(1)

PHYSICS 140B : STATISTICAL PHYSICS
HW ASSIGNMENT #2 SOLUTIONS
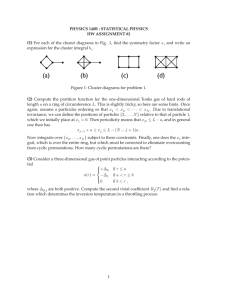
(1) For each of the cluster diagrams in Fig. 1, find the symmetry factor s
γ expression for the cluster integral b
γ
.
and write an
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 1: Cluster diagrams for problem 1.
Solution : Choose labels as in Fig. 2, and set x n
γ definition of b
γ
.
≡ 0 to cancel out the volume factor in the
2 2 3 3
1 5 1 5
1 1
4 5 4 5
2 6 2 6
3 3
4 4
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 2: Labeled cluster diagrams.
(a) The symmetry factor is s
γ
= 2 , so b
γ
=
1
2
Z d d x
1
Z d d x
2
Z d d x
3
Z d d x
4 f ( r
12
) f ( r
13
) f ( r
24
) f ( r
34
) f ( r
4
) .
(b) Sites 1, 2, and 3 may be permuted in any way, so the symmetry factor is s
γ then have b
γ
=
1
6
Z d d x
1
Z d d x
2
Z d d x
3
Z d d x
4 f ( r
12
) f ( r
13
) f ( r
24
) f ( r
34
) f ( r
14
) f ( r
23
) f ( r
4
= 6
) .
. We
(c) The diagram is symmetric under reflections in two axes, hence s
γ
= 4 . We then have b
γ
=
1
Z
4 d d x
1
Z d d x
2
Z d d x
3
Z d d x
4
Z d d x
5 f ( r
12
) f ( r
13
) f ( r
24
) f ( r
34
) f ( r
35
) f ( r
4
) f ( r
5
) .
(d) The diagram is symmetric with respect to the permutations (12) , (34) , (56) , and (15)(26) .
Thus, s
γ
= 2 4 = 16 . We then have b
γ
=
1
16
Z d d x
1
Z d d x
2
Z d d x
3
Z d d x
4
Z d d x
5 f ( r
12
) f ( r
13
) f ( r
14
) f ( r
23
) f ( r
24
) f ( r
34
) f ( r
35
) f ( r
45
) f ( r
3
) f ( r
4
) f ( r
5
) .
1
(2) Compute the partition function for the one-dimensional Tonks gas of hard rods of length a on a ring of circumference L . This is slightly tricky, so here are some hints. Once again, assume a particular ordering so that x
1
< x
2
< · · · < x
N
. Due to translational invariance, we can define the positions of particles { 2 , . . . , N } relative to that of particle 1 , which we initially place at one then has x
1
= 0 . Then periodicity means that x
N
≤ L − a , and in general x j
− 1
+ a ≤ x j
≤ L − ( N − j + 1) a .
Now integrate over { x
2
, . . . , x
N
} subject to these constraints. Finally, one does the x
1 integral, which is over the entire ring, but which must be corrected to eliminate overcounting from cyclic permutations. How many cyclic permutations are there?
Solution :
There are N cyclic permutations, hence
Z ( T, L, N ) = λ −
N
T
L
N
Z
Y
2 dx
2
Z
Y
3 dx
3 a x
2
+ a
· · ·
Y
N
Z dx
N
=
L ( L − N a ) N − 1 λ − N
T
N !
x
N
−
1
+ a
.
(3) Consider a three-dimensional gas of point particles interacting according to the potential u ( r ) =
+∆
0
− ∆
1
0 if r ≤ a if a < r ≤ b if b < r , where ∆
0 , 1 are both positive. Compute the second virial coefficient B
2
( T tion which determines the inversion temperature in a throttling process.
) and find a rela-
Solution :
The Mayer function is f ( r ) =
e −
∆
0 e ∆
1
/k
B
T
/k
B
T
− 1 if r ≤ 0
− 1 if a < r ≤ b
0 if b < r .
The second virial coefficient is
B
2
( T ) = −
1
2
Z d
3 r f ( r )
=
2 πa 3
3
· 1 − e − ∆
0
/k
B
T
+ ( s
3
− 1) 1 − e
∆
1
/k
B
T
,
2
where s = b/a . The inversion temperature is a solution of the equation B
2
( T ) = T B ′
2
( T ) , which gives s
3
− 1 =
1 +
1 +
∆
0 k
B
T
∆
1 k
B
T
− 1 e − ∆
0
/k
B
T
+ 1 e
∆
1
/k
B
T
.
3