Cell Features Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1665
advertisement

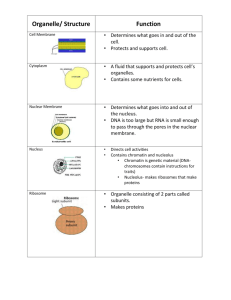
11/9/09 1 2 3 4 5 Cell Features Robert Hooke 1665 Observed cork “little boxes” called cells Crude microscope Anton van Leeuwenhoek 1675 Observed pond water Living creatures “Animalcules” The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of One or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 3. All cells arise from existing cells. Why must cells be small? 100 trillion cells in the body Cells surface-area to volume ratio must be high Small cells can exchange substances easier 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Common cell features to ALL cells (5 total) 1. Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) Regulates what enters and leaves the cell (gases, nutrients, wastes) Cell Membrane Common Features 2. Cytoplasm Houses the contents of the cell Cytoplasm Common Features 3. Cytoskeleton Microscopic fibers that give the cell shape Cytoskeleton Common Features 4. Ribosomes Where proteins are made in the cell Ribosomes 16 17 18 1 13 11/9/09 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Where proteins are made in the cell Ribosomes Common Features 5. DNA Stores genetic information DNA Prokaryotes Single celled organism No nucleus, no Membrane-bound Organelles Prokaryotes Early prokaryotes lived 3.5 billion years ago Modern prokaryotes are bacteria Bacteria cell parts Draw a Bacteria Using the Diagram below Bacteria Cell parts Cell wall (composed of polysaccharides & Amino Acids) Cell (Plasma) Membrane Flagella - enables movement DNA - in circular ring Capsule - enables it to cling to almost anything Eukaryotes Includes all plant and animal cells Can be single celled organism or multicellular (made up of many cells) Eukaryotes Some have Flagella or cilia for movement Has a nucleus and internal compartments called organelles Organelle “little organs” Which carry out specific activities Organelle groups Organelles for making Proteins Organelles for supporting the cell Organelles for Producing energy for the cell Organelles for breaking down and storing wastes Organelles for making proteins include Nucleus - “brain” directs all activities ER - smooth & Rough - Membrane system that move proteins Ribosomes - proteins are made on these Golgi Apparatus - packaging & distribution “post office” 26 27 2 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 11/9/09 Ribosomes - proteins are made on these Golgi Apparatus - packaging & distribution “post office” Nucleus, ER, Ribosomes and Golgi Organelles for supporting the cell Cell Membrane - Outer boundary of the cell, Controls what goes into and out of the Cell. Cell Wall (plant cell) - surrounds cell membrane in plant cells Cell Membrane cell wall Organelles that produce energy Mitochondria - Provides the energy the cell needs “powerhouse” Chloroplast (In plant cells Only) - Site of photosynthesis Mitochondria and Chloroplast Organelles that breakdown & Move & Store Lysosomes - Digest waste products “Garbage collectors” Vesicles - “vehicles” of the cell carry substances Central Vacuole (plant cell) - storage site for water Lysosomes, Vesicles, Central Vacuole Cell Membrane Selectively permeable Made up of phospholipids (2 fatty acids bonded to a phosphate) Draw Phospholipid Lipid Bilayer Form a lipid bilayer Polar heads that are hydrophilic (interact with water) Nonpolar tails that are hydrophobic (repel water) 35 36 Because of this some molecules are able to pass directly through the cell membrane and others need to travel through a protein embedded in the membrane. Protein function Proteins embedded in the membrane have different functions: Cell surface markers Receptor proteins Enzymes 37 38 39 3 36 11/9/09 37 38 39 40 Enzymes Transport proteins Cell Surface Markers Cell-surface marker - help other cells recognize their cell types Receptor Proteins Receptor protein - recognize and bind specific substances the cell needs Enzymes Enzymes - involved in Many reactions in the cell, Help to speed up reactions. Transport Proteins Transport Proteins Aid the movement of substances into and out of the cell that can’t go directly through the cell membrane 4