I. Endocrine glands – general A. Endocrine vs. exocrine glands
advertisement

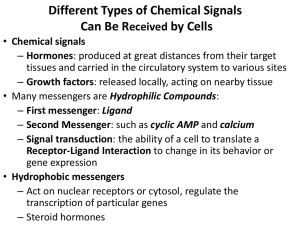
I. Endocrine glands – general A. Endocrine vs. exocrine - exocrine – sweat, oil, mucus, digestive glands - endocrine – “ductless” - secretions are hormones that travel directly into the blood stream – body regulators B. Nervous and endocrine systems – work together to coordinate functioning of all systems - nervous system releases chemical messengers called neurotransmitters which cause nerve impulse – milliseconds - endocrine system – releases chemical messengers called hormones which alter physiological activity of all tissues – several hours (pg 307) C. Hormonal effects 1. regulate chemical composition and volume of extracellular fluid 2. regulate metabolism and energy balance 3. regulate contraction of smooth and cardiac muscle – secretion of exocrine glands 4.maintain homeostasis despite infection, trauma, stress, dehydration, starvation, hemorrhage, and temperature change 5. regulates immune system 6.regulates smooth and sequencial growth 7. contribute to reproduction, gamete formation, fertilization, nourishment (fetal & newborn) D.Chemistry of hormones 1. steroids – derived form cholesterol and are lipid soluable 2. biogenic amines – simplest molecule – produced from amino acids and are H20 soluble 3. proteins and peptide – chains of amino acids (3 – 200) – H20 soluable 4.eicosanoids – derived from fatty acids II. Hormonal Action – determined by body requirements at any time A. Overview – hormone producing cells are sent information from sensing and signaling that regulates amount and duration of hormone release - hormones only affect target cells - cells have receptors (protein) that are specific B. Receptors – selective response - only target cells are influenced by hormones - different kinds of cells may have same receptors but will respond differently EX. Ca+2 is too low the parathyroid will trigger the bones to release Ca, the GI tract will absorb Ca, and the kidneys will reabsorb Ca from the urine C. Messengers - 1st messengers - H2o soluble hormones that bring messages to the cell – cannot penetrate the phospholipid layer of the plasma membrane - 2nd messengers - take messages into the cell - cyclic AMP(from ATP) – activates enzymes called protein kinases D.Feedback control – regulation is necessary to prevent the over production or the under production of hormones - negative feedback control 1. blood chemical levels -Ca - insulin and glucagon 2. nerve impulses – hormone is released by a direct impulse to an endocrine gland 3. hypothalamus secretions – chemical secretions by the hypothalamus controls the negative feedback system – a. releasing hormones – cause a release b. inhibiting hormones – prevent release