Universität Siegen, Organische Chemie I, Adolf-Reichwein-Str. 2, D-57068 Siegen, e-mail: -siegen.de
advertisement
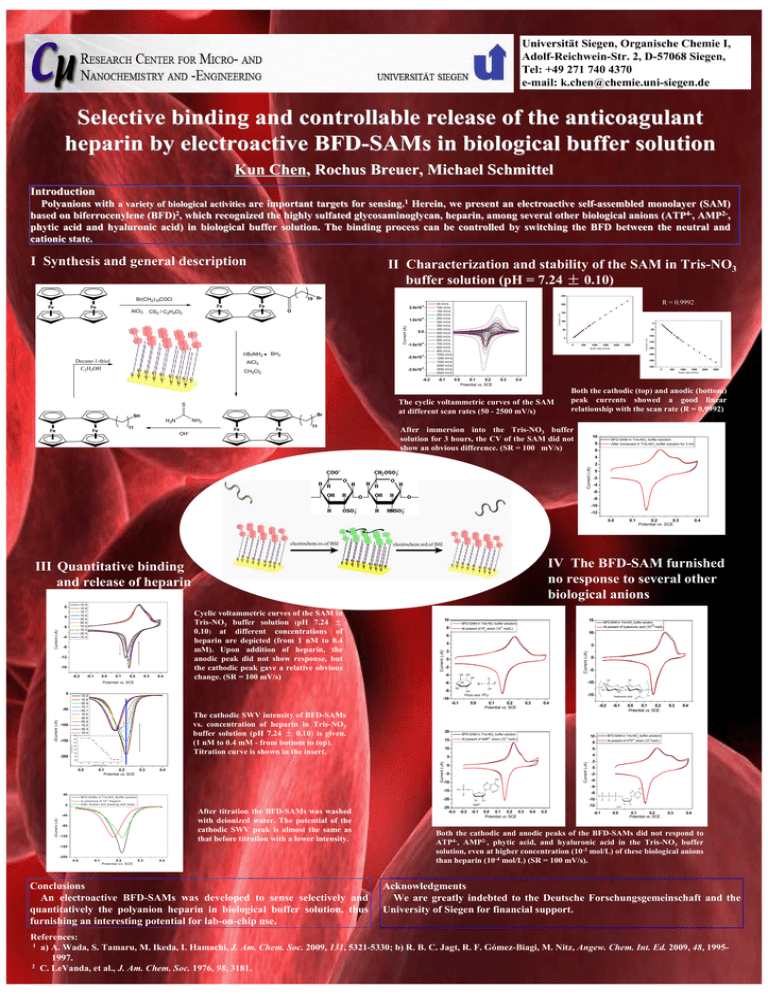
Universität Siegen, Organische Chemie I, Adolf-Reichwein-Str. 2, D-57068 Siegen, Tel: +49 271 740 4370 e-mail: k.chen@chemie.uni-siegen.de Selective binding and controllable release of the anticoagulant heparin by electroactive BFD-SAMs in biological buffer solution Kun Chen, Rochus Breuer, Michael Schmittel Introduction Polyanions with a variety of biological activities are important targets for sensing.1 Herein, we present an electroactive self-assembled monolayer (SAM) based on biferrocenylene (BFD)2, which recognized the highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, heparin, among several other biological anions (ATP4-, AMP2-, phytic acid and hyaluronic acid) in biological buffer solution. The binding process can be controlled by switching the BFD between the neutral and cationic state. I Synthesis and general description II Characterization and stability of the SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution (pH = 7.24 ± 0.10) Fe AlCl3 Fe -4 2.0x10 O CS2 / C2H4Cl2 -4 Current (A) 1.0x10 Fe Fe Fe Fe t-BuNH2 Decane-1-thiol C2H5OH BH3 0.0 -4 -1.0x10 -4 -2.0x10 AlCl3 -4 -3.0x10 CH2Cl2 S S -0.2 S S 50 mV/s 100 mV/s 150 mV/s 200 mV/s 250 mV/s 300 mV/s 350 mV/s 400 mV/s 450 mV/s 500 mV/s 600 mV/s 700 mV/s 800 mV/s 900 mV/s 1000 mV/s 1250 mV/s 1500 mV/s 2000 mV/s 2500 mV/s 2500 mV/s -0.1 Br SH 11 Fe 100 0 -50 -100 0 0 500 1000 1500 Scan rate (mV/s) 2000 2500 -150 -200 -250 -300 -350 0 0.0 0.1 0.2 Potential vs. SCE 0.3 500 1000 1500 Scan rate (mV/s) 2000 2500 0.4 The cyclic voltammetric curves of the SAM at different scan rates (50 - 2500 mV/s) Both the cathodic (top) and anodic (bottom) peak currents showed a good linear relationship with the scan rate (R = 0.9992) NH2 H2N Fe 150 50 gold substrate S R = 0.9992 200 Current (µA) Fe Current (µA) Br(CH2)10COCl Fe 250 10 Br OH- Fe Fe 11 After immersion into the Tris-NO3 buffer solution for 3 hours, the CV of the SAM did not show an obvious difference. (SR = 100 mV/s) 10 BFD-SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution After immersed in Tris-NO3 buffer solution for 3 hrs 8 6 4 Current (µA) 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 -10 -12 0.0 Current (µA) 0 -4 -8 -12 -16 -0.2 -0.1 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Cyclic voltammetric curves of the SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution (pH 7.24 ± 0.10) at different concentrations of heparin are depicted (from 1 nM to 0.4 mM). Upon addition of heparin, the anodic peak did not show response, but the cathodic peak gave a relative obvious change. (SR = 100 mV/s) 10 8 4 2 0 -2 -4 OR The cathodic SWV intensity of BFD-SAMs vs. concentration of heparin in Tris-NO3 buffer solution (pH 7.24 ± 0.10) is given. (1 nM to 0.4 mM - from bottom to top). Titration curve is shown in the insert. y = -41.8x-172.9 100 R = 0.9904 80 60 OR O OR R= P OR O 0.0 0.3 2- 15 -4 0.1 0.2 Potential vs. SCE 0.3 0.4 6 5 4 0 -5 NH2 N -15 -20 In presence of 10 H eparin A fter titration and w ashing w ith w ater After titration the BFD-SAMs was washed with deionized water. The potential of the cathodic SWV peak is almost the same as that before titration with a lower intensity. -40 -80 -120 -160 -200 0.0 0.1 0.2 P otential vs. S C E 0.3 0.4 Conclusions An electroactive BFD-SAMs was developed to sense selectively and quantitatively the polyanion heparin in biological buffer solution, thus furnishing an interesting potential for lab-on-chip use. -25 -0.3 OH -2 -4 NH2 N O -10 OH AMP2- -0.2 -0.1 -12 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 Potential vs. SCE -3 0 -8 N 0.4 0.5 0.4 2 N O 0.3 At present of ATP anion (10 mol/L) O B FD -S A M s in T ris-N O 3 B uffer solution 0.0 0.1 0.2 Potential vs. SCE -6 N O O -4 ∆Current (µA) P -0.1 4- 10 O n O BFD-SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution) 8 Current (µA) -5 Current (µA) -7 -6 lo g [p olym e ric u n it] NH Hyaluronic acid 10 -3 O O -0.2 At present of AMP anion (10 mol/L) O 0 HO OH 0.4 BFD-SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution O O -15 0.1 0.2 Potential vs. SCE -10 40 O O HO 20 0.0 OH OH -10 O OR 20 40 -8 -5 OR -0.1 120 -9 0 -10 140 -150 -200 5 Phytic acid (IP6) 160 ∆Current (µA) ∆Current (µA) -100 10 6 -8 -50 At present of hyaluronic acid (10-3 mol/L) -3 At present of IP6 anion (10 mol/L) -6 1E-9 1E-8 5E-8 1E-7 6E-7 1E-6 3E-6 5E-6 1E-5 3E-5 1E-4 0.4 BFD-SAM in Tris-NO3 buffer solution 3 Potential vs. SCE 0 15 BFD-SAM in Tris-NO buffer solution) Current (µA) 4 Current (µA) 1E-9 1E-8 1E-7 1E-6 3E-6 5E-6 7E-6 1E-5 3E-5 1E-4 0.2 0.3 Potential vs. SCE IV The BFD-SAM furnished no response to several other biological anions III Quantitative binding and release of heparin 8 0.1 -0.1 P O O O P O O O N O P N N O O OH OH ATP4- 0.0 0.1 0.2 Potential vs. SCE 0.3 0.4 Both the cathodic and anodic peaks of the BFD-SAMs did not respond to ATP4-, AMP2-, phytic acid, and hyaluronic acid in the Tris-NO3 buffer solution, even at higher concentration (10-3 mol/L) of these biological anions than heparin (10-4 mol/L) (SR = 100 mV/s). Acknowledgments We are greatly indebted to the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the University of Siegen for financial support. References: 1 a) A. Wada, S. Tamaru, M. Ikeda, I. Hamachi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5321-5330; b) R. B. C. Jagt, R. F. Gómez-Biagi, M. Nitz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 19951997. 2 C. LeVanda, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 3181.







