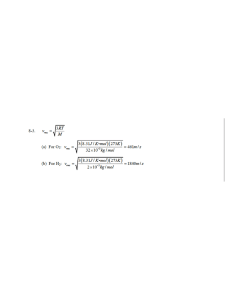
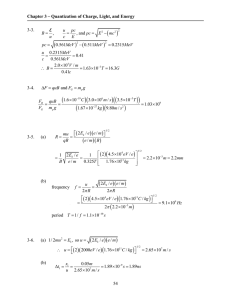
3-2. l r u s ! ! r r u For small values of ! , s " l; therefore, ! = Recalling that euB = 3-5. (a) mu 2 r " r= mu !#(2 Ek / e )(e / m )"$ R= = qB (e / m )(B ) mu eB s l " r r # !$ l eBl = mu / eB mu 1/ 2 4 1 2 Ek / e 1 " (2 )(4.5 $10 eV / e )# % & = = B e/m 0.325T % 1.76 $1011 kg &( ' (b) frequency M f = u = 2! R 1/ 2 = 2.2 $10!3 m = 2.2mm (2 Ek / e )(e / m ) 2! R #(2 )(4.5 %104 eV / e )(1.76 %1011 C / kg )$ ' =& "3 2! (2.2 %10 m ) 1/ 2 = 9.1%109 Hz period T = 1/ f = 1.1%10"10 s 3-6. (a) 1/ 2mu 2 = Ek , so u = (2 Ek / e )(e / m ) # u = !%(2 )(2000eV / e )(1.76 $1011 C / kg )"& (b) (Problem 3- "t1 = 1/ 2 x1 0.05m = = 1.89 #10!9 s = 1.89ns 7 u 2.65 #10 m / s (c) mu y = F !t1 = eE!t1 = 2.65 $107 m / s 6 continued) " u y = (e / m )E#t1 = (1.76 $1011 C / kg )(3.33 $103V / m )(1.89 $10!9 s )= 1.11$106 m / s 3-12. !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K (a) !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 9.66 #10"4 m = 0.966mm 3K (b) !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 9.66 #10"6 m = 9.66 µ m 300 K (c) !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 9.66 #10"7 m = 966nm 3000 K 3-13. Equation 3-4: R = ! T 4 . Equation 3-6: R = 1 cU . 4 From Example 3-4: U = (8! 5 k 4T 4 )/ (15h3c 2 ) != R (1/ 4 )cU 1 = = c (8" 5 k 4T 4 )/ (15h3c 2T 4 ) 4 4 T T 4 4 = 2" 5 (1.38 $10#23 J / K ) 15 (6.63 $10 #34 3 2 J % s ) (3.00 $10 m / s ) 3-14. Equation 3-18: u (! ) = 8 = 5.67 $10#8W / m 2 K 4 8" hc! #5 e hc / ! kT # 1 u ( f )df = u (! )d ! # u ( f ) = u ( f ) d! Because c = f ! , df d! = c/ f 2 df 5 8" hc ( f / c ) $ c % 8" f 2 hf u ( f )= & 2 '= 3 hf / kT hf / kT e (1 ) f * c e (1 3-15. (a) !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K % !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 1.07 #10"3 m = 1.07 mm 2.7 K (b) c = f ! $ f = c 3.00 #108 m / s = = 2.80 #1011 Hz "3 !m 1.07 #10 m (c) Equation 3-6: R= 1 c cU = (8! 5 k 4T 4 /15h3c3 ) 4 4 4 4 (3.00 #10 m / s )(8! )(1.38 #10 J / K ) (2.7 ) = (4 )(15)(6.63 #10 J $ s ) (3.00 #10 m / s ) 8 5 "34 "23 3 3 8 = 3.01#10"6 W / m 2 2 Area of Earth: A = 4! rE2 = 4! (6.38 "106 m ) 2 Total power = RA = (3.01#10"6 W / m 2 )(4! )(6.38 #106 m ) = 1.54 #109 W 3-16. !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K 2.898 "10!3 m # K = 4140 K (a) T = 700 "10!9 m (b) T = 2.898 "10!3 m # K = 9.66 "10!2 K 3 "10!2 m 2.898 "10!3 m # K = 9.66 "10!4 K (c) T = 3m 4 3-17. Equation 3-4: R1 = ! T14 3-18. (a) Equation 3-17: E = (b) E = R2 = ! T24 = ! (2T1 ) = 16! T14 = 16 R1 hc / (10hc / kT ) 0.1kT hc / ! = (hc / kT )/ (10 hc / kT ) = 0.1 = 0.951kT e "1 e "1 e "1 hc / ! kT hc / (0.1hc / kT ) 10kT hc / ! = = 10 = 4.59 #10"4 kT hc / ! kT hc / kT )/ (0.1hc / kT ) ( e "1 e "1 e "1 Equipartition theorem predicts E = kT . The long wavelength value is very close to kT, but the short wavelength value is much smaller than the classical prediction. 3-19. (a) !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K % T1 = R1 = ! T14 and 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 107 K 27.0 #10"6 m R2 = ! T24 = 2 R1 = 2! T14 ! T24 = 2T14 or T2 = 21/ 4 T1 = (21/ 4 )(107 K ) = 128 K (b) !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 23 #10"6 m 128 K 3-20. (a) !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K !m = (Equation 3-5) 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 1.45 #10"7 m = 145nm 2 #104 K (b) !m is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum. 3-21. Equation 3-4: R = ! T 4 Pabs = (1.36 "103W / m 2 )(! RE2 m 2 ) where RE = radius of Earth Pemit = (RW / m 2 )(4! RE2 )= (1.36 "103W / m 2 )(! RE2 m 2 ) # ! RE2 R = (1.36 %103W / m 2 )& 2 ( 4! RE $ 1.36 %103 W = "T 4 '= 2 4 m ) 1.36 "103W / m 2 T = # T = 278.3K = 5.3°C 4 (5.67 "10!8W / m 2 $ K 4 ) 4 3-22. (a) !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K % !m = f m = c / !m = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K = 8.78 #10"7 m = 878nm 3300 K 3.00 #108 m / s = 3.42 #1014 Hz "7 8.78 #10 m (b) Each photon has average energy E = hf and NE = 40 J / s. N= 40 J / s 40 J / s = = 1.77 "1020 photons / s !34 14 hf m (6.63 "10 J # s )(3.42 "10 Hz ) (c) At 5m from the lamp N photons are distributed uniformly over an area A = 4! r 2 = 100! m 2 . The density of photons on that sphere is (N / A )/ s ! m 2 . 2 The area of the pupil of the eye is ! (2.5 #10"3 m ) , so the number of photons entering the eye per second is: 2 n = (N / A )(! )(2.5 #10"3 m ) (1.77 #10 = 2 20 2 / s )(! )(2.5 #10"3 m ) 100! m 2 = (1.77 #1020 / s )(! )(2.5 #10"3 m ) = 1.10 #1013 photons / s 3-23. Equation u (! ) = 3-18: 8" hc! #5 A! #5 Letting A = " hc , B = hc / kT , and U ! = ( ) e hc / ! kT # 1 eB / ! #1 # ! "5 ("1)e B / ! (" B! "2 ) $ du d # A! "5 $ 5! "6 & % = " B/! % & = A% 2 B/! d ! d ! ' eB / ! " 1( e " 1& e " 1 ( ) ' ( "6 B / ! A! "6 # B B / ! $ A! e #B $ B/! = e " 5 e " 1 = " 5 (1 " e " B / ! )& = 0 ( ) 2 2 % & % ( (e B / ! " 1) ' ! ( (e B / ! " 1) ' ! The maximum corresponds to the vanishing of the quantity in brackets. Thus, 5! (1 " e " B / ! )= B . This equation is most efficiently solved by iteration; i.e., guess at a value for B/λ in the expression 5! (1 " e " B / ! ), solve for a better value of B/λ; substitute the new value to get an even better value, and so on. Repeat the process until the calculated value no longer changes. One succession of values is: 5, 4.966310, 4.965156, 4.965116, 4.965114, 4.965114. Further iterations repeat the same value (to seven digits), so we have: 6.63 #10"34 J $ s )(3.00 #108 m / s ) ( B hc hc = 4.965114 = % !mT = = !m ! m kT (4.965114 )k (4.965114 )(1.38 #10"23 J / K ) !mT = 2.898 #10"3 m $ K 3-26. (a) "t = (Equation 3-5) hc 1240eV $ nm = = 653nm, ! 1.9ev ft = ! 1.9eV = = 4.59 %104 Hz h 4.136 %10#15 eV $ s 1 $ hc % 1 $ 1240eV # nm % & 1.9eV ( = 2.23V (b) V0 = ' & ! ( = ' e) " * e ) 300nm * 1 $ hc % 1 $ 1240eV # nm % & 1.9eV ( = 1.20V (c) V0 = ' & ! ( = ' e) " * e ) 400nm * 3-27. (a) Choose λ =550nm for visible light. nhf = E ! dn dE hf = =P dt dt (0.05 #100W )(550 #10"9 m ) dn P P! = = = = 1.38 #1019 / s "34 dt hf hc (6.63 #10 J $ s )(3.00 #10 m / s ) (b) flux = number radiated / unit time 1.38 "1019 / s = = 2.75 "1017 / m 2 # s 2 area of the sphere 4! (2m ) 3-28. (a) hf = ! # ft = (b) f = c / ! = ! 4.22eV = = 1.02 $1015 Hz "15 h 4.14 $10 eV % s 3.00 #108 m / s = 5.36 #1014 Hz "9 560 #10 m No. Available energy/photon hf = (4.14 "10!15 eV # s )(5.36 "1014 Hz )= 2.22eV . This is less than ! . 3-32. (a) ! = hc 1240eV nm = = 1.90eV " 653nm (b) Ek = hc 1240eV nm #! = # 1.90eV = 2.23eV " 300nm