Algebra 2 Notes – Lesson 5.1 Name __________________________________
advertisement
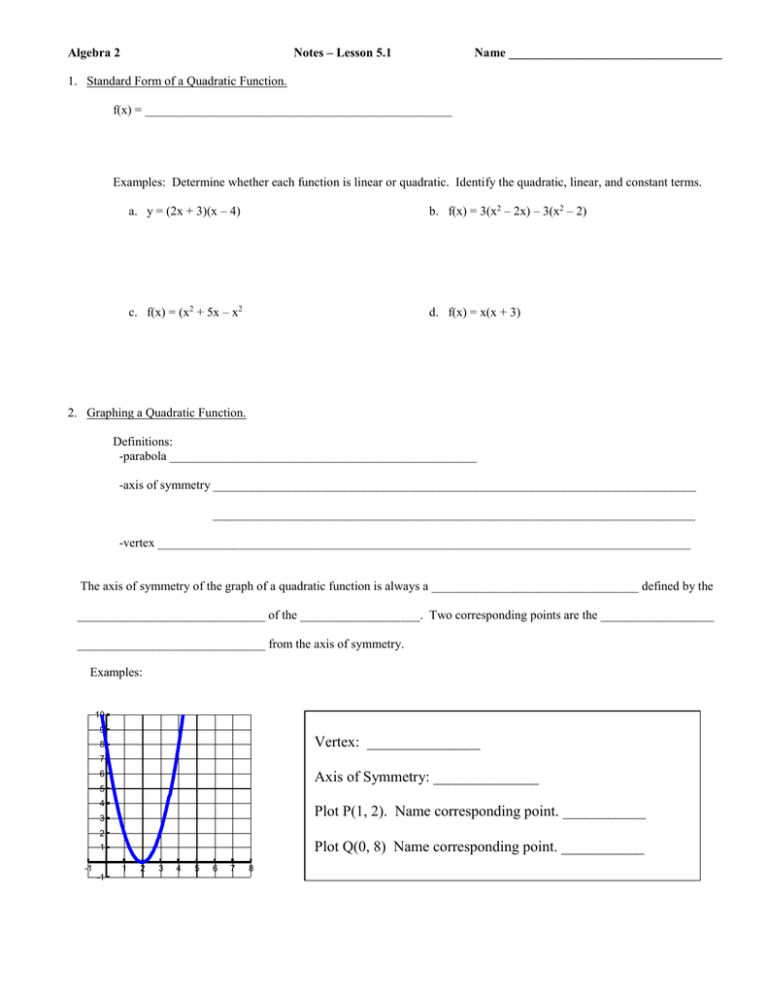
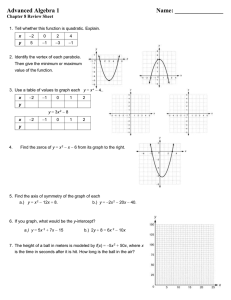
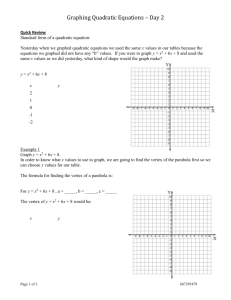
Notes – Lesson 5.1 Algebra 2 Name __________________________________ 1. Standard Form of a Quadratic Function. f(x) = _________________________________________________ Examples: Determine whether each function is linear or quadratic. Identify the quadratic, linear, and constant terms. a. y = (2x + 3)(x – 4) b. f(x) = 3(x2 – 2x) – 3(x2 – 2) c. f(x) = (x2 + 5x – x2 d. f(x) = x(x + 3) 2. Graphing a Quadratic Function. Definitions: -parabola _________________________________________________ -axis of symmetry _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ -vertex _____________________________________________________________________________________ The axis of symmetry of the graph of a quadratic function is always a _________________________________ defined by the ______________________________ of the ___________________. Two corresponding points are the __________________ ______________________________ from the axis of symmetry. Examples: 10 9 Vertex: _______________ 8 7 6 Axis of Symmetry: ______________ 5 4 Plot P(1, 2). Name corresponding point. ___________ 3 2 Plot Q(0, 8) Name corresponding point. ___________ 1 -1 1 -1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 3 Vertex: _______________ 2 1 Axis of Symmetry: ______________ -4 -3 -2 -1 1 2 3 4 -1 Plot P(-1, 3). Name corresponding point. ___________ -2 Plot Q(2, 0) Name corresponding point. ___________ -3 -4 3. Fitting a Quadratic Function to 3 Points. Write a quadratic function that goes through these 3 points. x 2 3 4 y 3 13 29 4. Calculator Steps. The table below show the height of a column of water as it drains from its container. Model the data with a quadratic function. Graph the data and the function. Use the model to estimate the water level at 35 seconds. Elapsed Time 0s 10 s 20 s 30 s 40 s 50 s 60 s Water Level 120 mm 100 mm 83 mm 66 mm 50 mm 37 mm 28 mm 1. Enter lists. 2. STAT – CALC - #5 – ENTER 3. Go to y = 4. VARS - #5 – EQ – ENTER 5. Go to 2nd Table and enter amount looking for. 5. A Function and a Given Point. The graph of each function contains the given point. Find the value of c. a. y = x2 + c; (0, 3) b. y = -5x2 + c; (2, -14) c. y= 3 4 x2 + c; (3, 1 2 )