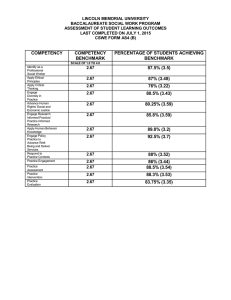
School of Education Unit Assessment Report Undergraduate Programs
advertisement

School of Education Unit Assessment Report Undergraduate Programs October 1, 2007 Submitted By Juli Hastings Taylor Assessment Coordinator Table of Contents Page Introduction ......................................................................................................................................1 PRAXIS I: Pre-Professional Skills Test ..........................................................................................2 PPST Reading (ETS) ...........................................................................................................2 PPST Writing (ETS) ............................................................................................................5 PPST Math (ETS) ................................................................................................................8 PPST Reading (Datatel) .....................................................................................................11 PPST Writing (Datatel) ......................................................................................................12 PPST Math (Datatel) ..........................................................................................................13 PPST Attempts and Pass Rates by Program (Datatel) .......................................................14 PRAXIS II: Content Test ...............................................................................................................15 Art Education .....................................................................................................................16 Business Education ............................................................................................................18 Elementary Education ........................................................................................................21 Family & Consumer Sciences Education ..........................................................................25 Health Education................................................................................................................27 Marketing Education..........................................................................................................29 Middle School – Special Education ...................................................................................31 Technology Education .......................................................................................................33 Teaching Minors ................................................................................................................35 Student Artifact Reflection Ratings ...............................................................................................36 Benchmark I .......................................................................................................................36 Benchmark II .....................................................................................................................37 Benchmark III ....................................................................................................................38 SOE Benchmark Summary ................................................................................................39 Reflections on Intended Learning by Program ..................................................................41 Reflections on New and Unanticipated Learning by Program ..........................................42 Reflections on Connections to Domains, Components and Wisconsin Teaching Standards by Program ................................................................43 Disposition Ratings ........................................................................................................................44 Undergraduate Dispositions Summary ..............................................................................44 Unit Summary by Disposition Category and Benchmark Level ......................................46 Disposition Highs and Lows by Program and Benchmark Level ......................................47 Attendance by Benchmark Level and Program .................................................................48 Preparedness by Benchmark Level and Program ..............................................................49 Continuous Learning by Benchmark Level and Program..................................................50 Positive Climate by Benchmark Level and Program .........................................................51 Reflective by Benchmark Level and Program ...................................................................52 Thoughtful & Responsive Listener by Benchmark Level and Program ............................53 Cooperative / Collaborative by Benchmark Level and Program .......................................54 Respectful by Benchmark Level and Program ..................................................................55 Table of Contents (continued) Page Pre-Student Teaching Ratings........................................................................................................56 Pre-Student Teaching Results ............................................................................................57 Student Teacher Performance Ratings ...........................................................................................59 Student Teaching Domain Means by Program ..................................................................60 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation .................................................................................61 Domain 2: Classroom Environment ..................................................................................62 Domain 3: Instruction ........................................................................................................63 Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities ...........................................................................64 Student Teaching High Means ...........................................................................................65 Student Teaching Low Means ...........................................................................................65 Student Teaching Wisconsin Teacher Standard Highs ......................................................66 Student Teaching Wisconsin Teacher Standard Lows.......................................................66 Wisconsin Teacher Standard Means by Program ..............................................................67 Art Education .....................................................................................................................68 Early Childhood Education ................................................................................................69 Family & Consumer Science Education ............................................................................70 Marketing & Business Education ......................................................................................71 Special Education...............................................................................................................72 Technology Education .......................................................................................................73 Teaching Minors ................................................................................................................74 Early Childhood Special Education ...................................................................................74 Health Education................................................................................................................75 History................................................................................................................................76 Educational Benchmarking Inventory (EBI) ................................................................ not available Appendix A – Student Teaching Domains and All Components by Program ..............................88 School of Education Unit Assessment Report October 2007 Introduction This report is a summary of the University of Wisconsin-Stout School of Education (SOE) assessment data gathered from the fall semester 2003 through December 2006. In the School of Education, data is gathered from several sources to inform unit and program decisions. Data from this report will be used to develop unit and program goals, inform curriculum changes, and enhance course delivery in order to improve teacher education candidate learning. This report contains data from the PRAXIS I: Pre-Professional Skills Test, PRAXIS II: Content Test, Student Artifact Reflections, Candidate Dispositions, Pre-Student Teaching and Student Teacher Performances, and the Educational Benchmarking Inventory (EBI). Program Specific Reports Program specific reports attached to this summary provide data and narrative descriptions of Graduate Follow-up Surveys, Student Teacher Exit Surveys, Student Teaching Seminar Surveys, and other sources which aid program directors in making program decisions. The program specific reports also describe how this assessment data is used to improve the program, program curriculum, and delivery of courses. In addition, program directors identify and describe program goals for the upcoming year. Assessment Data Uses The unit and program assessment reports are shared with School of Education and individual program advisory committees. Advisory committee members discuss trends and make recommendations for improvement to program directors and the SOE Dean. The Dean and Assessment Coordinator meet each semester with individual program directors to discuss program data, yearly goals, and progress toward achieving short-term and long-term goals. SOE unit and program goals are in alignment with University goals and priorities. This year, a comprehensive analysis will also be conducted to ensure SOE unit and program goals align with external standards developed by certification and accrediting agencies. Organization of Assessment Report This report is organized into nine sections. The table of contents may be used to navigate to a specific section or subsection of the report. To navigate without scrolling, go to the table of contents page. Then press and hold the CTRL key as you click on a section or subsection name in the list. To navigate back to the top of the report and repeat this process, press CTRL and HOME keys at the same time. When viewing the data tables throughout the report, the current year data column is shaded and the text is bolded. 1 PRAXIS I: Pre-Professional Skills Test Educational Testing Service Institutional Report The PRAXIS I: Pre-Professional Skills Test (PPST) is required for teacher certification by the Wisconsin Department of Public Instruction. Passing the PPST is required as part of meeting the SOE Benchmark I: Acceptance into Teacher Education Program and Pre-student Teaching Experiences. Teacher candidates are not admitted into the teacher education program until they pass the PPST. The PPST is administered through the Educational Testing Service (ETS). The PPST consists of three tests: reading, writing and mathematics. All three tests must be passed to meet Benchmark I requirements. These tests can be taken in a hand written format in traditional testing settings at designated sites and times or by computer at designated sites. ETS provides an annual institutional academic year summary report on all students attempting the PPST and passing rates. It also compares scores of UW-Stout students to those at the state level and the national level on the students who take the hand written traditional test. No such comparisons are available for UW-Stout students who take the computer PPST. PPST Reading The PPST Reading test results based on the ETS institutional report indicates that UW-Stout scores in 2004/05 are slightly higher than those in 2003/04. In 2005/06, the median scores dropped two points as did the percentage who met the Wisconsin passing score of 175. Stout males have a much higher pass rate than Stout females. PPST Reading Number of Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 101 Females 05/06 64 Males 05/06 31 185 185 183 185 156 161 159 159 164 176 171-180 177 173-178 175 169-180 174.5 168-178 178 174-182 175 58/105 175 56/87 175 58/101 175 32 175 22 55% 64% 57% 50% 71% 03/04 04/05 05/06 105 87 185 2 Stout teacher candidate average percent correct on the two reading test categories of Literal Comprehension and Critical/Inferential Comprehension increased from 2003/04 to 2004/05 but declined in 2005/06. Stout teacher candidate average scores remain lower than the state average percent correct, but are closer to national averages. Average Percent Correct Reading Test Points Category Available Literal Comprehension Critical and Inferential Comprehension 21-24 Stout State National 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % % % % % % 73 76 79 82 76 76 74 82 78 16-19 67 73 69 77 80 79 UW‐Stout PPST Reading: Average % Correct 76 74 72 70 68 66 64 62 2003/2004 % 2004/2005 % 2005/2006 % Literal Comprehension Critical & Inferential Comprehension 3 73 74 75 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 54,183 in 2003/04, 46,609 in 2004/05 and 40,472 in 2005/06. Reading Test Category Literal Comprehension Critical & Inferential Comp. 1st Q Lowest 03/04 27 26% 28 27% 04/05 20 23% 11 13% 2nd Q 05/06 29 29% 37 37% 03/04 43 41% 29 28% 04/05 27 31% 35 40% 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 05/06 35 35% 33 33% 03/04 20 19% 43 41% 04/05 29 33% 34 39% 05/06 26 26% 24 24% 03/04 15 14% 5 5% 04/05 11 13% 7 8% The Computer PPST Reading test results based on the ETS institutional report indicates that the number of examinees increased slightly from 2004/05 to 2005/06. UW-Stout high, low, and median scores remain constant for the three academic year periods from 2003 through 2006. It is interesting to note in all three academic year periods that Stout teacher candidates have a higher pass rate on the computer version of the reading test than they do on the written version of the test. Stout males have a higher pass rate than Stout females on the computer version of the reading test; however females have a 13% higher pass rate on the computer version as compared to the written version. ETS does not provide average percent correct and quartiles for students taking the computer based C-PPST tests. Computer PPST Reading Number of Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 174 Females 05/06 113 Males 05/06 61 187 186 185 186 155 158 158 158 161 177 172-180 177 172-180 176 172-181 176 171-180 177 173-181 175 188/286 175 110/166 175 113/174 175 71/113 175 42/61 66% 66% 65% 63% 69% 03/04 04/05 05/06 286 166 186 4 05/06 11 11% 7 7% PPST Writing The PPST Writing test results based on the ETS institutional report shows that a higher percentage of UW-Stout students had a WI passing score in 2004/05 (64%) than in 2003/04 (52%), but the pass rate dropped in 2005/06 (55%) on the traditional written test. Although more females than males took the writing exam, male and female scores and pass rates are comparable. 104 Females 05/06 63 Males 05/06 34 184 168 174.5 172-176 181 163 174 172-175 181 163 174 172-172 180 167 174 171-176 174 56/108 174 58/90 174 57/104 174 34/63 174 18/34 52% 64% 55% 54% 53% PPST Writing Number of UW-Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 04/05 05/06 108 90 184 165 174 171-176 In all four writing test categories, UW-Stout students continue to score below the state level. However, Stout teacher candidate average scores are typically within a few percentage points of the national averages. Average Percent Correct Writing Test Category Grammatical Relationships Structural Relationships Idiom/Word Choice Mechanics, No Error Essay Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % 10-12 52 58 61 48 State 04/05 % 62 National 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % 57 56 59 56 13-16 45 52 49 56 62 59 52 56 55 11-14 58 55 52 64 60 62 60 55 59 12 64 65 66 69 69 69 67 67 66 5 UW‐Stout PPST Writing: Average % Correct 70 60 50 40 2003/2004 % 30 2004/2005 % 20 2005/2006 % 10 0 Gram Relations Struct Mechs/ No Error Rel, Idiom/Word Choice Essay The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 55,040 in 2003/04, 46,919 in 2004/05 and 39,273 in 05/06. 1st Q Lowest Writing Test Category Grammatical Relation Structural Relationships Idiom/Word Choices Mechanics, No Error Essay 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 16 15% 24 22% 04/05 11 12% 21 23% 05/06 23 22% 40 38% 03/04 55 51% 43 40% 04/05 34 38% 31 34% 05/06 54 52% 32 31% 03/04 28 26% 34 31% 04/05 32 36% 26 29% 05/06 15 14% 25 24% 03/04 9 8% 7 6% 04/05 13 14% 12 13% 05/06 12 12% 7 7% 17 9 28 43 39 43 36 26 24 12 16 9 16% 10% 27% 40% 43% 41% 33% 29% 23% 11% 18% 9% 20 19% 13 14% 13 13% 45 42% 39 43% 43 41% 35 32% 29 32% 40 38% 8 7% 9 10% 8 8% 6 The Computer PPST Writing test results based on the ETS institutional report indicates that the number of examinees increased from 2004/05 to 2005/06. UW-Stout high scores remain fairly constant for the three academic year periods from 2003 through 2006. However, lowest scores observed of Stout teacher candidates increased in 2005/06. It is interesting to note in two of the three academic year periods, Stout teacher candidates have a higher pass rate on the computer version of the writing test than they do on the written version of the test. Stout females have a 10% higher pass rate than Stout males on the computer version of the writing test; however gender pass rates on the written version of the test vary by only 1%. ETS does not provide average percent correct and quartiles for students taking the computer based C-PPST tests. Computer PPST Writing* Number of Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 211 Females 05/06 123 Males 05/06 88 182 164 174 171-176 183 151 174 171-176 183 164 174 172-176 182 151 174 171-176 174 162/294 174 101/187 174 128/211 174 80/123 174 48/88 55% 54% 61% 65% 55% 03/04 04/05 05/06 294 187 183 163 174 171-176 7 PPST Mathematics The PPST Mathematics test results based on the ETS institutional report shows that pass rates of Stout teacher candidates continues to decrease. Males have significantly higher pass rates than females on the mathematics test. PPST Mathematics Number of Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 92 Females 05/06 55 Males 05/06 30 190 189 187 189 165 164 160 160 160 178 174-183 180 175-184 178 173-183 177 169-182 182 177-185 173 84/99 173 59/73 173 69/92 173 37/55 173 27/30 85% 81% 75% 67% 90% 03/04 04/05 05/06 99 73 188 Stout teacher candidates scored the same as or higher than the national average percent correct in all three test math test categories in all three academic years between 2003 and 2006. However, they scored lower than the state on average percent correct in all three academic years on all test categories. Average Percent Correct 17-18 03/04 % 68 Stout 04/05 % 64 05/06 % 60 11-12 71 71 9-10 70 67 Mathematics Test Category Points Available Conceptual Knowledge and Procedural Knowledge Representations of Quantitative Information Measurement and Informal Geometry, Formal Math Reasoning 8 State 03/04 04/05 05/06 70 69 68 National 04/05 05/06 % 63% 60% 60 68 75 76 75 68% 66% 67 63 73 71 72 65% 63% 62 03/04 UW‐Stout PPST Math: Average % Correct 72 70 68 66 64 62 60 58 56 54 2003/2004 % 2004/2005 % Conceptual Knowledge & Procedural Knowledge 2005/2006 % Representations of Measurement and Quantitative Informal Information Geometry, Formal Math Reasoning The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 54,765 in 2003/04, 46,120 in 2004/05 and 39,860 in 05/06. 1st Q Lowest Math Test Category Conceptual Knowledge & Procedural Knowledge Representations of Quantitative Information Measurement & Informal Geometry, Formal Math Reasoning 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 6 9 17 26 25 32 43 18 22 24 21 21 6% 3 3% 12% 6 8% 18% - 35% 24% 23% 35 32 35% 14 19% 13 38% 29 40% 24% 7 7% - 24 33% 43% 52 52% - 13% 26% 37 37% 14% 8 7 12 29 18 34 44 39 34 18 9 12 8% 10% 13% 29% 25% 37% 44% 53% 37% 18% 12% 13% 12 The Computer PPST Mathematics test results based on the ETS institutional report indicates that the number of examinees increased from 2004/05 to 2005/06. UW-Stout high and median scores remain fairly constant for the three academic year periods from 2003 through 2006. However, lowest scores observed of Stout teacher candidates increased in 2004/05 and stayed constant into 2005/06. It is interesting to note in the latter two of the three academic year periods, Stout teacher candidates have a higher pass rate on the computer version of the math test than they do on the written version of the test. Stout males have a slightly higher pass rate than Stout females 9 on the computer version of the math test. ETS does not provide average percent correct and quartiles for students taking the computer based C-PPST tests. Computer PPST Mathematics* Number of Stout Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Passing Score: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 139 Females 05/06 94 Males 05/06 45 188 190 187 190 154 164 164 164 165 178 174-183 179 175/183 178 175-183 178 174-182 178 175-183 173 200/240 173 110/123 173 118/139 173 79/94 173 39/45 83% 89% 85% 84% 87% 03/04 04/05 05/06 240 123 190 10 UW-Stout Datatel Report PPST data from UW-Stout Datatel System was extracted for the calendar years 2004, 2005 and 2006. For the PPST Reading test, the percent of UW-Stout students passed in 2004 was X%, but by December 2006, X% of these same students had passed according to the Datatel Report. Whereas 62.2% of students passed the PPST Reading test in 2004, by December 2006, X% passed the test. This shows a pattern of student persistence in test taking. Some UW-Stout students took the reading test up to 15 times. Number of Attempts at Reading Test (all programs) 2004 # times ever taken test frequency 1 645 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 111 43 35 20 10 5 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 2005 cumulative # test attempts 645 / 872 (74.0%) 756 799 834 854 864 869 870 871 872 frequency 542 103 39 34 16 7 4 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 cumulative # test attempts 2006 frequency 542 / 746 (72.7%) 645 684 718 734 741 745 746 - SOE Unit - Reading Test Results from Datatel 400 350 300 250 # Passed by May 06 200 # Passed Test 150 100 50 0 2003/04 n=443 2004/05 n=339 2005/06 n=222 11 493 76 26 23 12 4 3 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 cumulative # test attempts 493 / 638 (77.3%) 569 595 618 630 634 637 638 - For the PPST Writing test, the percent of UW-Stout students who passed was X%, but by December 2006, X% of these students passed. In 2005, X% of students passed, but by December 2006, X% of these students passed. For 2006, X% of students had passed. Some students took the Writing test up to 15 times. Number of Attempts at Writing Test (all programs) 2004 # times ever taken test frequency 1 600 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 137 59 25 20 14 7 5 3 0 1 2005 cumulative # test attempts 600 / 871 (68.9%) 737 796 821 841 855 862 867 870 871 frequency 513 121 50 20 17 12 6 4 3 0 0 cumulative # test attempts 2006 frequency 513 / 746 (68.8%) 634 684 704 721 733 739 743 746 - 457 95 41 19 12 6 4 3 1 0 0 cumulative # test attempts 457 / 638 (71.6%) 552 593 612 624 630 634 637 638 - SOE Unit - Writing Test Results from Datatel 400 350 300 250 # Passed by May 06 200 # Passed Test 150 100 50 0 2003/04 n=467 2004/05 n=399 2005/06 n=277 For the PPST Math test, some students took the math test up to 11 times. However, more students passed the math test the first time they took it. There are some problems with data from Datatel which indicates each student who did not pass in 2004 and 2005, passed the math test by 2006. 12 Number of Attempts at Math Test (all programs) 2004 # times ever taken test frequency 1 764 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 68 21 8 5 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 cumulative # test attempts 764 / 870 (87.8%) 832 853 861 866 868 869 870 2005 frequency 651 62 20 4 1 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 2006 cumulative # test attempts frequency 651 / 742 (87.7%) 713 733 737 738 740 741 742 SOE Unit - Math Test Results from Datatel no results from May of '06 250 200 150 # Passed Test 100 50 0 2003/04 n=357 2004/05 n=233 2005/06 n=170 13 573 46 13 1 0 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 cumulative # test attempts 573 / 637 (90.0%) 619 632 633 635 636 637 PPST Attempts and Pass Rates by Program APSCI Math Reading Writing 2004 # test attempts ------------- ARTED Math Reading Writing 19 a 23 a 29 a 14 = 74% 12 = 52% 17 = 59% 22 23 21 15 = 68% 15 = 65% 16 = 76% 15 12 19 10 = 67% 12 = 100% 8 = 42% ECE (EC) Math Reading Writing 97 a 155 a 132 a b 71 = 73% 69 = 45% 69 = 52% 77 108 108 57 = 74% 48 = 44% 46 = 43% 90 126 122 57 = 63% 58 = 46% 71 = 58% FCSE Math Reading Writing 16 17 22 11 = 69% 14 = 82% 14 = 64% 18 18 21 17 = 94% 16 = 89% 16 = 76% 16 19 18 11 = 69% 7 = 37% 10 = 56% MBE (MKTED) Math Reading Writing 23 31 38 20 = 87% 23 = 74% 24 = 63% 9 7 11 8 = 89% 5 = 71% 7 = 64% 15 19 14 9 = 60% 12 = 63% 10 = 71% TECED Math Reading Writing 79 109 c 172 c 73 = 92% 72 = 66% 61 = 35% 47 64 96 42 = 89% 44 = 69% 42 = 44% 47 72 92 44 = 94% 43 = 60% 45 = 49% SPED Math Reading Writing ------------- ------------- 8 9 11 7 = 88% 4 = 44% 6 = 55% 15 28 24 12 = 80% 11 = 39% 13 = 54% Math Reading Writing 32 33 32 26 = 81% 24 = 73% 21 = 66% 8 10 9 5 = 63% 6 = 60% 3 = 33% 6 4 7 5 = 83% 2 = 50% 4 = 57% Math Reading Writing 266 368 425 215 = 80.8% 214 = 58.2% 206 = 48.5% 189 239 277 151 = 80.0% 138 = 57.7% 136 = 49.1% 204 280 296 148 = 72.5% 145 = 51.8% 161 = 54.4% Teacher Educ Program VR (SPED certificate) undergraduate TOTALS PPST Test 2004 # (and %) passed ------------- 2005 # test attempts ------------- 2005 # (and %) passed ------------- 2006 # test attempts 1 1 1 2006 # (and %) passed 1 = 100% 1 = 100% 1 = 100% To be included in the above chart, the student must have a current major as of fall 2004 or fall 2005 or fall 2006, and have taken the Praxis I test during that calendar year. a - includes one double major (ARTED / ECE) b - includes one score “grandfathered in” as a passing score c - includes one exemption granted for a passing score Datatel System indicates that 100% of students who took Math test in 2004 and 2005 passed the test by 2006. Therefore, the pass/fail criteria for each test attempt was recalculated based on the math passing grade of 173. 14 PRAXIS II: Content Test Benchmark II: Admission to Student Teaching requires candidates to pass PRAXIS II the content test for their specific teacher certification. As of 8/31/2004, all Wisconsin teacher education students must pass the content test to be eligible to student teach. Students who took the content test during 2003-04 were “grandfathered in” as this was a no-fault year in Wisconsin. During the period from 2004/05 a total of 134 examinees were reported from ETS as UW-Stout students. This report is general and does not clearly differentiate among undergraduate teacher education students, graduate teacher education students or teachers who want to add-on an additional teacher certification or the “certification only” category. Of the 134 examinees, 124 had a required cut score. School Psychology examines take the content test to meet NASP accreditation requirements, but there was no cut score for 2004-05 in Wisconsin. Of these 124 examinees, 113 passed their designated content test for a pass rate of 91% for 2004/05. In comparison, 482 examinees took the content test in the no-fault year of 2003/04 and 371 passed their designated content test (77%). This comparison shows a positive gain in passing rate of 14% in 2004/05. Note that the number of examinees taking a designated content test varies by content test area. ETS did not include results of tests with fewer than 10 individuals in 2004/05 and or 5 individuals for 2005/06. Therefore, some content areas may not be included in the tables for those years. However, these content areas are included in the data reported by the UW-Stout Datatel System. The UW-Stout Datatel System / Data Warehouse provides information on the UW-Stout candidates who have taken PRAXIS II content test appropriate for their designated teaching certification. Data from that system is reported on a calendar year basis. As a School of Education unit, the total number of examinees in calendar years 2004, 2005 and 2006 (for their program specific content test) are 443, 142, and 234. The numbers may be larger in 2004 as students took advantage of the no-fault year. The total number of examinees for 2006 is probably more representative of future years. In addition, the percentage of examinees that passed the PRAXIS-II content test appropriate for their major (meeting the Wisconsin cut score) from 2004 to 2006 has increased from 78% to 90% to 92%. The following pages illustrate UWStout scores by content area from 2003/04, 2004/05 and 2005/06 so that comparisons can be made. Note: Comparing the ETS content test data with the Datatel content test data reveals a number of discrepancies. This is due to the way individual information (i.e. first name, middle name or initial, and last name) is entered into ETS by candidates at the time of testing. The inputted format must match Datatel information exactly in order for the two systems to match for reporting and comparison purposes. Thus, some content areas may depict a pass rate of less than 100% in ETS which is not accurate. Likewise, the number of tests may not correctly match the Datatel system. The School of Education is working with students, the state, and ETS to remedy this issue. 15 Art Education Praxis Test Code - 10133 According to the ETS report, Art Education had an overall average pass rate of 92% in 2004/05. Note the “grandfathered in” scores from 2004 are tallied as actual pass/fail. Datatel reported a pass rate of 86% in 2004. Data from both systems revealed a pass rate of 100% in 2005 and 2006. Art Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Content Test - Datatel 2005 8 ETS 05/06 8 Datatel 2006 8 178 - 186 186 194 146 146 - 157 155 155 162.5 160-171 - - - 164 158-168 - 155 155 - 155 155 155 29/31 19/22 - 8/8 8/8 8/8 91% 86% - 100% 100% 100% Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: ETS 03/04 32 Datatel* 2004 22 ETS** 04/05 191 *scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing **fewer than 10 tests in Art Education, therefore no ETS report for 2004/05 Average Percent Correct Art Test Category Traditions in Art, Architecture, Design & the Making of Artifacts Art Criticism & Aesthetics The Making of Art Points Available 40-46 27-31 43-48 Stout % 03/04 05/06 % % 59 55 64 72 16 67 79 State % 03/04 05/06 % % 61 63 66 73 75 82 National % 03/04 05/06 % % 64 63 70 75 73 78 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 4,006 in 2003/04 and X in 2005/06. 1st Q Lowest Art Test Category Traditions of Art, Architecture, Design & the Making of Artifacts Art Criticism & Aesthetics The Making of Art 2nd Q 03/04 04/05 - 15 25% - 10 31% 8 25% - 03/04 04/05 8 05/06 03/04 04/05 - 8 47% - 13 41% 14 44% - 17 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 05/06 03/04 04/05 - 1 - 25% - 3% - 6 19% 7 22% - 3 9% 3 9% - 05/06 05/06 Business Education Praxis Test Code - 10100 According to the ETS report, fewer Business Education candidates are taking the exam each year. However, the lowest observed score in 2005/06 increased by 160 points from the previous year. Business Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Business Education – from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 2004* 25 760 520 580 20/25 80% 2004 6 730 580 580 6/6 100% 2005 17 750 450 580 15/17 88% 2006 11 720 600 580 11/11 100% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 30 760 520 630 610-680 580 25/30 83% 04/05 18 750 450 635 600-660 580 17/18 94% 05/06 15 730 610 660 650-680 580 15/15 100% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Business Education had 1/7 categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than state average percent correct and 1/7 at the national level. This is a decrease at the national level from 3/7 in 2003/04 to 1/7 in 2004/05. 18 Average Percent Correct Business Points Educ Test Available Category US Econ Sys Money Mgmt Bus & Its Envirnm Prof Bus Ed Process Info Off Pro & Mgt, Comm, Employ Account & Mrkt Stout State National 11-13 03/04 % 64 04/05 % 63 05/06 % 73 03/04 % 70 04/05 % 70 05/06 % 69 03/04 % 72% 04/05 % 69% 05/06 % 65 15-17 66 62 66 67 70 70 71% 70% 66 12-15 60 61 59 67 67 65 71% 68% 66 22-25 82 79 87 78 79 80 77% 75% 73 19-21 83 77 87 85 81 84 83% 81% 79 16-18 81 79 80 83 84 81 81% 82% 79 16-18 55 56 66 59 66 65 60% 59% 60 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 3,887 in 2003/04, 4,183 in 2004/05 and 3,764 in 2005/06. 19 Bus Educ Test Category U.S. Econ Sys Money Mgt Bus. & Its Envirn Prof Bus Ed Process Info Off Pro & Mgt, Comm, Employ Account/Mrkt 1st Q Lowest 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 11 37% 5 28% 9 30% 6 5 2 33% 23% 28% 10% 11% 9 8 9 3 3 1 30% 33% 30% 44% 30% 17% 10% 6% 8 4 15 8 5 5 7 47% 4 27% 0 3 6 6 40% 5 33% 10 7 9 0 0% 4 27% 4 2 1 2 13% 2 13% 1 27% 22% 44% 28% 6% 6 8 6 8 5 13% 6% 33% 33% 27% 33% 27% 28% 8 5 8 8 5 4 5 1 33% 28% 30% 44% 20% 22% 17% 6% 3 8 10 4 14 2 0% 4 27% 9 60% 3 7% 8 67% 1 7% 4 27% 5 17% 1 27% 0 0% 0 0% 3 50% 1 3 4 7% 10 67% 2 13% 4 10% 44% 20% 33% 22% 33% 47% 11% 20% 10% 22% 27% 8 3 9 4 2 50% 17% 22% 8 53% 2 43% 5 33% 5 17% 0 0% 13 27% 13% 11% 2 13% 20 Elementary Education Praxis Test Code - 10014 According to the ETS report and Datatel, the number of examinees taking Elementary Education tests for Early Childhood Education increased from 2004/05 to 2005/06. Although the highest observed score and median score increased, the pass rate decreased slightly between those years. Elementary Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Early Childhood Education (Early Childhood – regular/special education) (Middle Childhood – regular education) Content Knowledge – from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 2004* 2004 2005 2006 175 193 122 147 130/176 74% 4 143 169 147 3/4 75% 41 183 134 147 38/41 93% 82 195 125 147 63/82 77% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Scores: 03/04 205 193 122 156 146-164 147 150/205 73% 04/05 37 183 134 156 151-169 147 32/37 86% 05/06 49 189 124 160 148-168 147 40/49 82% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Early Childhood Education had 0/4 categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than state or national average in 2005/06. Average Percent Correct Elementary Test Category Language Arts Mathematics Social Studies Science Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % 24-30 74 74 79 78 29-30 63 68 70 67 28-30 58 60 61 56 29-30 61 66 63 62 State 04/05 % 80 74 63 67 National 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % 80 79 81 79 68 68 74 69 61 61 62 60 63 64 65 64 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the 21 testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 33,214 in 2003/04, 38,821 in 2004/05 and 48,055 in 2005/06. Elementary Test Category Language Arts Mathematics Social Studies Science 1st Q Lowest 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 82 40% 45 22% 50 24% 44 21% 15 41% 6 16% 6 16% 1 3% 11 22% 13 27% 13 27% 12 24% 48 23% 96 47% 73 36% 78 38% 13 35% 14 38% 15 41% 16 43% 17 35% 16 33% 22 45% 15 31% 60 29% 51 25% 48 23% 56 27% 5 14% 11 30% 8 22% 13 35% 16 33% 13 27% 5 10% 9 18% 15 7% 13 6% 34 17% 27 13% 4 11% 6 16% 8 22% 7 19% 5 10% 7 14% 5 10% 9 18% 22 Pedagogical Test Data for Teacher Candidates Seeking Licensure in States other than Wisconsin Early Childhood Pedagogical Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Scores: 03/04 04/05 05/06 - - 19 730 460 660 620-700 Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Early Childhood Education had 3/6 categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than state average and 5/6 categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than national average in 2005/06. Average Percent Correct Early Childhood Test Category Nature of Growth/Dev/ Lrng of Young Child Factors that Influence Individual Growth/Dev App of Dev & Curr Theory Planning & Implementing Curriculum Eval/Report Student Progress & Effect of Instruction Understanding Professional / Legal Responsibilities Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % State 04/05 % National 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % 33-36 - - 73 - - 75 - - 72 11-12 - - 76 - - 76 - - 72 13-15 - - 61 - - 61 - - 63 35-36 - - 78 - - 78 - - 76 14 - - 82 - - 83 - - 76 8 - - 80 - - 81 - - 74 23 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 3,397 in 2005/06. Early Childhood Test Category Nature of Growth/Dev/ Lrng of Young Child Factors that Influence Individual Growth/Dev App of Dev & Curr Theory Planning & Implementing Curriculum Eval/Report Student Progress & Effect of Instruction Understanding Professional / Legal Responsibilities 1st Q Lowest 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 - - 3 - - 4 - - 7 - - 5 - - 16% - - 21% - - 37% - - 26% - - 1 - - 6 - - 8 - - 4 - - 5% - - 32% - - 42% - - 21% - - 3 16% 3 - - 9 47% 5 - - 7 37% 6 - - 0 0% 5 - - 16% - - 26% - - 32% - - 26% - - 4 - - 3 - - 4 - - 4 - - 21% - - 16% - - 21% - - 21% - - 0 - - 7 - - 10 - - 10 - - 0% - - 37% - - 53% - - 53% 24 Family & Consumer Sciences Education Praxis Test Code - 10120 According to the ETS report, the number of Family & Consumer Sciences Education (FCSE) examinees increased in 2005/06 as did the lowest observed score and median score. FCSE data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Family & Consumer Sciences Education – from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 2004* 2004 2005 2006 20 730 470 590 14/20 70% 3 670 560 590 2/3 67% 5 670 560 590 4/5 80% 12 710 550 590 10/12 83% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 23 730 510 600 600-660 590 18/23 78% 04/05 10 740 490 645 600-710 590 8/10 80% 05/06 18 740 600 665 620-710 590 18/18 100% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Family and Consumer Sciences Education results were the same as or higher than state and national average percent correct in all categories. Average Percent Correct FCSE Test Category Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % The Family 14-16 85 86 85 93 Human Dev. 13 75 80 75 81 Management 11-12 75 86 76 84 Consumer 13-15 58 72 60 69 Econ Nutrition / Food Clothing / Textiles Housing FCS Educ. State 04/05 % 88 78 82 72 National 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % 87 86 88 85 77 75 79 77 77 77 81 80 68 66 69 68 17-20 73 70 82 72 70 76 75 72 74 11 75 76 78 68 75 72 76 76 75 9-12 22-23 77 81 78 79 81 85 75 79 78 82 80 83 78 81 77 78 79 78 25 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 1,021 in 2003/04, 1,113 in 2004/05 and 1,263 in 2005/06. 1st Q Lowest FCSE Test Category The Family Human Development Management Consumer Economics Nutrition / Food Clothing / Textiles Housing FCS Education 03/04 9 39% 6 26% 4 17% 10 43% 4 17% 3 13% 5 22% 5 22% 04/05 1 10% 1 10% 1 10% 1 10% 3 30% 2 20% 2 20% 1 10% nd 2 Q 05/06 0 0% 2 11% 0 0% 3 17% 3 17% 3 17% 2 11% 1 6% 03/04 8 35% 6 26% 7 30% 6 26% 11 48% 12 52% 7 30% 7 30% 04/05 4 40% 4 40% 1 10% 4 40% 2 20% 4 40% 2 20% 3 30% 26 4th Q Highest rd 3 Q 05/06 5 28% 5 28% 7 39% 7 39% 3 17% 8 44% 4 22% 3 17% 03/04 5 22% 8 35% 9 39% 4 17% 7 30% 5 22% 8 35% 4 17% 04/05 5 50% 2 20% 3 30% 1 10% 2 20% 2 20% 2 20% 4 40% 05/06 7 39% 5 28% 4 22% 3 17% 5 28% 6 33% 10 56% 8 44% 03/04 1 4% 3 13% 3 3% 3 13% 1 4% 3 13% 3 13% 7 30% 04/05 0 0% 3 30% 5 50% 4 40% 3 30% 2 20% 4 40% 2 20% 05/06 6 33% 6 33% 7 39% 5 28% 7 39% 1 6% 2 11% 6 33% Health Education Praxis Test Code - 20550 Health Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Content Test Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: ETS** 03/04 - Datatel* 2004 6 ETS** 04/05 - Datatel 2005 14 ETS 05/06 9 Datatel 2006 15 - 790 - 810 830 830 - 580 - 610 630 610 - - - - 720 710-750 - - 610 - 610 610 610 - 5/6 - 14 9/9 15/15 - 83% - 100% 100% 100% *scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing **fewer than 10 tests, therefore no ETS reports for 2003/04 and 2004/05 Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Health Education results were the same as or higher than state and national average percent correct in all categories except Healthy Relationships and Disease prevention. Health Ed Test Category Health Ed as a Discipline Promoting Healthy Lifestyles Community Health Advocacy Healthy Relationships Disease Prevention Health Ed Pedagogy Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % 17-19 72 - State 04/05 % - 05/06 03/04 % % 68 - National 04/05 05/06 % % 67 36 - - 74 - - 72 - - 72 12 - - 81 - - 73 - - 73 22-24 - - 69 - - 71 - - 70 17-18 - - 69 - - 62 - - 66 11-12 - - 78 - - 69 - - 67 27 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 2,100. Health Ed Test Category Health Ed as a Discipline Promoting Healthy Lifestyles Community Health Advocacy Healthy Relationships Disease Prevention Health Ed Pedagogy 1st Q Lowest 2nd Q 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 03/04 - 04/05 - 05/06 1 11% 1 11% 03/04 - 04/05 - 05/06 2 22% 3 33% 03/04 - 04/05 - 05/06 3 33% 3 33% 03/04 - 04/05 - 05/06 3 33% 2 22% - - 2 22% - - 1 11% - - 2 22% - - 4 44% - - 1 11% 0 0% 0 0% - - 6 67% 5 56% 3 33% - - 1 11% 3 33% 3 33% - - 1 11% 1 11% 3 33% 28 Marketing Education Praxis Test Code – 10560 Data from the ETS report for Marketing Education reveals a decrease in examinees between 2003/04 and 2004/05. The passing rate was 62% in 2003/04 but increased in both subsequent years to a 100% pass rate. Marketing Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Marketing Education – from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 2004* 21 810 480 600 14/21 67% 2004 6 820 660 600 6/6 100% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 29 810 450 660 550-720 04/05 14 820 570 685 660-750 05/06 15 820 610 720 660-750 600 600 600 18/29 12/14 15/15 62% 86% 100% 29 2005 13 810 580 600 12/13 92% 2006 13 820 610 600 13/13 100% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Marketing Education had two categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than state average percent correct and six categories the same or higher at the national. Average Percent Correct Marketing Ed Test Category M Ed, Curr Instr, Career Planning General Marketing Merchandising Mktg Math Comm & HR Ad & Sales Pro Personal Selling Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % 23-25 74 79 74 80 State 04/05 % 79 National 05/06 03/04 04/05 05/06 % % % % 77 77 80 77 21-23 69 79 82 74 78 83 77 80 80 14-21 11-12 16 13-14 14-15 61 56 77 66 73 67 64 83 74 77 64 68 84 76 82 67 62 79 70 75 67 65 84 74 77 69 70 83 79 83 71 66 83 76 80 69 66 85 74 80 69 66 83 75 79 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 362 in 2003/04 and 412 in 2005/06. Marketing Ed Test Category M Ed, Curr & Instr, Career Plng General Marketing Merchandising Mktg Math Comm & HR Ad & Sales Promotion Personal Selling 1st Q Lowest nd 4th Q Highest rd 2 Q 3 Q 03/04 7 04/05 4 05/06 2 03/04 7 04/05 3 05/06 7 03/04 6 04/05 6 05/06 2 03/04 9 04/05 1 05/06 4 24% 29% 13% 24% 21% 47% 21% 43% 13% 31% 7% 27% 13 45% 15 2% 9 31% 8 28% 14 48% 9 31% 4 29% 15 7% 3 21% 6 43% 2 14% 2 14% 2 13% 3 20% 2 13% 4 27% 2 13% 1 7% 8 28% 9 31% 9 31% 14 8% 6 21% 13 45% 3 21% 6 43% 6 43% 3 21% 5 36% 7 50% 5 33% 6 40% 6 40% 2 13% 5 33% 8 53% 4 14% 5 17% 9 31% 6 21% 5 17% 6 21% 5 36% 6 43% 3 21% 4 29% 5 36% 4 29% 6 40% 4 27% 6 40% 9 60% 4 27% 3 20% 4 14% 0 10% 2 7% 1 3% 4 14% 1 13% 2 14% 0 7% 2 14% 1 7% 2 14% 1 7% 2 13% 2 13% 1 7% 0 0% 4 27% 3 20% 30 Middle School Subjects – Special Education Praxis Test Code - 20146 According to the ETS report, there were fewer than 10 tests in Middle School Subjects for Special Education; therefore no ETS data was reported for 2004/05. Special Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Special Education (Middle School) (Cognitive/Hearing/Emotional/Visual/LD) 2004* 2004 2005 2006 Content Knowledge – from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 49 184 101 146 29/49 59% 1 151 151 146 1/1 100% 9 170 130 146 7/9 78% 28 185 122 146 15/28 54% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: Score Needed to Pass: Number with Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 59 04/05 - 05/06 15 184 101 149 136-163 146 34/59 58% - 185 128 148 143-159 146 9 60% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Special Education Stout results continue to be below the state and national average percent. Average Percent Correct Special Education Test Category Literature Mathematics History / Social Studies Science Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % State 04/05 % 05/06 03/04 % % National 04/05 05/06 % % 27-30 29-30 28-30 59 53 53 - 65 58 56 63 63 54 - 72 71 58 63 62 55 - 71 66 59 28-30 59 - 58 63 - 63 62 - 62 31 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 4,892 in 2003/04 and 4,714 in 2005/06. Special Education Test Category Literature Mathematics History / Social Studies Science 1st Q Lowest 03/04 20 34% 22 37% 11 19% 17 29% 04/05 - nd 2 Q 05/06 4 27% 7 47% 4 27% 2 13% 03/04 14 24% 25 42% 27 46% 15 25% 04/05 - 32 4th Q Highest rd 3 Q 05/06 7 47% 5 33% 7 47% 10 67% 03/04 16 27% 7 12% 13 22% 16 27% 04/05 - 05/06 3 20% 2 13% 0 0% 2 13% 03/04 9 15% 5 8% 8 14% 11 19% 04/05 - 05/06 1 7% 1 7% 4 27% 1 7% Technology Education Praxis Test Code – 10050 Technology Education data from the ETS report and Datatel is as follows: Technology Education – PRAX-10050 from Datatel Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 2004* 2004 2005 2006 84 750 560 590 79/84 94% 10 700 600 590 10/10 100% 42 730 580 590 40/42 95% 69 750 580 590 67/69 97% 04/05 45 740 580 650 630-690 590 44/45 98% 05/06 56 750 580 655 630-680 590 55/56 98% * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Content Test from ETS Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score: Median: Average Performance Range: WI Score Needed to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score: Percent with WI Passing Score: 03/04 104 750 560 650 610-680 590 97/104 93% Comparing the category scores for UW-Stout with Wisconsin and national percent correct shows that Technology Education had 4/5 categories where Stout results were the same as or higher than the state average percent correct and 5/5 categories the same or higher than the national in 2005/06. Average Percent Correct Tech Ed Test Category Ped. & Prof (T Ed) Infor & Communic Technology Construct Tech Manuf Tech Energy / Power/ Trans Tech Stout Points 03/04 04/05 05/06 03/04 Available % % % % State 04/05 % 05/06 03/04 % % National 04/05 05/06 % % 32-36 78 78 82 78 80 81 78 77 79 21-23 70 71 73 70 72 73 70 69 73 15-17 77 78 80 76 81 80 76 74 78 20-24 75 78 76 75 80 75 75 80 75 22-23 74 78 74 74 78 75 72 70 71 33 The following table displays the number and percent of Stout Examinees Scoring in Each Quartile in Each Category. Quartiles are calculated using all examinees taking this test during the testing period. The number of examinee records used to compute the quartiles was 962 in 2003/04, 952 in 2004/05 and 957 in 2005/06. Tech Ed Test Category Ped & Prof (T Ed) Inform & Comm Tech Construct Tech Manuf Tech Energy/Power/ Trans Tech 1st Q Lowest 03/04 04/05 27 26% 13 13% 17 16% 27 26% 12 12% 7 16% 9 20% 4 9% 5 11% 2 4% 2nd Q 05/06 6 11% 5 9% 7 13% 10 18% 5 9% 03/04 04/05 36 35% 47 45% 34 3% 17 16% 44 42% 15 33% 12 27% 12 27% 15 33% 13 29% 34 4th Q Highest 3rd Q 05/06 16 29% 24 43% 26 46% 12 21% 18 32% 03/04 04/05 28 27% 27 26% 33 32% 44 42% 23 22% 14 31% 13 29% 21 47% 12 27% 15 33% 05/06 24 43% 18 43% 17 30% 17 30% 26 46% 03/04 04/05 13 13% 17 16% 20 19% 16 15% 25 24% 9 20% 11 24% 8 18% 13 29% 15 33% 05/06 10 18% 9 16% 6 11% 17 30% 7 13% Teaching Minors Data on Teaching Minors from Datatel is as follows: Broadfield Social Studies (Economics/Geography/History/Sociology/ Psychology/Political Science/Citizenship) 2004* 2005 2006 Content Knowledge – PRAX-10081 Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 1 180 180 153 1/1 100% 0 153 - 1 183 183 153 1/1 100% 2004* 2004 2005 2006 1 154 154 135 1/1 100% 1 135 135 135 1/1 100% 0 135 - 1 141 141 135 1/1 100% (Literature/Journalism/Speech/Composition) 2004 2005 2006 Content Knowledge PRAX-10041 Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score 0 160 - 1 145 145 160 0/1 0% 0 160 - * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Mathematics Content Knowledge – PRAX-10061 Number of Examinees: Highest Observed Score: Lowest Observed Score WI Score Need to Pass: Number with WI Passing Score Percent with WI Passing Score * - scores from no-fault year – “grandfathered in” as passing Broadfield Language Arts 35 Student Artifact Reflection Ratings for Benchmarks I, II and III Beginning in fall 2004, all students in School of Education courses were required to develop artifacts as evidence of their learning. This is part of the Performance Based Assessment Requirements for the School of Education at UW-Stout. For each selected artifact, students were required to write a reflection related to: the intended learning, new or unanticipated learning gained from completing the artifact, and how each artifact related to Danielson’s domains and components and the ten Wisconsin Teacher Standards. SOE faculty who graded the artifacts then rated the reflections associated with that artifact. Each faculty member was required to submit a copy of the reflection rating form to the SOE Dean’s Office for compilation of the data. Artifacts and artifact reflections are required to meet the SOE Benchmarks. Course artifacts and reflection ratings are reviewed by two faculty members during each transition point / Benchmark stage. There is a Benchmark I interview and portfolio review required for each student at Benchmark I: Acceptance into Teacher Education Program and Pre-student Teaching Experiences. The Benchmark I means for each category on the reflection rubric ratings increased from 2004 to 2005 and from 2005 to 2006 as follows: Benchmark I Intended Unanticipated Connections 2004 mean (N) 2.66 (379) 2.51 (379) 2.49 (379) 2005 Mean (N) 2.78 (338) 2.77 (389) 2.62 (389) 2006 mean (N) 3.06 (356) 2.96 (356) 2.76 (353) Benchmark I Reflections SOE Unit 3.5 3 2.5 2004 mean 2 2005 mean 1.5 1 2006 mean 0.5 0 Intended Unanticipated Connections It is interesting to note that for three consecutive years, means for Benchmark I reflections have increased in all categories. In all years, teacher candidates are pretty good at reflecting on Intended Learning. In other words, they have a good understanding of what they are supposed to be learning from the learning process and artifacts they created. Teacher candidates scored 36 slightly lower overall for all three years in the category of Connections. Candidates seem to have more difficulty connecting their learning to prior learning. Another interview and portfolio review is required at Benchmark II: Admission to Student Teaching. The Benchmark II means on the reflection rubric ratings increased in every category except Intended Learning from 2004 to 2005 and from 2005 to 2006 as follows: Benchmark II Intended Unanticipated Connections 2004 mean (N) 2.74 (510) 2.63 (510) 2.76 (510) 2005 mean (N) 2.72 (776) 2.73 (776) 2.80 (774) 2006 mean (N) 2.80 (618) 2.76 (628) 2.88 (626) Benchmark II Reflections SOE Unit 2.9 2.85 2.8 2004 mean 2.75 2.7 2005 mean 2.65 2.6 2006 mean 2.55 2.5 Intended Unanticipated Connections The final interview and portfolio review is at Benchmark III: Program Completion which takes place at the end of student teaching. During student teaching, candidates are required to develop at least two artifacts which are then rated by their cooperating teachers using the School of Education reflection rubric. The Benchmark III means on the reflection rubric ratings increased from 2004 to 2005 but decreased in all three categories from 2005 to 2006 as follows: Benchmark III Intended Unanticipated Connections 2004 mean (N) 3.42 (257) 3.36 (257) 3.39 (257) 2005 mean (N) 3.54 (237) 3.51 (237) 3.64 (237) 37 2006 mean (N) 3.36 (290) 3.27 (290) 3.38 (284) The overall pattern on reflection ratings increased in all three categories from 2004 to 2005 for all three benchmarks. The overall pattern on reflection ratings from 2005 to 2006 was an increase in reflection ratings in all three categories at the Benchmark I and II levels. However, from 2005 to 2006, Benchmark III reflection ratings decreased in all three categories. Summary of All SOE Programs Benchmark I Intended Unanticipated Connections Benchmark II Intended Unanticipated Connections Benchmark III Intended Unanticipated Connections 2004 mean (N) 2.66 (379) 2.51 (379) 2.49 (379) 2005 mean (N) 2.78 (338) 2.77 (389) 2.62 (389) 2006 mean (N) 3.06 (356) 2.96 (356) 2.76 (353) 2.74 (510) 2.63 (510) 2.76 (510) 2.72 (776) 2.73 (776) 2.80 (774) 2.80 (618) 2.76 (628) 2.88 (626) 3.42 (257) 3.36 (257) 3.39 (257) 3.54 (237) 3.51 (237) 3.64 (237) 3.36 (290) 3.27 (290) 3.38 (284) The charts on the following page are graphic representations of the data above. One would anticipate seeing growth in each category (Intended, Unanticipated, and Connections) as teacher candidates progress from level to level. In other words, Benchmark II means should be higher than Benchmark I means. In that case, our assessment system needs to establish inter-rater reliability. In addition, it would be better to track teacher candidate progress from level to level in the year that they progress. In other words, look at 2004 Benchmark I completers and means, then 2005 Benchmark II completers and means, then 2006 Benchmark III completers and means. Currently, the SOE assessment system does not track candidate development in this manner. 38 Intended Learning: BM I, II & III 4 3.5 3 2004 mean 2.5 2 2005 mean 1.5 1 2006 mean 0.5 0 BM I BM II BM III Unanticipated Learning: BM I, II & III 4 3.5 3 2004 mean 2.5 2 2005 mean 1.5 1 2006 mean 0.5 0 BM I BM II BM III Connections to Domains, Components & WI Teacher Standards: BM I, II & III 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 2004 mean 2005 mean 2006 mean BM I BM II BM III 39 The grades earned by each artifact were also compiled for 2004 and 2005 for Benchmarks I and II. Cooperating teachers were not asked to grade the artifacts for student teaching (Benchmark III). The pattern of artifact grades is very similar in 2004 and 2005. • A for 50% in 2004 and 50% in 2005 • B for 16.6% in 2004 and 8.3% in 2005 • C for 2% in 2004 and 1.3% in 2005 • D and F less than 0.1% • No grade given for 31% in 2004 and 40.1% in 2005. Starting in the fall of 2006, the grades received on the reflections documents were no longer entered into the Datatel system. 40 The table below depicts the reflection ratings for the category of Intended Learning by SOE program for 2004, 2005, and 2006. Reflections – Intended Learning Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.07 (15) 2.58 (137) 2.53 (43) 3.00 (91) 2.84 (31) 2.51 (63) 2.66 (379) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.82 (28) 2.82 (157) 2.68 (60) 2.56 (43) 2.69 (13) 2.89 (84) 2.78 (338) Mean (N) 2006 2.67 (3) 3.41 (22) 3.06 (119) 3.26 (19) 2.90 (61) 3.00 (56) 3.05 (61) 3.06 (356) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 1.89 (9) 2.80 (332) 2.63 (54) 3.30 (61) 2.33 (24) 1.80 (30) 2.74 (510) 2.52 (21) 2.79 (580) 2.69 (32) 2.48 (40) 2.37 (19) 2.47 (83) 2.72 (776) 1.50 (2) 2.62 (13) 2.76 (386) 3.24 (89) 3.06 (70) 2.38 (26) 2.04 (28) 2.80 (618) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.10 (20) 3.44 (117) 3.38 (26) 3.32 (50) 3.70 (27) 3.53 (17) 3.42 (257) 3.29 (17) 3.63 (106) 3.47 (15) 3.53 (60) 3.75 (8) 3.31 (32) 3.54 (237) 3.25 (8) 3.49 (147) 3.54 (26) 2.97 (36) 3.00 (9) 3.29 (49) 3.36 (290) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the reflection data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 41 The table below depicts the reflection ratings for the category of New and Unanticipated Learning by SOE program for 2004, 2005, and 2006. Reflections – New and Unanticipated Learning Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.07 (15) 2.35 (137) 2.42 (43) 2.86 (91) 2.52 (31) 2.51 (63) 2.51 (379) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.79 (28) 2.78 (157) 2.63 (60) 2.67 (43) 2.77 (13) 2.88 (85) 2.77 (389) Mean (N) 2006 2.67 (3) 3.55 (22) 3.03 (119) 3.32 (19) 2.80 (61) 2.63 (56) 2.93 (61) 2.96 (356) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.00 (9) 2.68 (332) 2.67 (54) 2.77 (61) 2.45 (64) 2.17 (30) 2.63 (510) 2.57 (21) 2.78 (580) 2.59 (32) 2.60 (40) 2.53 (19) 2.53 (83) 2.73 (776) 2.00 (2) 2.31 (13) 2.75 (391) 3.01 (90) 3.07 (70) 2.34 (29) 2.13 (30) 2.76 (628) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.20 (20) 3.24 (117) 3.54 (26) 3.44 (50) 3.47 (74) 3.53 (17) 3.36 (257) 3.35 (17) 3.57 (106) 3.33 (15) 3.52 (60) 3.75 (8) 3.34 (32) 3.51 (237) 3.13 (8) 3.38 (147) 3.27 (26) 2.86 (36) 3.33 (9) 3.22 (49) 3.27 (290) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the reflection data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 42 The table below depicts the reflection ratings for the category of Connections Drawn to Domains/Components and Wisconsin Teacher Standards by SOE program for 2004, 2005, and 2006. Reflections – Connections to Domains, Components and Wisconsin Teacher Standards Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.27 (15) 2.58 (137 2.60 (43) 2.16 (91) 2.80 (50) 2.54 (63) 2.49 (379) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.68 (28) 2.75 (157) 2.42 (60) 2.07 (43) 2.62 (13) 2.76 (85) 2.62 (389) Mean (N) 2006 2.33 (3) 3.18 (22) 2.97 (119) 3.05 (19) 2.44 (61) 2.52 (56) 2.61 (61) 2.76 (353) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.11 (9) 2.89 (332) 2.67 (54) 2.64 (61) 2.36 (64) 2.20 (30) 2.76 (510) 2.37 (19) 2.95 (580) 2.34 (32) 2.13 (40) 2.32 (19) 2.41 (83) 2.80 (774) 2.50 (2) 2.23 (13) 3.06 (389) 2.76 (90) 2.61 (70) 2.21 (29) 2.50 (30) 2.88 (626) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.00 (20) 3.46 (117) 3.42 (26) 3.26 (50) 3.45 (74) 3.53 (17) 3.39 (257) 3.35 (17) 3.74 (106) 3.73 (15) 3.67 (60) 3.75 (8) 3.41 (32) 3.64 (237) 3.38 (8) 3.53 (146) 3.58 (26) 2.64 (36) 3.44 (9) 3.42 (48) 3.38 (284) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the reflection data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 43 Disposition Ratings The School of Education has developed a system to assess candidate dispositions from the beginning of the program through program completion. Dispositions of Teaching ratings are completed for candidates in the undergraduate teacher education programs and the graduate pupil services programs. The dispositions ratings are comprised of eight professional disposition categories: attendance, preparedness, continuous learning, creating a positive climate, reflective, thoughtful and responsive learner, cooperative/collaborative and respectful. These dispositions of teaching are linked to the Wisconsin Teacher Standards and Wisconsin Pupil Service Standards. Disposition of Teaching ratings have a four point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. Mean scores are then calculated based on this scale. At the undergraduate teacher education level, candidates receive disposition ratings from the course instructor for the introduction to the major course and the Foundations of Education course for Benchmark I. Benchmark II candidates receive disposition rating from two of their program methods/curriculum class instructors. For Benchmark III, cooperating teachers at each student teaching placement rate each candidate at the completion of student teaching. Although all undergraduate teacher education programs and graduate pupil services programs use the same eight dispositions, the definitions of disposition ratings vary. The undergraduate programs all use the same definitions. However, the two graduate programs use the definitions given below. As you can see, the terminology for rating level four differs between the two graduate programs. The definitions of the disposition ratings are as follows: 1=Unsatisfactory : Rarely demonstrates disposition 2=Minimal: Occasionally demonstrates disposition 3=Satisfactory: Usually demonstrates disposition 4= Proficient: Consistently demonstrates disposition. Undergraduate Dispositions Summary For the undergraduate dispositions, ratings increased on 7 of the 8 disposition areas from 2004 to 2005 for Benchmark I & II: preparedness, continuous learning, positive climate, reflective, thoughtful and responsive listener, cooperative/collaborative and respectful. Those categories with the largest increase of 0.3 or more were preparedness (2.66 to 2.96), continuous learning (2.59 to 2.93), and positive climate (2.7 to 3.03). One category, attendance, decreased by 0.3 (3.47 to 3.16) in that same time period. Overall, candidates had the lowest means at Benchmarks I and II for 2004 and 2005 in the following disposition categories: preparedness, continuous learning, reflective, and thoughtful and responsive listener. From 2005 to 2006 at the Benchmark I level, ratings increased in all eight disposition categories. At the Benchmark II level during that period, ratings increased in all categories except attendance. For 2006, teacher candidates had the lowest means at Benchmarks I and II in the disposition categories of continuous learning and reflective. At Benchmark II, teacher candidates had the highest means in the categories of cooperative/collaborative and respectful. The overall pattern of means for all three assessment years (2004, 2005, and 2006) found Benchmark I candidates rated highest on the dispositions of attendance and being respectful. 44 Cooperating teachers rate the dispositions for undergraduate student teachers at the Benchmark III level. Comparing mean averages from 2004 to 2005, there was an increase in all eight dispositions. All eight disposition means for 2004 and 2005 were above 3.0. At Benchmark III, the four disposition categories with the lowest means in 2004 and 2005 were: preparedness, continuous learning, reflective, and cooperative/collaborative. Again, the overall pattern of means for all three assessment years (2004, 2005, and 2006) found Benchmark III candidates rated highest on the dispositions of attendance and being respectful. At the Benchmark III level during 2006, ratings stayed the same or increased in all categories except preparedness. For 2006 Benchmark III, the disposition categories with the lowest means were preparedness, continuous learning, and cooperative/collaborative. 45 The table below depicts SOE unit means by Disposition category for each benchmark level. SOE Unit Means by Category for Each Disposition Level Attendance BM I BM II BM III Mean (N) 2004 3.38 (268) 3.55 (188) 3.68 (192) Mean (N) 2005 3.18 (342) 3.49 (455) 3.79 (174) Mean (N) 2006 3.43 (499) 3.43 (366) 3.84 (152) Preparedness BM I BM II BM III 2.33 (268) 3.13 (188) 3.49 (192) 2.45 (342) 3.27 (456) 3.70 (174) 2.88 (498) 3.37 (368) 3.57 (152) Continuous Learning BM I BM II BM III 2.28 (268) 2.99 (188) 3.43 (192) 2.33 (342) 3.13 (456) 3.53 (174) 2.70 (498) 3.19 (368) 3.57 (152) Positive Climate BM I BM II BM III 2.37 (268) 3.16 (188) 3.60 (192) 2.51 (342) 3.31 (454) 3.68 (174) 2.94 (498) 3.43 (368) 3.67 (152) Reflective BM I BM II BM III 2.35 (268) 2.98 (188) 3.47 (192) 2.34 (342) 3.06 (453) 3.57 (174) 2.71 (498) 3.20 (369) 3.60 (152) Thoughtful & Responsive Listener BM I BM II BM III 2.38 (268) 3.03 (188) 3.56 (192) 2.45 (342) 3.11 (454) 3.67 (174) 2.78 (498) 3.28 (369) 3.68 (152) Cooperative / Collaborative BM I BM II BM III 2.44 (268 3.16 (188) 3.45 (192) 2.47 (341) 3.30 (453) 3.59 (174) 2.99 (498) 3.57 (369) 3.57 (152) Respectful BM I BM II BM III 2.69 (268) 3.47 (188) 3.69 (192) 2.69 (341) 3.55 (454) 3.83 (174) 3.18 (498) 3.75 (369) 3.83 (152) Disposition Category Level Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 46 The Benchmark I, II and III patterns of highest and lowest category means for 2004, 2005 and 2006 vary by program. The highest and lowest disposition means patterns for specific programs/certifications are as follows: Disposition Highs and Lows by Program Program APSCI ARTED ECE FCSE MBE SPED TE Level Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III Benchmark I Benchmark II Benchmark III 2004 Highest Attendance No data Respectful/Reflective Reflective Attendance Attendance Attendance Respectful Respectful Attendance Cooptive/Collaborative Attendance Attendance Attendance Respectful Attendance No clear pattern Attendance/Respectful 2005 Lowest Preparedness No data Preparedness Continuous Learning Thought/Resp Listener Reflective Reflective Reflective/Preparedness Reflective Reflective Continuous Learning Cooptive/Collaborative Reflective Reflective Preparedness Reflective/Cont Lrng No clear pattern Preparedness 47 Highest No clear pattern No data No data Respectful Respectful Respectful Attendance Attendance Attendance/Prepared Attendance Attendance Respectful Respectful Respectful Respectful Respectful Attendance Attendance Attendance Respectful Respectful 2006 Lowest No clear pattern No data No data Reflective Preparedness Reflective Continuous Learning Reflective Continuous Learning Reflective Reflective Reflective Attendance Attendance Continuous Learning Continuous Learning Reflective/Cont Lrng Respectful/Cont Lrng Preparedness Attendance Reflective/Prepard/CL Highest Lowest Attendance No data No data Respectful All others tied Respectful Attendance Respectful Attendance Attendance Attendance Respect/Thought Respectful Respectful Attendance Attendance Attendance Att/Respect/CL Attendance No data Respectful Reflective/Preparedness No data No data Thought/Resp Listener Attendance Continuous Learning Continuous Learning Continuous Learning Continuous Learning Reflective Preparedness Preparedness Continuous Learning Continuous Learning Pos Climate/Reflective Continuous Learning Reflective/Cont Lrng Prepared/Pos Climate Preparedness No data Preparedness Dispositions – Attendance by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 3.38 (29) 3.30 (125) 3.52 (25) 3.23 (39) 3.65 (23) 3.54 (28) 3.38 (268) Mean (N) 2005 3.00 (1) 3.04 (25) 3.28 (156) 3.36 (33) 2.25 (36) 3.24 (38) 3.41 (49) 3.18 (342) Mean (N) 2006 3.67 (3) 3.31 (29) 3.49 (194) 3.33 (21) 3.00 (43) 3.48 (75) 3.52 (108) 3.43 (499) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.64 (118) 2.78 (18) 3.60 (48) 3.75 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.55 (188) 3.08 (13) 3.62 (308) 3.28 (36) 3.31 (45) 3.53 (17) 2.89 (37) 3.49 (455) 3.00 (1) 3.43 (272) 3.37 (51) 3.37 (30) 3.77 (13) 3.43 (366) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.19 (32) 3.89 (71) 3.44 (16) 3.75 (24) 3.67 (9) 3.76 (38) 3.68 (192) 3.50 (20) 3.80 (96) 3.70 (10) 3.91 (23) 4.00 (4) 3.82 (22) 3.79 (174) 3.88 (8) 3.86 (72) 3.63 (24) 3.91 (11) 4.00 (4) 3.85 (27) 3.84 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 48 Dispositions – Preparedness by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.55 (29) 2.16 (125) 2.68 (25) 2.59 (39) 2.35 (23) 2.21 (28) 2.33 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.48 (25) 2.31 (156) 2.58 (33) 2.53 (36) 2.79 (38) 2.45 (49) 2.45 (342) Mean (N) 2006 2.33 (3) 3.28 (29) 2.73 (193) 3.10 (21) 3.05 (43) 2.65 (75) 3.03 (108) 2.88 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.07 (118) 2.61 (18) 3.46 (48) 3.25 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.13 (188) 3.00 (13) 3.29 (309) 2.89 (36) 3.33 (45) 3.12 (17) 3.46 (37) 3.27 (456) 4.00 (1) 3.46 (272) 3.02 (51) 3.25 (32) 3.23 (13) 3.37 (368) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.13 (32) 3.61 (71) 3.63 (16) 3.67 (24) 3.22 (9) 3.47 (38) 3.49 (192) 3.55 (20) 3.80 (96) 3.40 (10) 3.57 (23) 3.75 (4) 3.50 (22) 3.70 (174) 3.88 (8) 3.61 (72) 3.38 (24) 3.55 (11) 3.50 (4) 3.48 (27) 3.57 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 49 Dispositions – Continuous Learning by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.59 (29) 2.10 (125) 2.60 (25) 2.56 (39) 2.30 (23) 2.04 (28) 2.28 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.40 (25) 2.09 (156) 2.55 (33) 2.50 (36) 2.58 (38) 2.53 (49) 2.33 (342) Mean (N) 2006 3.00 (3) 3.24 (29) 2.34 (193) 3.10 (21) 2.93 (43) 2.47 (75) 3.15 (108) 2.70 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.87 (118) 2.78 (18) 3.35 (48) 3.00 (4) 3.00 (1) 2.99 (188) 3.08 (13) 3.08 (309) 3.00 (36) 3.47 (45) 2.76 (17) 3.35 (37) 3.13 (456) 4.00 (1) 3.22 (272) 3.08 (51) 3.16 (32) 3.08 (13) 3.19 (368) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.19 (32) 3.51 (71) 3.31 (16) 3.50 (24) 3.33 (9) 3.53 (38) 3.43 (192) 3.65 (20) 3.57 (96) 3.00 (10) 3.39 (23) 3.25 (4) 3.50 (22) 3.53 (174) 3.63 (8) 3.51 (72) 3.42 (24) 3.45 (11) 4.00 (4) 3.78 (27) 3.57 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 50 Dispositions – Positive Climate by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 ----2.76 (29) 2.15 (125) 2.68 (25) 2.69 (39) 2.35 (23) 2.25 (28) 2.37 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.72 (25) 2.19 (156) 2.76 (33) 2.94 (36) 2.74 (38) 2.71 (49) 2.51 (342) Mean (N) 2006 2.67 (3) 3.45 (29) 2.56 (193) 3.05 (21) 3.42 (43) 2.85 (75) 3.32 (108) 2.94 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.05 (118) 2.94 (18) 3.52 (48) 3.25 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.16 (188) 3.23 (13) 3.29 (309) 3.11 (36) 3.44 (45) 3.12 (17) 3.54 (35) 3.31 (454) 4.00 (1) 3.47 (272) 3.20 (51) 3.47 (32) 3.31 (13) 3.43 (368) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.22 (32) 3.75 (71) 3.50 (16) 3.58 (24) 3.78 (9) 3.66 (38) 3.60 (192) 3.55 (20) 3.74 (96) 3.20 (10) 3.78 (23) 3.50 (4) 3.64 (22) 3.68 (174) 3.88 (8) 3.71 (72) 3.54 (24) 3.36 (11) 3.50 (4) 3.78 (27) 3.67 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 51 Dispositions – Reflective by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.69 (29) 2.36 (125) 2.20 (25) 2.49 (39) 2.26 (23) 2.04 (28) 2.35 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.32 (25) 2.19 (156) 2.15 (33) 2.58 (36) 2.63 (38) 2.49 (49) 2.34 (342) Mean (N) 2006 2.33 (3) 3.38 (29) 2.37 (193) 2.71 (21) 2.98 (43) 2.49 (75) 3.17 (108) 2.71 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.88 (118) 2.61 (18) 3.38 (48) 3.00 (4) 3.00 (1) 2.98 (188) 2.85 (13) 3.03 (309) 2.72 (36) 3.45 (44) 2.76 (17) 3.34 (35) 3.06 (453) 4.00 (1) 3.24 (272) 3.04 (52) 3.19 (32) 3.08 (13) 3.20 (369) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.25 (32) 3.59 (71) 3.25 (16) 3.46 (24) 3.44 (9) 3.53 (38) 3.47 (192) 3.45 (20) 3.63 (96) 3.10 (10) 3.57 (23) 3.50 (4) 3.50 (22) 3.57 (174) 3.88 (8) 3.58 (72) 3.50 (24) 3.36 (11) 3.75 (4) 3.67 (27) 3.60 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 52 Dispositions – Thoughtful & Responsive Listener by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.69 (29) 2.18 (125) 2.72 (25) 2.67 (39) 2.30 (23) 2.36 (28) 2.38 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.64 (25) 2.18 (156) 2.29 (33) 2.89 (36) 2.87 (38) 2.53 (49) 2.45 (342) Mean (N) 2006 2.67 (3) 3.21 (29) 2.53 (193) 2.95 (21) 3.00 (43) 2.64 (75) 3.06 (108) 2.78 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.84 (118) 2.94 (18) 3.52 (48) 3.00 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.03 (188) 3.08 (13) 3.08 (309) 2.97 (36) 3.41 (44) 2.76 (17) 3.31 (36) 3.11 (454) 4.00 (1) 3.31 (272) 3.19 (52) 3.25 (32) 3.08 (13) 3.28 (369) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.25 (32) 3.69 (71) 3.56 (16) 3.50 (24) 3.56 (9) 3.58 (38) 3.56 (192) 3.65 (20) 3.72 (96) 3.10 (10) 3.65 (23) 3.50 (4) 3.59 (22) 3.67 (174) 3.88 (8) 3.61 (72) 3.83 (24) 3.55 (11) 3.75 (4) 3.67 (27) 3.68 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 53 Dispositions – Cooperative / Collaborative by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 2.62 (29) 2.20 (125) 2.72 (25) 2.82 (39) 2.78 (23) 2.25 (28) 2.44 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.60 (25) 2.19 (159) 2.61 (33) 2.63 (35) 2.89 (38) 2.67 (49) 2.47 (341) Mean (N) 2006 3.00 (3) 3.31 (29) 2.54 (193) 3.29 (21) 3.51 (43) 2.96 (75) 3.42 (108) 2.99 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 2.92 (118) 2.94 (18) 3.83 (48) 3.25 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.16 (188) 2.92 (13) 3.29 (309) 3.00 (36) 3.43 (44) 3.06 (17) 3.77 (35) 3.30 (453) 4.00 (1) 3.65 (272) 3.23 (52) 3.59 (32) 3.31 (13) 3.57 (369) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.16 (32) 3.62 (71) 3.31 (16) 3.42 (24) 3.44 (9) 3.50 (38) 3.45 (192) 3.45 (20) 3.69 (96) 3.00 (10) 3.52 (23) 3.50 (4) 3.55 (22) 3.59 (174) 3.75 (8) 3.54 (72) 3.54 (24) 3.36 (11) 3.50 (4) 3.70 (27) 3.57 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 54 Dispositions – Respectful by Level and Program Benchmark I APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * Mean (N) 2004 3.34 (29) 2.36 (125) 3.00 (25) 3.10 (39) 2.35 (23) 2.96 (28) 2.69 (268) Mean (N) 2005 2.00 (1) 2.84 (25) 2.28 (156) 2.82 (33) 3.19 (36) 3.35 (37) 2.92 (49) 2.69 (341) Mean (N) 2006 2.67 (3) 3.55 (29) 2.95 (193) 3.24 (21) 3.67 (43) 3.01 (75) 3.45 (108) 3.18 (498) Benchmark II APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.39 (118) 3.17 (18) 3.77 (48) 3.50 (4) 3.00 (1) 3.47 (188) 3.38 (13) 3.57 (309) 3.25 (36) 3.59 (44) 3.24 (17) 3.81 (36) 3.55 (454) 4.00 (1) 3.85 (272) 3.27 (52) 3.88 (32) 3.38 (13) 3.75 (369) Benchmark III APSCI ARTED ECE (EC) FCSE MBE (MKTED) SPED / VR TE Aggregate * 3.25 (32) 3.83 (71) 3.69 (16) 3.67 (24) 3.89 (9) 3.76 (38) 3.69 (192) 3.80 (20) 3.84 (96) 3.50 (10) 3.96 (23) 3.25 (4) 3.86 (22) 3.83 (174) 4.00 (8) 3.83 (72) 3.83 (24) 3.45 (11) 4.00 (4) 3.89 (27) 3.83 (152) Program Means calculated on a 4-point scale where 1=unsatisfactory, 2=emerging, 3=basic, and 4=advanced basic. * - Aggregate “N” is slightly lower than the actual sum of “N” from all programs. This occurs when the disposition data is included twice because students may be enrolled in multiple programs. 55 Pre-Student Teaching Ratings Beginning in fall 2004, SOE pre-student teaching final ratings were related to the final student teacher evaluation. Both the pre-student teacher and student teacher evaluation ratings were based on the Danielson four domains/components and the Wisconsin Teacher Standards. The pre-student teaching experience varies among programs and depends to some extent upon how comfortable the cooperating teacher is with involving the candidate with students in the classroom. Cooperating teachers rate the candidates on the extent to which they meet the competency on a scale of NA= not achieved/unsatisfactory, 1=very limited achievement, 2=limited achievement. In the case of Early Childhood Education, faculty members who teach the participation class observe the candidates participating with school children in tutoring or one-one-one sessions. These Early Childhood Education instructors then do the final ratings at the kindergarten and primary levels. At the infant, toddler and preschool level, the lab teachers who are the head teachers in the classroom do the ratings. However, the items and language differs on the forms and the data from this is not included in this report. The table on the following page shows the compiled frequency results for the calendar years of 2004, 2005, and 2006. The frequency patterns indicates that candidates achieved most of the competencies related to the domains/components and selected Wisconsin Teacher Standards. Because of this, only the competencies not appropriate/not achieved will be identified by domain. The competencies not achieved/appropriate are as follows: o Domain I: Planning and Preparation Elements o Item 4: Shows some understanding of assessing student learning o Domain II: The Classroom Environment o Item 3: Aware of classroom procedures o Domain III: Instruction o Item 7: Assists in classroom activities o Domain IV: Professional Responsibilities/Personal Characteristics o WI Teacher Standards o Standard 8: Knows how to test students for progress. For graduate student preclinical data, see the Graduate Programs section of this report. 56 Pre-student Teaching Results This table includes only data from the general form and does not include all majors. 2004 Frequencies Domain I: Planning and Preparation 1. Shows knowledge of content and pedagogy 2. Shows knowledge of student characteristics 3. Shows some understanding of instructional objectives 4. Shows some understanding of assessing student learning. Domain II: The Classroom Environment 1. Displays respect and rapport 2. Notices sensitivity to learning, cultural and racial differences in pupils 3. Aware of classroom procedures 4 Shows understanding of behavior management 5. Initiates interaction with students Domain III: Instruction 1. Exhibits appropriate oral language usage 2. Exhibits appropriate written language usage 3. Exhibits appropriate voice projection 4. Recognizes the importance of student involvement 5. Provides appropriate feedback to student 6. Displays a sense of flexibility and responsiveness 7. Assists in classroom activities 8. ? Check Datatel code 2005 Frequencies 2006 Frequencies NA 1 2 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 6 0 132 5 7 119 14 1 164 6 0 132 5 11 115 8 0 171 8 0 130 1 4 126 13 0 166 101 0 37 56 10 65 61 0 118 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 1 0 137 4 1 126 0 0 179 28 1 109 6 5 120 3 0 176 75 0 63 94 0 37 69 1 109 29 7 102 9 4 118 4 4 171 2 9 127 7 7 117 3 7 169 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 5 0 133 1 5 125 3 0 176 15 0 123 12 2 117 14 0 165 7 1 130 3 8 120 8 2 169 7 0 131 2 2 127 6 0 173 4 3 131 5 4 122 4 5 170 3 1 134 2 2 127 5 1 173 72 2 64 52 3 76 69 3 107 137 0 1 128 0 3 175 0 4 Scale: NA-Not applicable in this teaching situation, 1 –Unsatisfactory/not achieved, s2–Emerging/achieved with limited degree 57 2004 Frequencies Domain IV: Professional Responsibilities / Personal Character 1. Demonstrates potential to grow & develop professionally 2. Shows active interest & willingness to participate in classroom activities 3. Has poise & confidence 4. Indicates sense of responsibility and dependability. 5. Exhibits good judgment, self-control & tact 6. Shows interest in students 7. Presents a professional appearance 8. Displays a positive attitude Select Wisconsin Teacher Standards 1. Knows the subjects they are teaching 2. Knows how children grow 3. Understands that children learn differently 6. Communicates well 7. Plans instruction based on knowledge of subject matter, students and curriculum goals 8. Knows how to test for student progress 2005 Frequencies 2006 Frequencies NA 1 2 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 1 0 137 2 5 124 0 0 179 3 2 133 11 4 116 99 1 79 3 2 5 6 130 130 1 2 6 1 124 128 0 0 3 3 176 176 3 0 135 1 3 127 9 1 169 2 2 2 1 134 135 0 0 3 5 128 126 9 9 2 1 168 169 2 0 136 2 0 129 8 0 171 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 NA 1 2 12 6 120 7 5 119 16 1 162 16 41 3 2 119 95 10 10 2 3 119 118 18 15 3 1 158 163 9 107 1 1 128 30 5 35 5 3 121 93 13 70 2 0 164 109 135 0 3 78 0 53 117 0 62 Scale: NA-Not applicable in this teaching situation, 1 –Unsatisfactory/not achieved, 2–Emerging/achieved with limited degree 58 Student Teacher Performance Ratings on Domains/Component and Wisconsin Teacher Standards The School of Education uses Danielson’s domains/components and the Wisconsin Teacher Standards as part of the framework for student teacher competency evaluations. Cooperating teachers utilize these competencies to rate student teachers on their final performance evaluation. A four point scale is used. Examination of the overall domain mean scores in 2004, 2005 and 2006 reveals that, although means decreased for all four domains, there is a consistent pattern on each of the domains with the same rank order for all three years. Danielson’s Domain Mean Rank 2004 2005 2006 Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities Highest 3.39 3.50 3.42 Domain 2: The Classroom Environment 2nd 3.34 3.40 3.28 Domain 3: Instruction 3rd 3.28 3.38 3.25 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation 4th Lowest 3.26 3.34 3.22 Error! Not a valid link. 59 As each student teacher was assessed on the Danielson Domains at the end of student teaching in 2006, program means were calculated and compared to SOE Unit means as follows. See Appendix A for a detailed breakdown of Domains and Components by program. Student Teaching Domain Means by Program Student Teaching Domains Rank Domain 1: Planning & Preparation 1 TECED 2 ECE 3 MBE 4 SPED 5 FCSE 6 ARTED Domain 2: Classroom Environment 1 TECED 2 ECE 3 FCSE 4 SPED 5 MBE 6 ARTED Domain 3: Instruction 1 TECED 2 ECE 3 MBE 4 SPED 5 FCSE 6 ARTED Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities 1 ECE 2 TECED 3 SPED 4 MBE 5 FCSE 6 ARTED Ï or Ð SOE Unit Mean 3.22 3.39 Ï 3.22 Ï 2.93 Ð 2.89 Ð 2.87 Ð ----- 3.28 3.40 Ï 3.28 Ï 3.08 Ð 3.04 Ð 2.78 Ð ----- 3.25 3.45 Ï 3.24 Ð 2.92 Ð 2.91 Ð 2.84 Ð ----- 3.42 3.48 Ï 3.44 Ï 3.06 Ð 2.82 Ð 2.77 Ð ----- 60 Within each of Danielson’s four domains, the SOE unit had a consistent pattern of highs and lows on means for academic years 2004 and 2005, calendar years 2005 and 2006 and average totals as follows: Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High: 1e: Designing coherent instruction Low: 1d: Demonstrating knowledge of resources Domain 1: Planning and Preparation 3.45 3.4 3.35 3.3 2004 2005 2006 3.25 3.2 3.15 3.1 3.05 3 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy 1c. Selecting instructional goals 1e. Designing coherent instruction 61 Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High: 2e: Organizing physical space Low: 2d: Managing student behavior Domain 2: The Classroom Environment 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3 2.9 2004 2005 2006 2a. Creating 2b. 2c. Managing 2d. Managing 2e. an Establishing classroom student Organizing environment a culture of procedures behavior physical of respect & learning space rapport 62 Domain 3: Instruction High: 3e: Demonstrating flexibility & responsiveness High: 3d: Providing feedback to students (tie for 1st in 2006) Low: 3b: Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 3: Instruction 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3 2.9 2004 2005 2006 3a. Communicating clearly & accurately 3b. Using questioning & discussion techniques 3c. Engaging students in learning 63 3d. Providing feedback to students 3e. Demonstrating flexibility & responsiveness Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High: 4d: Showing professionalism Low: 4c: Communicating with families Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3 2.9 2004 2005 2006 4a. Reflecting on teaching 4b. Maintaining 4c. 4d. Contributing 4e. Growing & 4f. Showing accurate Communicating to school & developing professionalism records with families district professionally 64 Likewise a check of the 22 components in Danielson’s framework reveals a consistent pattern of mean score rankings in 2004, 2005 and 2006. The six components with the highest mean scores and highest average total means are as follows: Danielson’s Component 4f. Showing professionalism 4d. Contributing to the school & district 4a. Reflecting on teaching 4b. Maintaining accurate records 2e. Organizing physical space 4e. Growing & developing professionally Mean Rank Calendar Year 2004 Calendar Year 2005 Calendar Year 2006 Average All Years Highest 3.67 3.77 3.57 3.67 2nd highest 3.50 3.57 3.52 3.54 3rd highest 3.43 3.52 3.45 3.48 4th highest 3.41 3.53 3.44 3.48 5th highest 3.46 3.52 3.41 3.47 Lowest 3.36 3.50 3.38 3.43 Inspection of the components with the lowest mean scores shows a consistent pattern in 2004, 2005 and 2006. In 2006, 1f assessing student learning and 3b using questioning and discussion techniques are new to the list. The six components with the lowest mean scores and lowest average total means are as follows: Danielson’s Component 2d. Managing student behavior 3b. Using questioning and discussion techniques 1d. Demonstrating knowledge of resources 4c. Communicating with families 1f. Assessing student learning 2c. Managing classroom procedures 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of content and pedagogy Mean Rank Calendar Year 2005 Calendar Calendar Year Year 2005 2006 Lowest 3.26 3.27 3.11 3.21 2nd lowest 3.25 3.28 3.12 3.22 3rd lowest 3.15 3.31 3.15 3.23 Average All Years 4th lowest-tied 4th lowest-tied 5th lowest-tied 3.23 3.29 3.22 3.26 3.23 3.33 3.18 3.26 3.23 3.32 3.21 3.27 5th lowest-tied 3.27 3.31 3.22 3.27 65 Each student teacher was also assessed on the 10 Wisconsin State Teacher Standards at the end of student teaching in 2004, 2005 and 2006. A consistent pattern was found on the mean scores. The UW-Stout candidates rated highest on two Wisconsin teacher standards with mean scores and average total means as follows: Wisconsin Teacher Standard 10. Collaboration highest mean 9. Reflection 2nd highest mean Calendar Year 2004 Calendar Year 2005 Calendar Year 2006 Average All Years 3.28 3.48 3.37 3.41 3.34 3.46 3.34 3.40 The three lowest teacher standard means for 2004, 2005 and the average total mean scores were revealed as follows: Wisconsin Teacher Standard 3. Diverse learners lowest mean—tied 4. Instructional strategies lowest mean—tied 8. Assessment lowest mean—tied Calendar Year 2004 Calendar Year 2005 Calendar Year 2006 Average All Years 3.18 3.29 3.16 3.23 3.18 3.29 3.15 3.22 3.19 3.28 3.13 3.21 Wisconsin Teacher Standards 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3 2.9 1. C 2. o D ev nte 3. n el 4. D op t iv In e m st en ru rse c L 5. tio ea t Le na r ar l S ner ni s ng tra t e En gi es 6. vi r 7. Com onm Pl en an mu t ni ni ca ng t io In n st ru 8. ct As se ion ss m 9. en 10 Re t . C f le ct ol io la bo n ra tio n 2004 2005 2006 66 As each student teacher was assessed on the 10 Wisconsin State Teacher Standards at the end of student teaching in 2006, program means were calculated and compared to SOE Unit means as follows. These results should be compared to the EBI ratings provided by exiting student teachers within each program (see page 87). Wisconsin Teacher Standards – Means by Program Wisconsin Teacher Standards Rank Ï or Ð SOE Unit Mean 3.25 6. Communication 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.49 Ï 3.24 Ð 3.00 Ð 2.92 Ð 2.78 Ð ------ TECED ECE MBE SPED FCSE ARTED 1. Content Knowledge TECED ECE FCSE MBE SPED ARTED 3.23 2. Development TECED ECE FCSE SPED MBE ARTED 1 2 2 4 5 6 TECED ECE FCSE SPED MBE ARTED 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.31 Ï 3.16 Ï 3.00 Ð 2.78 Ð 2.73 Ð ----- 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.33 Ï 3.14 Ð 2.83 Ð 2.80 Ð 2.67 Ð ----- 3.15 4. Instructional Strategies TECED ECE MBE FCSE SPED ARTED 3.29 5. Learning Environment TECED ECE SPED FCSE MBE ARTED 1 2 3 4 5 6 Rank Ï or Ð SOE Unit Mean 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.45 Ï 3.25 Ï 2.92 Ï 2.67 Ï 2.60Ð ----- 3.24 3.27 7. Planning Instruction 3.35 Ï 3.24 Ï 3.00 Ð 2.89 Ð 2.75 Ð ----- 3.16 3. Diverse Learners Wisconsin Teacher Standards FCSE TECED ECE MBE SPED ARTED 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.40 Ï 3.35 Ï 3.29 Ï 2.83 Ð 2.67 Ð ----- 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.52 Ï 3.10 Ð 3.00 Ð 2.80 Ð 2.78 Ð ----- 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.52 Ï 3.40 Ï 3.33 Ð 3.00 Ð 2.83 Ð ----- 3.13 8. Assessment TECED ECE MBE FCSE SPED ARTED 3.34 9. Reflection TECED FCSE ECE SPED MBE ARTED 3.37 10. Collaboration TECED ECE SPED MBE FCSE ARTED 3.41 Ï 3.32 Ï 3.00 Ð 2.80 Ð 2.75 Ð ----- 67 1 2 3 4 5 6 3.65 Ï 3.35 Ð 3.33 Ð 2.83 Ð 2.60 Ð ----- Each of the program/certification areas has been inspected to determine patterns in student teacher competency ratings from cooperating teachers. The highest and lowest component rating means and the Wisconsin Teacher Standards rating means for each program for calendar years 2004, 2005, and 2006 and average total mean revealed are displayed below and on the following pages. See Appendix A for a detailed breakdown of Domains and all Components by program. Art Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years 3.07 3.07 None 3.07 2.72 2.90 None 2.81 3.14 3.31 None 3.22 2.90 2.90 None 2.90 3.07 3.14 None 3.10 2.86 3.00 None 2.93 2.83 3.03 None 2.93 3.00 2.50 3.17 2.95 None None 3.09 2.76 3.04 2.71 3.21 2.93 None None 3.12 2.82 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1a. Low 1b. Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy Demonstrating knowledge of students Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High 2a. Low 2d. Creating an environment of respect & rapport Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction High 3b. Low 3a. 3d. Using questioning & discussion techniques Communicating clearly & accurately Providing feedback to students Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4a. 4c. Reflecting on teaching Communicating with families WI Teacher Standards High Low 5. 8. Learning Environment Assessment Note: ArtEd did not have question 4f in previous years. An accommodation was not made when determining means and averages for the chart above. 68 Early Childhood Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years 3.51 3.44 3.31 3.40 3.11 3.22 3.09 3.15 3.52 3.39 3.56 3.31 3.43 3.12 3.50 3.25 3.44 3.48 3.30 3.40 3.27 3.29 3.11 3.22 3.72 3.39 3.79 3.41 3.63 3.28 3.71 3.35 3.49 3.15 3.52 3.21 3.33 3.10 3.44 3.16 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1b. Low 1d. Demonstrating knowledge of students Demonstrating knowledge of resources Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High Low 2e. 2d. Organizing physical space Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction High 3e. Low 3b. Demonstrating flexibility & responsiveness Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4f. 4c. Showing professionalism Communicating with families WI Teacher Standards High Low 9. 8. Reflection Assessment 69 Family & Consumer Sciences Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1c. Selecting instructional goals 3.36 3.38 2.80 3.29 Low 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy Assessing student learning 3.14 3.25 2.80 3.14 3.21 3.19 2.80 3.14 3.00 3.14 3.50 3.31 3.40 2.80 3.33 3.17 3.36 3.50 3.00 3.37 3.21 3.25 2.60 3.14 3.57 3.00 3.75 3.06 3.20 2.00 3.60 2.88 3.43 3.07 3.50 3.56 3.00 2.60 3.40 3.23 1f. Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High Low 2e. 2b. Organizing physical space Establishing a culture of learning Domain 3: Instruction High 3e. Low 3b. Demonstrating flexibility & responsiveness Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4b. 4c. Maintaining accurate records Communicating with families WI Teacher Standards High Low 3. 10. Diverse Learners Collaboration Note: FCSE did not have question 2e in previous years. An accommodation was not made when determining means and averages for the chart above. 70 Marketing and Business Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years 3.65 3.46 3.25 3.47 3.53 3.15 2.75 3.18 3.73 3.35 3.50 3.11 3.00 2.50 3.48 3.06 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1d. Low 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of resources Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High Low 2e. 2d. Organizing physical space Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction High 3d. Providing feedback to students 3.53 3.39 3.25 3.40 Low 3a. Communicating clearly & accurately 3.47 3.18 2.75 3.18 3.71 None 3.54 3.00 3.17 2.86 3.52 2.88 3.41 3.65 3.41 3.46 3.38 3.18 2.92 2.83 2.75 3.35 3.35 3.16 Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4b. 4f. Maintaining accurate records Showing professionalism WI Teacher Standards High Low 6. 7. 2. Communication Planning instruction Development Note: MBE did not have question 4f in previous years. An accommodation was not made when determining means and averages for the chart above. 71 Special Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years 3.38 3.46 3.00 3.30 3.13 3.31 3.00 3.17 3.38 3.31 2.78 3.17 3.63 3.69 3.22 3.53 3.13 3.15 3.00 3.10 3.38 3.54 3.11 3.37 3.25 3.38 2.67 3.13 3.50 3.25 3.46 None 3.11 3.00 3.37 3.00 3.50 3.38 3.50 3.46 3.38 3.31 3.33 2.67 2.67 3.43 3.17 3.17 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1b. Low 1a. 1f. Demonstrating knowledge of students Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy Assessing student learning Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High 2a. Low 2c. Creating an environment of respect & rapport Managing classroom procedures Domain 3: Instruction High 3e. Low 3b. Demonstrating flexibility & responsiveness Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4b. 4f. Maintaining accurate records Showing professionalism WI Teacher Standards High Low 10. 4. 6. Collaboration Instructional strategies Communication Note: SpEd did not have question 4f in previous years. An accommodation was not made when determining means and averages for the chart above. 72 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years Demonstrating knowledge of resources Low 1b. Demonstrating knowledge of student Domain 2: The Classroom Environment 3.50 3.59 3.45 3.54 3.14 3.46 3.35 3.39 High Creating an environment of respect & rapport Low 2d. Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction 3.71 3.68 3.59 3.66 3.21 3.38 3.20 3.31 High 3d. 3.21 3.59 3.59 3.55 Low 3b. Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities 3.07 3.39 3.29 3.33 High 4b. Maintaining accurate records Low 4c. Communicating with families WI Teacher Standards 3.29 3.38 3.68 3.34 3.55 3.26 3.60 3.32 High Low 3.50 3.14 3.64 3.41 3.65 3.35 3.63 3.37 Technology Education Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1d. 2a. 10. 2. Providing feedback to students Collaboration Development Note: TE did not have question 4f in previous years. An accommodation was not made when determining means and averages for the chart above. 73 Student Teaching Minors In addition to student teaching in their majors (programs), UW-Stout students can add a teaching minor. A teaching minor requires student teaching in that area for certification. In 2004, 2005, and 2006, 30 ECE (5 additional students added this report) candidates student taught in Early Childhood Special Education (took SPED-482), 4 FCSE candidates student taught in Health Education, and 2 TECED candidates student taught in History Education (no new students). The student teaching data for each of these minors in 2004, 2005, 2006 and average total are given as follows: Early Childhood Special Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years 3.60 3.65 3.80 3.67 3.50 3.32 3.75 3.41 3.60 3.78 4.00 3.79 3.60 3.47 3.40 3.48 3.80 3.79 3.80 3.79 3.20 3.55 3.60 3.50 3.80 3.80 3.75 3.55 3.80 3.60 3.77 3.60 3.50 3.25 3.80 3.25 4.00 3.40 3.79 3.28 Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1b. Low 1d. Demonstrating knowledge of student Demonstrating knowledge of resources Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High 2b. Low 2d. Establishing a culture of learning Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction High 3e. Low 3b. Demonstrating flexibility and responsiveness Using questioning & discussion techniques Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4a. 4c. Reflecting on teaching Communicating with families WI Teacher Standards High Low 9. 8. Reflection Assessment 74 Health Education 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1f. Assessing student learning 3.00 3.20 None 3.17 Low 1a. Demonstrating knowledge of content & pedagogy Demonstrating knowledge of resources Designing coherent instruction 3.00 2.80 None 2.83 3.00 2.80 None 2.83 3.00 2.80 None 2.83 3.00 3.20 None 3.17 2.00 2.80 None 2.67 3.00 3.25 None 3.20 2.00 2.80 None 2.67 None 2.00 3.25 2.60 None None 3.25 2.50 3.00 3.00 3.40 2.60 None None 3.33 2.67 1d. 1e. Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High 2a. Low 2d. Creating an environment of respect and rapport Managing student behavior Domain 3: Instruction High 3a. Low 3c. Communicating clearly & accurately Engaging students in learning Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4f. 4d. Showing professionalism Contributing to the school and district WI Teacher Standards High Low 8. 9. Assessment Reflection 75 2004 2005 2006 Average All Years None 3.50 None 3.50 None 2.50 None 2.50 Creating an environment of respect and rapport Establishing a culture of learning Managing student behavior None 3.00 None 3.00 None 3.00 None 3.00 None 3.00 None 3.00 Managing classroom procedures Organizing physical space None 2.50 None 2.50 None 2.50 None 2.50 None 3.00 None 3.00 None 3.00 None None 3.00 2.50 None 3.00 2.50 None None 3.50 2.50 None None 3.50 2.50 None None None 4.00 2.50 2.50 None None None 4.00 2.50 2.50 History Education Domain 1: Planning and Preparation High 1d. Low 1b. Demonstrating knowledge of resources Demonstrating knowledge of students Domain 2: The Classroom Environment High 2a. 2b. 2d. Low 2c. 2e. Domain 3: Instruction High 3a. 3b. Low 3c. 3d. Communicating clearly & accurately Using questioning & discussion techniques Engaging students in learning Providing feedback to students 3.00 Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities High Low 4a. 4d. Reflecting on teaching Contributing to the school and district WI Teacher Standards High Low 10. 2. 3. Collaboration Development Diverse Learners 76 Educational Benchmarking Inventory (EBI) for Exiting Student Teachers The Educational Benchmarking Inventory (EBI) of exiting student teachers is administered via computer at the end of student teaching for the purpose of unit assessment. EBI data cannot be published in public domains and is available for internal use only. 77 86 87 Appendix A Student Teacher Competency Final Ratings Domain 1: Planning and Preparation 1a: Demonstrating knowledge of content and pedagogy 1b: Demonstrating knowledge of students 1c: Selecting instructional goals 1d: Demonstrating knowledge of resources 1e: Designing coherent instruction 1f: Assessing student learning Domain 2: The Classroom Environment 2a: Creating an environment of respect and rapport 2b: Establishing a culture of learning 2c: Managing classroom procedures 2d: Managing student behavior 2e: Organizing physical space Domain 3: Instruction 3a: Communicating clearly and accurately 3b: Using questioning and discussion techniques 3c: Engaging students in learning 3d: Providing Feedback to Students 3e: Demonstrating Flexibility and Responsiveness ArtEd 2004 2005 2006 N=29 N=29 N= ECE FCSE 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 N=89 N=225 N=213 N=14 N=16 2006 N=5 MBE 2004 2005 2006 N=17 N=39 N=12 SPED TECED SOE UNIT 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 2006 N=8 N=15 N=9 N=14 N=92 N=51 N=172 N=431 N=294 2.89 2.97 3.35 3.35 3.22 3.19 3.29 2.87 3.54 3.29 2.93 3.25 3.19 2.89 3.21 3.07 3.07 3.31 3.32 3.23 3.14 3.25 2.80 3.53 3.15 2.75 3.13 3.13 3.00 3.29 2.72 2.90 3.51 3.44 3.31 3.07 3.31 3.00 3.47 3.18 2.83 3.38 3.27 3.00 3.14 2.90 2.93 3.38 3.36 3.24 3.36 3.38 2.80 3.53 3.21 3.00 3.25 3.13 2.89 2.86 3.07 3.11 3.22 3.09 3.07 3.31 3.00 3.65 3.46 3.25 3.13 3.20 2.93 2.90 3.48 3.45 3.29 3.29 3.31 2.80 3.53 3.31 2.92 3.25 2.86 2.97 3.27 3.31 3.17 3.21 3.19 2.80 3.53 3.41 2.83 3.00 3.12 3.43 3.41 3.28 3.17 3.43 3.08 3.50 3.29 3.14 3.31 3.40 3.42 3.29 3.14 3.50 3.20 3.53 3.07 3.17 3.49 3.46 3.34 3.14 3.31 2.80 2.86 3.04 3.33 3.33 3.22 3.29 3.50 2.90 2.90 3.39 3.31 3.12 3.07 3.04 3.19 3.38 3.56 3.43 2.92 3.11 3.37 3.39 2.86 3.00 3.38 3.07 3.14 2.93 3.39 3.26 3.34 3.22 3.37 3.27 3.31 3.22 3.46 3.35 3.30 3.37 3.29 3.00 3.53 3.33 3.28 3.35 3.23 2.89 3.50 3.59 3.45 3.15 3.31 3.15 3.27 2.78 3.07 3.49 3.41 3.34 3.40 3.28 3.38 3.13 2.78 3.29 3.57 3.41 3.23 3.33 3.18 2.78 3.37 3.36 3.04 3.44 3.52 3.40 3.34 3.40 3.28 3.36 3.00 3.63 3.53 3.22 3.71 3.68 3.59 3.39 3.47 3.33 3.47 3.26 2.83 3.50 3.43 3.11 3.36 3.57 3.41 3.38 3.43 3.32 2.80 3.41 3.21 2.67 3.13 3.00 3.00 3.14 3.46 3.31 3.23 3.32 3.21 3.38 3.20 3.35 3.11 2.50 3.25 3.20 2.78 3.21 3.38 3.20 3.26 3.27 3.11 3.00 3.50 3.40 3.73 3.50 3.00 3.38 3.62 3.11 3.79 3.53 3.47 3.46 3.52 3.41 3.24 3.24 3.43 2.84 3.51 2.92 3.35 3.20 2.91 3.17 3.45 3.28 3.38 3.25 3.39 3.34 3.29 3.56 2.40 3.47 3.18 2.75 3.38 3.13 3.00 3.00 3.50 3.35 3.26 3.36 3.29 3.27 3.29 3.11 3.21 3.25 2.60 3.59 3.16 2.83 3.25 3.13 2.67 3.07 3.39 3.29 3.25 3.28 3.12 3.14 3.26 3.33 3.18 3.14 3.38 3.40 3.41 3.34 2.75 3.38 3.13 2.67 3.21 3.52 3.47 3.21 3.35 3.21 2.83 3.03 3.46 3.44 3.28 3.21 3.50 2.80 3.53 3.39 3.25 3.38 3.33 3.11 3.21 3.59 3.59 3.31 3.44 3.32 2.93 3.24 3.44 3.48 3.30 3.36 3.50 3.00 3.53 3.45 3.00 3.38 3.27 3.11 3.36 3.58 3.53 3.35 3.47 3.32 88 3.31 3.52 3.48 3.51 Student Teacher Competency Final Ratings Domain 4: Professional Responsibilities 4a: Reflecting on Teaching 4b: Maintaining Accurate Records 4c: Communicating with Families 4d: Contributing to the School and District 4e: Growing and Developing Professionally 4f: Showing Professionalism WI Teacher Standards #1: Teachers know the subjects they are teaching #2: Teachers know how children grow #3: Teachers understand that children learn differently #4: Teachers know how to teach #5: Teachers know how to manage a classroom #6: Teachers communicate well #7: Teachers are able to plan different kinds of lessons #8: Teachers know how to test for student progress #9: Teachers are able to evaluate themselves #10: Teachers are connected with other teachers and the community ArtEd 2004 2005 2006 N=29 N=29 N= ECE FCSE 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 N=89 N=225 N=213 N=14 N=16 2006 N=5 MBE 2004 2005 2006 N=17 N=39 N=12 SPED TECED SOE UNIT 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 2006 2004 2005 2006 N=8 N=15 N=9 N=14 N=92 N=51 N=172 N=431 N=294 2.82 3.10 3.57 3.61 3.48 3.14 3.47 2.77 3.53 3.37 2.82 3.35 3.16 3.06 3.43 3.52 3.44 3.38 3.50 3.42 3.00 3.17 3.55 3.60 3.50 3.14 3.44 3.00 3.71 3.45 2.92 3.25 3.21 3.11 3.50 3.57 3.48 3.43 3.52 3.45 2.89 3.00 3.48 3.53 3.45 3.57 3.75 3.20 3.71 3.54 3.17 3.50 3.33 3.11 3.29 3.68 3.55 3.41 3.53 3.44 2.50 2.95 3.39 3.41 3.28 3.00 3.06 2.00 3.07 3.03 2.22 3.38 2.93 3.11 3.38 3.34 3.26 3.23 3.29 3.22 2.69 3.21 3.82 3.73 3.61 3.00 3.25 2.60 3.71 3.45 2.75 3.38 3.27 3.00 3.46 3.52 3.48 3.50 3.57 3.52 2.86 3.10 3.55 3.60 3.45 3.00 3.63 2.80 3.35 3.34 2.82 3.25 3.07 3.00 3.57 3.48 3.35 3.36 3.50 3.38 3.00 3.72 3.79 3.63 3.31 3.79 3.00 3.00 2.86 3.00 3.56 3.67 3.77 3.57 2.87 3.11 3.32 3.36 3.24 3.23 3.47 2.94 3.46 3.33 2.84 3.41 3.21 2.86 3.26 3.51 3.42 3.25 3.37 3.24 3.04 3.10 3.25 3.34 3.24 3.21 3.44 3.00 3.59 3.36 2.92 3.38 3.13 2.78 3.29 3.52 3.49 3.26 3.36 3.25 2.79 3.03 3.39 3.38 3.24 3.14 3.44 3.00 3.41 3.18 2.75 3.38 3.27 2.89 3.14 3.41 3.35 3.25 3.34 3.23 2.68 3.03 3.22 3.27 3.16 3.43 3.50 3.00 3.35 3.23 2.73 3.38 3.27 2.78 3.29 3.43 3.31 3.18 3.29 3.16 2.86 3.17 3.20 3.22 3.14 3.21 3.56 2.80 3.47 3.28 2.83 3.38 3.13 2.67 3.14 3.50 3.33 3.18 3.29 3.15 3.04 3.21 3.39 3.47 3.32 3.14 3.50 2.80 3.35 3.36 2.75 3.38 3.20 3.00 3.36 3.51 3.41 3.31 3.44 3.29 3.04 3.10 3.26 3.32 3.25 3.29 3.50 2.60 3.41 3.46 2.92 3.50 3.13 2.67 3.00 3.51 3.45 3.24 3.35 3.24 2.89 3.07 3.42 3.41 3.29 3.29 3.31 3.40 3.65 3.38 2.83 3.38 3.20 2.67 3.14 3.47 3.35 3.32 3.38 3.27 2.71 2.93 3.15 3.21 3.10 3.36 3.56 2.80 3.59 3.26 3.00 3.50 3.20 2.78 3.50 3.53 3.35 3.19 3.28 3.13 2.89 3.28 3.49 3.52 3.33 3.21 3.31 3.40 3.47 3.33 2.83 3.38 3.27 3.00 3.21 3.53 3.52 3.34 3.46 3.34 2.81 3.21 3.40 3.48 3.35 3.07 3.56 2.60 3.29 3.44 2.83 3.50 3.27 3.33 3.50 3.64 3.65 3.28 3.48 3.37 89 3.00