3.4 Linear Programming DAY 1 34 day 1 web.notebook October 13, 2008
advertisement
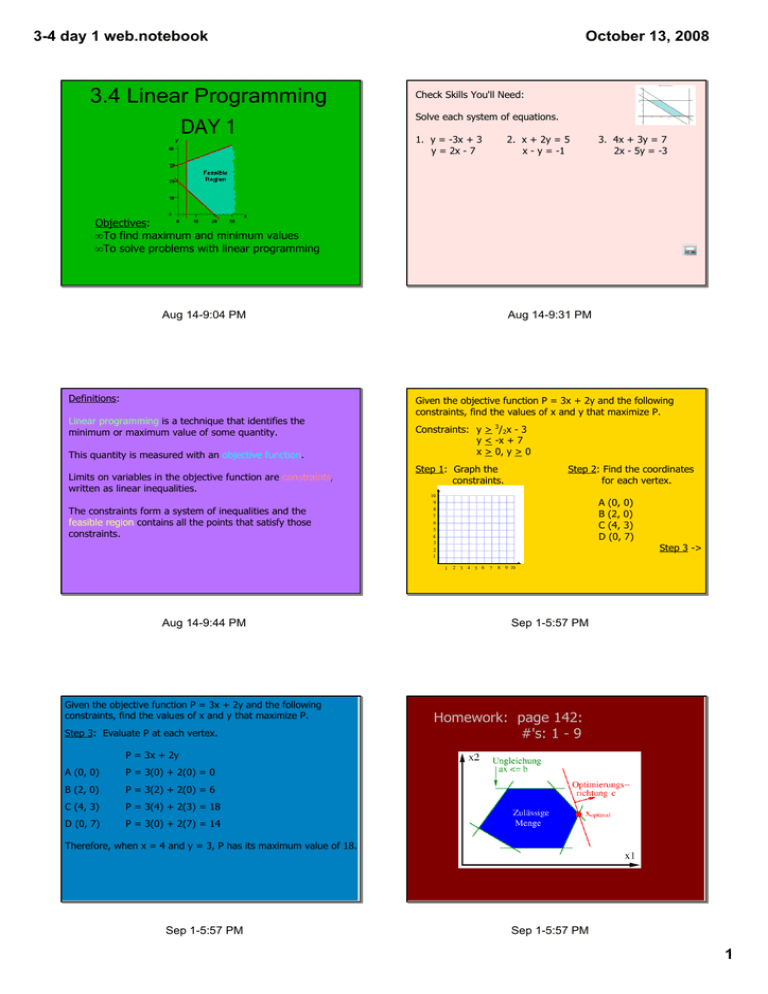
3­4 day 1 web.notebook 3.4 Linear Programming DAY 1 October 13, 2008 Check Skills You'll Need: Solve each system of equations. 1. y = ­3x + 3 y = 2x ­ 7 2. x + 2y = 5 x ­ y = ­1 3. 4x + 3y = 7 2x ­ 5y = ­3 Objectives: • To find maximum and minimum values • To solve problems with linear programming Aug 14­9:04 PM Definitions: Linear programming is a technique that identifies the minimum or maximum value of some quantity. This quantity is measured with an objective function. Limits on variables in the objective function are constraints, written as linear inequalities. The constraints form a system of inequalities and the feasible region contains all the points that satisfy those constraints. Aug 14­9:31 PM Given the objective function P = 3x + 2y and the following constraints, find the values of x and y that maximize P. Constraints: y > 3/2x ­ 3 y < ­x + 7 x > 0, y > 0 Step 1: Graph the constraints. Step 2: Find the coordinates for each vertex. 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 A (0, 0) B (2, 0) C (4, 3) D (0, 7) Step 3 ­> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Aug 14­9:44 PM Given the objective function P = 3x + 2y and the following constraints, find the values of x and y that maximize P. Step 3: Evaluate P at each vertex. Sep 1­5:57 PM Homework: page 142: #'s: 1 ­ 9 P = 3x + 2y A (0, 0) P = 3(0) + 2(0) = 0 B (2, 0) P = 3(2) + 2(0) = 6 C (4, 3) P = 3(4) + 2(3) = 18 D (0, 7) P = 3(0) + 2(7) = 14 Therefore, when x = 4 and y = 3, P has its maximum value of 18. Sep 1­5:57 PM Sep 1­5:57 PM 1