Scientific Method Section 1-3 Biology
advertisement

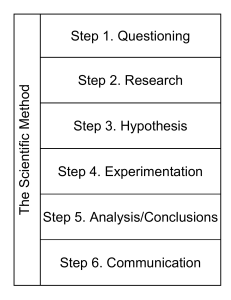
Scientific Method Section 1-3 Biology Common Steps in Science 1. Collecting Observations Quantitative observations involve numbers and measurement Qualitative observations include color, texture, shape, state 2. Asking questions Usually called the Problem or Purpose for the experiment 3. Forming Hypothesis and making Predictions If, then statements used. Based on research and prior experimentation More steps 4. Experimentation Controlled Experiments have one variable called the independent variable that is varied between the control and experimental groups the dependant variable is what is measured to see if change occurred 5. Drawing conclusions Hypothesis may be supported or rejected based on analysis of the data collected. Often further testing is needed. 6.Theory Work is published for peer review. Work verified by many scientists, A collection of hypothesis that have much evidence to support them after repeated testing becomes scientific theory Theories The Cell Theory, The Theory of Evolution, Plate Tectonics Theory, The Big Bang Theory The Germ Theory Do not lead to laws, Laws are rules of nature: Change, Are revised with new evidence, new Law of gravitational technologies attraction, Sometimes totally Law of Conservation rejected of Mass Must be useful for predicting the outcome of future experiments, Are supported by large bodies of evidence