What Progress Have We Made So Far With Evolutionary Development?
advertisement
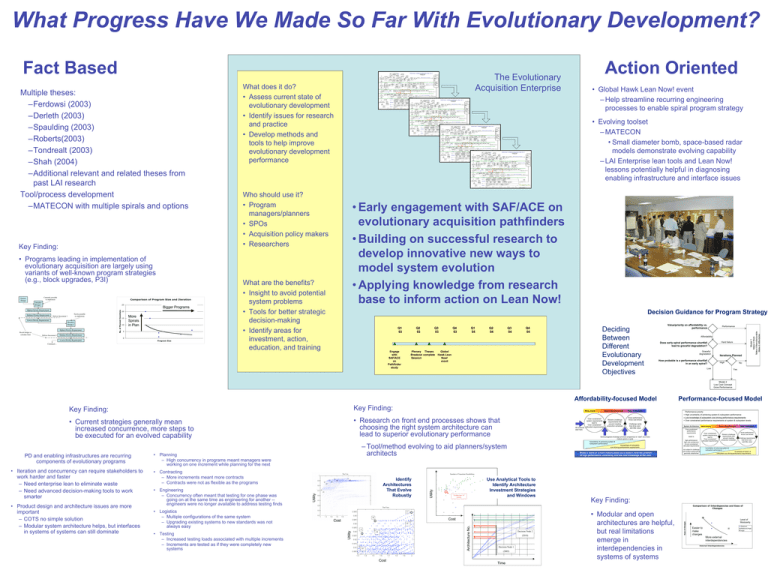
What Progress Have We Made So Far With Evolutionary Development? Fact Based Key Finding: • Programs leading in implementation of evolutionary acquisition are largely using variants of well-known program strategies (e.g., block upgrades, P3I) Currently possible to implement System Design Comparison of Program Size and Iteration Detailed Design 1 Highest Priority Requirements Medium Priority Requirements Newly possible to implement Deliver Increment 1 Lowest Priority Requirements Detailed Design 2 Highest Priority Requirements Reach budget or schedule limit Deliver Increment 2 No. of Planned Iterations 25 Bigger Programs larger program size 20 15 10 More Spirals in Plan 5 Medium Priority Requirements 0 Lowest Priority Requirements Program Size Continued… What does it do? • Assess current state of evolutionary development • Identify issues for research and practice • Develop methods and tools to help improve evolutionary development performance • Global Hawk Lean Now! event – Help streamline recurring engineering processes to enable spiral program strategy • Evolving toolset – MATECON • Small diameter bomb, space-based radar models demonstrate evolving capability – LAI Enterprise lean tools and Lean Now! lessons potentially helpful in diagnosing enabling infrastructure and interface issues Who should use it? • Program managers/planners • SPOs • Acquisition policy makers • Researchers • Early engagement with SAF/ACE on evolutionary acquisition pathfinders • Building on successful research to develop innovative new ways to model system evolution • Applying knowledge from research base to inform action on Lean Now! What are the benefits? • Insight to avoid potential system problems • Tools for better strategic decision-making • Identify areas for investment, action, education, and training Decision Guidance for Program Strategy Q1 03 Q2 03 Engage with SAF/ACE on Pathfinder study Q3 03 Plenary Theses Breakout complete Session Q4 03 Q1 04 Q2 04 Q3 04 Deciding Between Different Evolutionary Development Objectives Q4 04 Global Hawk Lean Now! event Value/priority on affordability vs. performance Performance Affordability Hard failure Does early spiral performance shortfall lead to graceful degradation? Graceful degradation Iterations Planned How probable is a performance shortfall in an early spiral? High Low Model 1 Make it Work Make it Manufacturable Make it Affordable Multiple theses: –Ferdowsi (2003) –Derleth (2003) –Spaulding (2003) –Roberts(2003) –Tondrealt (2003) –Shah (2004) –Additional relevant and related theses from past LAI research Tool/process development –MATECON with multiple spirals and options The Evolutionary Acquisition Enterprise Action Oriented No Yes Model 2 Low Cost Concept Grow Performance Affordability-focused Model Key Finding: Key Finding: • Current strategies generally mean increased concurrence, more steps to be executed for an evolved capability • Research on front end processes shows that choosing the right system architecture can lead to superior evolutionary performance Contracting – More increments meant more contracts – Contracts were not as flexible as the programs • Product design and architecture issues are more important – COTS no simple solution – Modular system architecture helps, but interfaces in systems of systems can still dominate • • • Engineering – Concurrency often meant that testing for one phase was going on at the same time as engineering for another -engineers were no longer available to address testing finds Logistics – Multiple configurations of the same system – Upgrading existing systems to new standards was not always easy Testing – Increased testing loads associated with multiple increments – Increments are tested as if they were completely new systems #2 #3 #4 Identify Architectures That Evolve Robustly #1 Uncertainty of achieving system & subsystem performance Knowledge of subsystem cost driving performance requirements Model 2 starts at a more mature phase so it doesn’t have the problem of high performance uncertainty and low cost knowledge at the start C 0.94 0.92 0.9 Architecture 15 (Root) 0.88 B Cost Evolutionary Strategy Decision Tree from Architecture 15 Root 0.84 450 r 2 3 4 5 Cost e7 6 Life cycle Cost b($B) Life cycle Cost ($B) m #5 u N #4 #3 400 8 9 10 11 350 D I e r u t c e t i h c r A A 300 Decision Node 2 250 (2010) 200 150 Decision Node 1 100 (2005) 50 Cost Make it work Over-constrained performance requirements Make it Manufacturable “Over constrained” system requirements lead to “Over constrained” allocated requirements leads to high performance/ high cost architecture & over-constrained allocated requirements not subject to challenge until system performance generally established Waivers (challenge requirements that prevent meeting production schedule) Make it Affordable Know performance Know cost drivers Challenge requirements that drive cost / add little value Uncertainty of achieving system & subsystem performance Knowledge of system & subsystem cost driving performance requirements 0 2002 Time (year) 2003 2004 2005 2006 Time Time (year) 2007 2008 2009 Key Finding: Comparison of Interdepencies and Ease of Changes Evolutionary Strategy Decision Tree from Architecture 15 Root 0.82 0.8 System Architecture 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0.86 his would be beneficial to MATE because it would significantly reduce calculation time, thus allowing more complex modeling and enumeration of larger tradespaces. Challenge rqmts that drive cost / add little value Some programs leverage previous program(s) to “start” at a more mature spiral or cycle Use Analytical Tools to Identify Architecture Investment Strategies and Windows 0.96 y t i l i t U Know performance Know cost drivers Performance priority + High uncertainty of achieving system & subsystem performance + Low knowledge of subsystem cost driving performance requirements = Over constrained performance requirements at system & subsystem levels Number of Transition Possibilities: 2002 to Possibilities 2005 (decreasing altitude) Number of Transition 0.98 #5 Waivers (challenge requirements that prevent meeting production schedule) Make it Affordable 2010 • Modular and open architectures are helpful, but real limitations emerge in interdependencies in systems of systems Ease of Changes • Architecture No. Architecture ID Number • Iteration and concurrency can require stakeholders to work harder and faster – Need enterprise lean to eliminate waste – Need advanced decision-making tools to work smarter Utility Utility Planning – High concurrency in programs meant managers were working on one increment while planning for the next Utility • Make it Manufacturable “Over constrained” system requirements lead to “Over constrained” All products allocated requirements start here – Tool/method evolving to aid planners/system architects Utility PD and enabling infrastructures are recurring components of evolutionary programs Make it work Performance-focused Model Level of Modularity Easier to make changes Medium Medium/High High More external interdependencies External Interdependencies






