ªThe Nature of Science Chapter 1 Honors Earth Science
advertisement

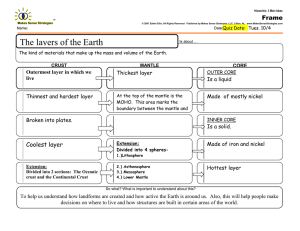
ªThe Nature of Science Chapter 1 Honors Earth Science Four major branches of Earth Science _1._______________________________ªThe study of the origin, history, and structure of matter on a solid celestial body 2. __________________________________The study of Earth’s ____________________________ 3. Astronomy ªThe study of ____________________________________________________ 4 .Oceanography___________________________________________________________ __ II. Earth’s system includes 4 spheres that interact 1. The Atmosphere consists of the _____________________________________ 2. The ________________________(also called lithosphere) consist of the rocks, minerals, soils, ocean basins and Earth’s interior 3. The ___________________________includes the water in oceans, rivers, groundwater, clouds, lakes, ice caps and glaciers 4. The Biosphere includes all things __________________________________________ ªEarth’s Sphere’s Interact ªAn erupting volcano releases lava, volcanic bombs _____________________________________and gases and ash into the air ________________________________the animals are suffocated __________________________plants burn up ______________________ash flows fill rivers _____________________________________ ªMore interaction examples ªPlants and animals take in ______________________from the atmosphere and release ____________________________________ ªPeople remove plants, release chemicals into the air and water ªSpheres Continued ªLithosphere is Rigid _________________________of the planet, broken into pieces called plates . ªIncludes the __________________________________________ ªEarth’s Crust: Continents _________________________________________ ªOceanic Crust Made up of mostly___________________________________________________, this is denser than Granite ªNext layer of mantle is called the ________________________________________________________ ªThis layer is a solid that flows like a _________________________________________ ª1600 degrees C but extreme ________________________keeps it solid ªThe ______________________________ floats on the _______________________________ ªEarth’s layers ªEarths lower mantle is mostly very dense, dark rock called _________________________________ ªBeneath the mantle is earth’s __________________________which is mostly made up of _________________________________ ªOuter ______________________core and ªInner ____________________core ªSteps used in Scientific Method ª1ª2ª3ª4ªSelect ____________________________ ªDetermine ________________________________ ªObserve ªRecord __________________________________________ ª5- __________________________________________________ ª6- _____________________________________________ ªLook at data and from conclusions ªRe-evaluate _____________________________________ ªFormulate new ________________________________n ªExperimentation (See p. 930 Skills) ªIndependent variables (also called experimental variable) ªThe factor that is _____________________________________________________ ªDependent variables________________________________________________________________ _______ Examples ªIf you are testing the effect of adding specific amounts of fertilizer to water on plant growth, and you measure the plants daily… ªThe independent variable is ________________ ªThe dependent variable is __________________ ªExample 2 ªIf you are testing the effects adding acid to water on the breakdown of rocks and you weigh the rocks daily… ªThe independent variable is ________________ ªThe dependent variable is __________________ ªControl Group ªUsed to prove that the results of and experiment are the actual results of a condition ªWhat would be used for a control group in the two examples? ªControl group Exp. 1 = ªControl group Exp. 2 = ªControlled Variables or Constants ªWhat conditions would you need to control in order to make these valid experiments? (These are called constants or controlled variables) ªWhy is this so important? ªControlled variables for Exp. 1 = ªControlled variables for Exp. 2 = ªHypothesis vs. Theory vs. Law ªHypothesis is an ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________usually comes first ªInvolves ____________________________(If, then) ªIncludes _____________________________not just a wild guess ªTheories ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ___________ ªCan be revised or rejected as new ___________________________provide new evidence ªExamples ªTheory of ___________________________________ ªTheory of _________________________________ ªGerm Theory ªLaws ªAlso called ___________________________________________because they work every time but are not always fully understood ªEx. ___________________________________________ªEnergy cannot be created or destroyed by ordinary chemical means. _______________________________________________ A body in motion remains in motion unless acted on by an outside force ªSI Units ªWhat does SI stand for? ªWhat are the SI units for: ªLength ªMass ªArea ªVolume ªDensity ªWeight ªTemperature ªDensity