Genetics: Monohybrid & Dihybrid Crosses, Punnett Squares
advertisement

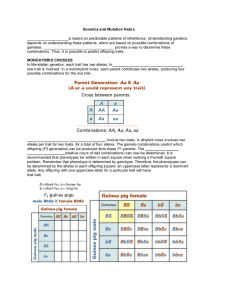
Genetics and Mutation Notes Genetics is based on predictable patterns of inheritance. Understanding genetics depends on understanding these patterns, which are based on possible combinations of gametes. Punnett squares provide a way to determine these combinations. Thus, it is possible to predict offspring traits. MONOHYBRID CROSSES In Mendelian genetics, each trait has two alleles. In monohybrid crosses, one trait is involved. In a monohybrid cross, each parent contributes two alleles, producing four possible combinations for the one trait. Dihybrid crosses involve two traits. A dihybrid cross involves two alleles per trait for two traits, for a total of four alleles. The gamete combinations predict which offspring (F2 generation) can be produced from these F1 parents. The phenotypic ratio (relative count of trait combinations) can now be determined. It is recommended that phenotypes be written in each square when working a Punnett square problem. Remember that phenotype is determined by genotype. Therefore, the phenotypes can be determined by the alleles in each offspring square: an uppercase letter represents a dominant allele. Any offspring with one uppercase letter for a particular trait will have that trait.