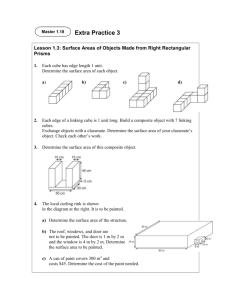
Content:
advertisement

Content: 1. V74:B. SC IN HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM STUDIES 2. V76 :B. SC IN HOSPITALITY STUDIES AND CATERING SERVICES 3. V97: Bachelor of Science (Media Graphics & Animation) 4. V30: Bachelor of Science (Interior Design) 5. V31: Bachelor of Science (Fashion Design) 6. V77:M.SC IN HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM STUDIES 7. V78 :M.SC IN FOOD SCIENCE 8. V32: Master of Science (Fashion Design) 9. P94: Master of Arts (Fashion Administration) 10. V34: Master of Science (Environment Science) Name Of Programmes: B.Sc. in Hospitality & Tourism Studies (B.Sc HTS) V-74 First Year Course 1: BTH 101: Business Communication Skill (TH) Unit 1: Essentials of Grammar: Noun and Pronoun: Adjectives : Verbs and Adverbs: Prepositions and Conjunctions: ArticlesUnit 2: Vocabulary Extension: Vocabulary: Synonyms and Antonyms : Idioms, Phrases and Correct: Sentences Unit 3: Paragraph Writing and Comprehension: Sentences Unit 4: Mechanics of Writing: Mechanics of Writing Unit 5: Business Correspondence: Formal and Informal Conversation Course 2: BTH 102: Introduction to Hospitality Management (TH) Unit 1: Growth and Development of Hospitality: The Hospitality Industry: Growth and Development: Tourism and the Indian Economy Unit 2: Developments of Hotel and Tourism Business: Tourism: Organization, Promotion, and Management Unit 3:The Departments of Hotel Organization and Operation: The Departments of Hotel Organization and Operation Unit 4: Recreation and Leisure: Recreation and Leisure: Meeting Industry Unit 5: Meeting, Conventions and Expositions Course 3: BTH 103: Computer Application (Th) Unit 1:Computer Fundamental: Fundamentals of Computers : Input/Output Units and Computer Memory: Data Representation Operating System Unit 2: Microsoft Windows: Microsoft Windows Unit 3: Computer Application in Business: Computer Application in Business Unit 4: Communication and Networking: Networking Concepts Course 4: BTH 104: Basic Of Accounting (TH) Unit 1: Accountancy Meaning and scope, journal and Edger, Subsidiary Books : Accounting Theory and Practices: Journalizing Transactions Unit 2: Trial Balance: Ledger Posting and Trial Balance: Subdivision of Journal Unit 3: Bank Reconciliation Statement, Capital and Revenue Transaction : Bank Reconciliation Statement Unit 4: Accounting For Bad Debts and Depreciation Accounting : Rectification of Errors: Final Accounts of Solo Trading Organizations : Company Financial Statements: Depreciation Accounting : Capital and Revenue Unit 5: Final Accounts Course 5: BTH 105: Front Office Operation-1 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction to Front Office Department: Introduction to Front Office Department Unit 2: The Guest Room, Tariffs and Plans: The Guest Room, Tariffs and Plans Unit3: The Guest Cycle, Reservation and Registration System : The Guest Cycle, Reservation and Registration System Course 6: BTH106: Principles of Cookery (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Cookery: Introduction to Cookery Unit2: Kitchen Organization: Kitchen Organization Unit3: Stock, Basic Sauces and Soups: Stock, Basic Sauces and Soups Unit4: Production Management: Production Management Unit5: Menu Planning: Menu Planning Course 7: BTH107: Hotel Housekeeping (Th+Pr) Unit1: The Housekeeping Department: Introduction to the Housekeeping Department Unit2: Organization Structure and Qualities of Housekeeping Staff : Organization Structure and Qualities of Housekeeping Staff Unit3: Types of Rooms, Registers and Files Maintained: Types of Rooms, Registers and Files Maintained Unit4: Public Area Cleaning and Room Cleaning Procedures : Public Area Cleaning and Room Cleaning Procedures Unit5: Laundry Services and Other Housekeeping Practices and Glossary : Laundry Services and Other Housekeeping Practices and Glossary Course 8: BTH108: Food and Beverage Service-1 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Place of Catering in Hospitality Industry: Place of Catering in Hospitality Industry Unit2: Different Types of Services in Hotels: Types of Services in Hotels Unit3: Staff organization in Restaurants and Kitchens: Staff organization in Restaurants and Kitchens Unit4: Food and Beverage service Areas: Food and Beverage service Areas Unit5: Food and Beverage service Areas: Food and Beverage service Area SECOND YEAR Course 1: BTH 201: Corporate Communication (TH) Unit1: Principal of Communication: Communication Skills: Principles of Communication Unit 2: Listening Skills: Listening Skills Unit3: Oral Skills: Oral Skills: Presentation Skill Unit4: Non-verbal Communication: Non-verbal Communication Unit5: Public Speaking, Interview Skills: Public Speaking: Overcoming Fear and Developing Confidence: Interviews: Meetings and Conference: Group Discussion: Voice Course 2: BTH 202: Food Production (TH+PR) Unit1: Introduction to Cookery: Introduction to Cookery: Food Production Management Unit2: Kitchen Organizations/Brigade: Kitchen Organizations Unit3: Grade Manager / Cold Kitchen: Grade Manager / Cold Kitchen Unit4: Bakery and Patisseries: Bakery and Patisseries Unit5: Quality Cooking Course 3: BTH 203: Food & Beverage Service – II (Th+Pr) Unit1: Menu knowledge and accompaniments: Menu Knowledge and Accompaniments Unit2: Types of Breakfast and afternoon tea: Types of Breakfast and afternoon tea Unit3: Non-alcoholic Beverages: Non-alcoholic Beverages Unit4: Introduction to Guerdons Service: Introduction to Guerdons Service Unit5: Supervisory Aspect of Food and Beverage Service: Supervisory Aspect of Food and Beverage Course 4: BTH 204: Eco-Tourism (Th) Unit1: Ecotourism: Concepts and Issues: Ecotourism: Concepts and Issues Unit2: Demystification of Ecotourism with Reference of India: Demystification of Ecotourism with Reference of India Unit3: Concept of Waste Management: Concept of Waste Management Unit4: Human Contribution of Ecotourism: Human Contribution of Ecotourism Unit5: Indian Ecotourism Scenario: Indian Ecotourism Scenario Course 5: BTH205: Hotel Accountancy (Th) Unit1: Company Accounts Unit2: Room Sales Accounting: Unit3: Miscellaneous Accounting: Unit4: Fund Flow and Cash Flow Statement: Unit5: Fund Flow and Cash Flow Statement: Course 7: BTH 207: Front Office Operation-2 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Front Office Responsibilities: Front Office Responsibilities Unit2: The Guest Cycle: The Guest Cycle Unit3: Handling and Identifying Complaints: Handling and Identifying Complaints Unit4: The Night Auditor: The Night Auditor Unit5: Planning and Evaluation Operations: Planning and Evaluation Operations THIRD YEAR Course1: BTH 310: French (Th) Unit1: Introduction to French: Introduction to French Unit2: Fundamentals of French: Fundamentals of French Unit3: General Vocabulary and Grammar: General Vocabulary and Grammar Unit4: Vocabulary Related to Front Office and Travel: French Hotel Vocabulary Unit5: French Recipes: French Recipes Course 2: BTH 320: Hotel Marketing (TH) Unit1: Overview Of Hotel Marketing: An Overview Of Hotel Marketing Unit2: Customer Behavior: Customer Behavior Unit3: Price and Promotion: Price and Promotion Unit4: Hotel Product Planning: Hotel Product Planning Unit5: Hotel Advertising: Hotel Advertising Course 3: BTH 321: Principle of Management Unit1: Nature and Functions of Management: Introduction to Principles of Management Unit2: Co-ordination, Planning and Decision Making: Planning and Decision-Making Unit3: Directing: Motivating People at Work: Staffing, Directing and Coordination : Motivation: Leadership Unit4: Nature and Importance of Organizing: Controlling: Organizing Course 4: BTH330: Cultural Heritage of India (Th) Unit1: Cultural and Heritage Tourism Unit2: Heritage Tourism In India And Tourism Aspects Unit3: Monuments and Museums Unit4: Living Culture And Performing Arts Unit5: Cultural Tourism In India – Its Promotion and Publicity Course 5: BTH 331: Principles & Practices of Tourism (Th) Unit1: Concepts of Tourism and Industrial Background: Concepts of Tourism and Industrial Unit2: Psychological Dimensions and Motivation of Travel: Psychological Dimensions and Motivation of Travel Unit3: Tourism: Types, Products and Attractions: Tourism: Types, Products and Attractions Unit4: Tourism and Transportation Unit5: Tourism: Planning Policies, Organization and Marketing Course 6: BTH 340: Banqueting Management (Th) Unit1: Sequence of Sales in Handling Inquiries and Process of selling : Banqueting: Sequence and Process of Selling Unit2: Samples of Various Styles of Banquet Rate Lists and Menus : Menu Planning for Banquets Unit3: Item Suggestion for Various Buffets and Flower Arrangement : Buffets and Flower Arrangements Unit4: Various Types of Function and Setup along with Service Styles : Banquet Procedures Unit5: Buffet Services: Buffet Services Course 7: BTH341: Bar Management (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Bar and Beverage Management Operations Unit2: Social Concerns and Management Unit3: The Bar, Bartender, and the Art of Mixing Cocktails Unit4: Service Procedures and Selling Techniques Unit5: Marketing Bar and Beverage Operations Course 8: BTH 342: Stores and Purchasing Management (TH) Unit1: Storage Control- Food: Storage Control- Food Unit2: Beverage Receiving, Storing and Issuing Control: Storage Control for Beverage Unit3: The Concept of Selection and Procurement: Concept of Selection and Procurement Unit4: The Organization and Administration of Purchasing: The Organization and Administration of Purchasing Unit5: Meat and Meat Products, Dairy Products and Beverages: Meat, Dairy and Beverages Course 9: BTH343: Food & Beverage Management (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Food and Beverage Management Unit2: Food and Beverage Management in Various Catering Establishments Unit3: Food and Beverage Control Unit4: Menu, Beverage List and Revenue Control Unit5: Labour Cost and Costing Name of Programmes: B.Sc. in Hospitality Studies and Catering Services (B.Sc HSCS) V-76 FIRST YEAR Course1: BCH 101: Basic Food Production (TH+PR) Unit1: Introduction to Cookery and Kitchen Staff: Introduction to Cookery and Kitchen Staff Unit2: Methods of Cooking Unit3: Egg, Fish and Meat Cookery: Egg, Fish and Meat Cookery: Shortening, Stock and Soup Unit4: Milk and Milk Product: Milk and Milk Products Course 2: BCH102: FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE I (TH+PR) Unit1: Food And Beverage Service Outlets. Unit2: Evaluation of the Hotel And Catering Industry and Organization Unit3: The Menu Unit4: Restaurant set up prior to service and types of services Unit5: Non alcoholic Beverages Course 3: BCH 103: Basic House keeping (TH+PR) Unit1: Housekeeping Department: Housekeeping Department Unit2: Organization Structure and Qualities of Housekeeping Staff : Organization Structure and Qualities of Housekeeping Staff Unit3: Types of Rooms, Registers and Files Maintained: Types of Rooms, Registers and Files Maintained Unit4: Public Area and Room Cleaning Procedure: Public Area and Room Cleaning Procedure Unit5: Laundry Services and Housekeeping Practices: Laundry Services and Housekeeping Practices Course 4: BCH104: Catering Science-1 (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Catering and Colloidal Chemistry Unit2: Food and Microorganisms Unit3: Hygiene in Food Production and Service Area Unit4: Food Preservation and Storage Unit5: Nutrition Course 5: BCH105: FRONT OFFICE OPERATION – I (TH+PR) Unit1: Introduction to the Front Office Department Unit2: Guest Room, Tariffs and Plans Unit3: Reservation and Registration System Unit4: Luggage Handling, Checkout and Settlement Unit5: Handling and Identifying Complaints Course 6: BCH106: Communication Skills (TH) Unit1: Communication Skills: Communication Skills Unit2: Non-Verbal Communication and Barriers of Communication: Verbal Communication: Non Verbal Communication and Barriers to Communication Unit3: Writing Skills and Letter Writing: Writing Skills and Letter Writing Unit4: Stress on Language Skills: Voice: Effective Reading: Stress on Language Skills: Body Language: Listening Skills Unit5: Comprehension Passage and Report Writing: Comprehension Passage and Report Writing Course 7: BCH107: Basic Accounts (TH) Unit1: Accounting Theory and Practices: Accounting Theory and Practices Unit2: Journal and Ledger: Journalizing Transactions: Ledger Posting and Trial Balance: Subdivision of Journal Unit3: Cash Book and Bank Reconciliation Statement: Bank Reconciliation Statement Unit4: Trial Balance, Petty Cash Book, and Rectification of Errors: Rectification of Errors Unit5: Final Accounts of Solo Trading Organizations: Final Accounts of Solo Trading Organizations: Company Financial Statements: Depreciation Accounting: Capital and Revenue Course 8: BCH108: Bakery and Confectionary (TH+PR) Unit1: Wheat and Flour: Wheat and Flour Unit2: Commercial Baking Technology: Commercial Baking Technology Unit3: Partially Prepared Bakery Products: Partially Prepared Bakery Products Unit4: Breakfast Cereals and Snack Foods: Breakfast Cereals and Snack Foods Unit5: Icing and Sugar: Icing and Sugar Course 9: BCH109: Principles of Management (TH) Unit1: Introduction: Introduction to Principles of Management Unit2: Planning: Planning and Decision- Making Unit3: Directing, Motivating and Leadership: Staffing and Directing: Motivation: Leadership Unit4: Controlling: Controlling Unit5: Organizing: Organizing: Communication in Organizations SECOND YEAR Course 1: BCH 201: Quantity Food Production (Th+Pr) Unit1: Kitchen Equipments: Kitchen Equipments Unit2: Menu Planning: Menu Planning Unit3: Species: Species Unit 4: Fish, Egg and Meat Cookery: Fish, Egg and Meat Cookery Unit5: Indian and Western Culinary Terms: Indian and Western Culinary Terms Course 2: BCH 202: Food and Beverage Operation-1 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Wines: Wines Unit2: Service of Wines: Service of Wines Unit3: Aperitifs: Aperitifs, Digestives and Liqueurs Unit4: Service Standards: Service Standards Unit5: Cocktails: Cocktails Course 3: BCH 203: Hotel House Keeping (Th+Pr) Unit1: Planning the Housekeeping Operation: The Housekeeping Department Unit2: Linen and Uniform Room: Organization, Structure and Qualities of Housekeeping staff Unit3: Laundry Services: Types of Rooms, Registers and Files Maintained Unit4: Housekeeping Control Desk and Public Area: Public Area and Room Cleaning Unit5: Other Housekeeping: Laundry Services and Other Housekeeping Practices Course 4: BCH 204: Hotel Engineering Services (Th) Unit1: Hotel Industry Maintenance Department: Hotel Industry Maintenance Department : Types of Maintenance and Fuels used in the Industry: Electricity Unit2: The Energy Management Program: Water Supply and Sanitation : Refrigeration and Air Conditioning: Fire Preservation Unit3: Water Supply and Maintenance Unit4: Energy Management: Energy Management Unit5: Facilities Planning and Strategies: Facilities Planning and Strategies Course 5: BCH 205: Front Office Operation-2 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Communications of the Front Office: Communications of the Front Office Unit2: The Guest Cycle: The Guest Cycle Unit3: Handling and Identifying Complaints: Handling and Identifying Complaints Unit4: The Night Auditor: The Night Auditor Unit5: Planning and Evaluation Operations: Planning and Evaluation Operations Course 6: BCH 206: Computer Application (Th) Unit1: Computer Fundamental: Introduction to Computers: Input/Output Devices and Other Components: Information and Data Processing: Operating System : Computer Application in Business: Computer Languages and Programming Concepts : Telecommunication and Networking: Microsoft Windows and Office 2007 : Introduction to MS Word 2007 and Its Component: Introduction to MS Excel and Its Components: Introduction to MS PowerPoint 2007 and Its Components: Internet and Its Working: Electronics Commerce Unit2: Operating System Unit3: Microsoft Windows Unit4: Computer Application Unit5: Communication and Networking Course 9: BCH 209: Hotel Accountancy (TH) Unit1: Company Accounts: Company Accounts Unit2: Room Sales Accounting: Room Sales Accounting Unit3: Miscellaneous Accounting: Fund Flow and Cash Flow Statement Unit4: Fund Flow and Cash Flow Statement: Fund Flow and Cash Flow Statement Unit5: Uniform System of Accounting: Uniform System of Accounting THIRD YEAR Course 1:BCH 301: Specialized Food Production (Th+Pr) Unit1: Kitchen: Kitchen Unit2: Production Equipments: Production Equipments Unit3: Modern Techniques in Preparation: Modern Techniques in Preparation Unit4: Tea, Coffee and Coccoa: Tea, Coffee, Coccoa and Chocolate Unit5: Indian and Western Culinary Terms: Indian and Western Culinary Terms Course 2: BCH 302: Accommodation Operations (Th+Pr) Unit1: Managing Housekeeping Department: Managing Housekeeping Department Unit2: Composition, Care and Cleaning of Different Surfaces: Contract Services Unit3: Supervision in Accommodation: Supervision in Accommodation: Other Housekeeping Practices: Fabrics and Furnishings Unit4: Eco-Friendly Housekeeping: Eco-Friendly Housekeeping Course 3: BCH 303: Marketing Services (Th) Unit1: Over View of Marketing & Marketing Management: Marketing Management An Overview Unit2: Customer Demand and Market Segmentation: Customer Demand and Market Segmentation Unit3: Product, Price & Distribution: Product, Price & Distribution Unit4: Promotion, Advertising, Public Relation & Publicity: Promotion, Advertising, Public Relation & Publicity Unit5: Sales Promotion and Merchandising: Sales Promotion and Merchandising Course 4: BCH 304: Food and Beverage Management (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction to Food and Beverage Management: Introduction to Food and Beverage Management Unit2: Food and Beverage Management in Various Catering Establishments : Food and Beverage Management in Various Catering Establishments Unit3: Food and Beverage Control: Food and Beverage Control Unit4: Menu and Beverage List and Revenue Control: Menu and Beverage List and Revenue Control Unit5: Labour Cost and Costing: Labour Cost and Costing Course5: BCH 305: Food and Beverage Inventory Control (Th) Unit1: Inventory and Cycle of Control Unit2: Purchasing: Purchasing Food and Beverage Commodities Unit3: Receiving: Receiving Food and Beverage Commodities: Storing and Issuing: Accounting Course 6: BCH 306: Human Resource Management Unit1: Concepts of Human Resource Development: Concepts of Human Resource Development: Human Resource Planning: Job Analysis and Role Description : Selection, Recruitment and Induction: Employee Counseling Unit2: Management Development and Leadership Motivation: Management Development: Human Relation: Motivating Human Resource: Promotion, Demotion, Transfer, Separation, Absenteeism and Turnover: Quality of Work Life: Concept of Occupational Health and Safety Name of Programmes: B.Sc. Media Graphics Animation (B.Sc MGA) T-97 First Year Course 1: BMG 101: Introduction to Computer & Internet (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Computers: Introduction to Computers Unit2: Computer Organization: Computer Organization Unit3: Software Application: Software Application Unit4: Input to Computers: Input to Computers Unit5: Data Processing: Data Processing Unit6: Output Devices: Output Devices Unit7: Data Storage: Data Storages Unit8: Internet Basks: Internet Basics Unit9: Internet Study: The Study of the Internet Unit10: Microsoft Word Xp 2003 Or 2002: Microsoft Word Xp 2003 Course 2: BMG 102: Drawing and Sketching (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Drawing: Introduction to Drawing Unit2: Drawing Shapes and Forms: Drawing Shapes and Forms Unit3: Drawing Realistic and Cartoon Characters: Drawing Realistic and Cartoon Characters Unit4: Drawing Realistic and cartoon Characters: Drawing Realistic and cartoon Characters Unit5: Drawing Animals: Drawing Animals Unit6: Cartoon and Comic Drawing: Cartoon and Comic Drawing Unit7: Perspective Drawing: Perspective Drawing Course 3: BMG 103: Color Theory (TH) Unit1: Color Theory: Overview: Colour Theory: Overview Unit2: Color Basics: Color Basics Unit3: Color Harmony: Color Harmony Unit4: Color Meanings: Color Meanings Unit5: Color Model: Color Model Unit6: Psychology of Color: Psychology of Color Course 4: BMG 104: Typography (TH) Unit1: Type Technology: History and Emergences: Paulomi M Jindal Unit2: Typography: Typography Unit3: Typographic Design Consideration: Typographic Design Consideration Unit4: In-Design Tutorial for Typographic Designs: In-Design Tutorial for Typographic Designs Unit5: Copy Preparation, Design and Layout: Copy Preparation, Design and Layout Unit6: File and Font Format: File and Font Formats Course 5: BMG 105: Computer Graphics Part-1 Adobe Photoshop (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction: Introduction to Photoshop Unit2: Photoshop Workplace: Photoshop Workplace Unit3: Creating Images: Creating Images Unit4: Creating and Using Selections: Creating and Using Selections Unit5: Photoshop’s Layer: Photoshop’s Layers Unit6: Editing Images: Editing Images Unit7: Editing Vector Shapes: Editing Vector Shapes Unit8: Creating Static Image: Creating Static Image Course 6: BMG 106: Computer Graphics Part-2 Adobe Illustrator (TH+PR) Unit1: Understanding Illustrator: Understanding Illustrator Unit2: Creating Documents: Creating Documents Unit3: Draw with the Pencil and Brush Tools: Draw with the Pencil and Brush Tools Unit4: Draw with the Pen Tool: Draw with the Pen Tool Unit5: Work with Shapes: Work with Shapes Unit6: Scale, Skew, and Rotate: Scale, Skew, and Rotate Unit7: Text Formatting: Text Formatting Unit8: Import Artwork: Import Artwork Unit9: Filters and Effects: Filters and Effects Course7: BMG 107:Technical and Creative Writing (Th) Unit1: Essential Grammar: Essential Grammar Unit2: Business Correspondence and Application Lectures: Business Correspondence and Application Lectures Unit3: Book Design: Book Design Unit4: Technical Writing: Technical Writing Unit1: Creative Writing: Creative Writing Unit6: Creative Writing: Creative Writing Course 8: BMG 108: Introduction to Multimedia and Its Applications (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Multimedia Systems: Introduction to Multimedia Systems Unit2: Multimedia System and Applications: Multimedia System and Applications Unit3: Computer Graphics: Computer Graphics Unit4: Computer Animation: Computer Animation Unit5: Interactive Media: Interactive Medias Unit6: Multimedia in Education: Multimedia in Education Unit7: Multimedia in Education: Multimedia in Education Unit8: Multimedia and Virtual Reality: Multimedia and Virtual Reality Unit9: Multimedia: Application and Future: Multimedia: Application and Future Course 9: BMG 109: Developing Presentation (Th) Unit1: Delivering Presentation: Delivering Presentation Unit2: Visual Presentation: Visual Presentation Unit3: Knowing Projectors: Knowing Projectors Unit4: Introduction: Introduction Unit5: PowerPoint Image Basics: PowerPoint Image Basics Unit6: Making PowerPoint Slides: Making PowerPoint Slides Unit7: Entering Text On A PowerPoint Slide: Entering Text On A PowerPoint Slide Unit8: Viewing Your PowerPoint Show: Viewing Your PowerPoint Show Course 10: BMG 110: Design Principles (TH) Unit1: The Principles of Universal Design: The Principles of Universal Design Unit2: Principles of Good GUI Design: Principles of Good GUI Design Unit3: Composition and Design: Composition and Design Unit4: Creative Thinking Techniques: Creative Thinking Techniques Unit5: Teaching Creativity: Teaching Creativity Unit6: Design Methods: Design Methods Course 11: BMG 111: Print Media Part-1: Corel Draw (Th+ Pr) Unit1: Object Overview: Object Overview Unit2: Tools: Tool Unit3: Pattern Fill: Pattern Fill Unit4: Fill Tool: Fill Tool Unit5: Text Tool: Text Tool Unt6: Vectors and Bitmaps: Vectors and Bitmap Unit7: Import/ Export Overview: Import/ Export Course 12: BMG 112: Print Media Part-2: Quark Express Unit1: Introduction: Introduction to Quark Express Unit2: Setting Up Quark Express References: Part One: Setting Up Quark Express References: Part One Unit3: Setting Up Quark Express References: Setting Up Quark Express References Unit4: Images with Embedded Clipping Paths in Quark Express: Images with Embedded Clipping Paths Unit5: Working with Master Pages in Quark Express: Creating Page Elements Unit6: Recovering from and Preservating Data Loss In Quark: Recovering from and Preservating Data Appending H & JS in Quark Express Unit7: Appending H & JS in Quark Express: Appending Hyphenation and Justification Unit8: Creating Stroked Text in Quark Express: Stroked Texts Unit9: Working with EPS Files in Quark Express and Photoshop Part One: Working with EPS Files: Web Layout SECOND YEAR Course1: BMG 201: Introduction to Web Development (TH) Unit1: Web Development Process Unit2: Site Design Unit3: Images Unit4: Issues In Web Designing Unit5: The Basics of Navigation Unit6: Web Type Unit7: Client Server Architecture Unit8: Introduction to E-Commerce Unit9: Web Services Unit10: Web Advertising Course2: BMG 202: HTML (TH) Unit1: Introduction to HTML Unit2: Overview Unit3: Content and Character Formatting and Lists Unit4: Images Unit5: Links Unit6: Table Unit7: Frames Unit8: Forms Unit9: Java Unit10: ActiveX Support Unit11: Animated Pages Unit12: Page Layout Unit13: Cascading Style Sheet Course3: BMG 203: Computer Animation: Introduction to Flash (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Flash Unit2: Creating Graphics in Flash Unit3: Using Text Effectively in Flash Unit4: Flash Animation Unit5: Understanding Movie Clips Unit6: Adding Sound and Video Unit7: Publishing Your Movies Unit8: Navigating a Movie in Flash Course4: BMG 204: Content Digitization (TH) Unit1: The Digitization Process Unit2: Capturing Video in Movie Maker 2 Unit3: Digitizing Sound Unit4: Digital Video Capturing Unit5: Digitizing File Formats Unit6: Digitization – Scanning, OCR and Re-keying Unit7: Microform Unit8: Recommendation for Microfilm Digitization Unit9: GIS and Scanning Technology Unit10: Digitization Project Management Course5: BMG 205: Content Authoring on Web using Macromedia Dream weaver (TH+PR) Unit1: The Dream weaver Workspace Unit2: Creation of Web Pages Unit3: Using Text Unit4: Hyperlinks Unit5: Using Graphics Unit6: Working with HTML Tables Unit7: Using Frames Unit8: Interactive Forms Unit9: Behaviors Unit10: HTML and Dream weaver Course6: BMG 206: Developing Dynamic Web Pages using Java and VB scripts (TH) Unit1: JavaScript Syntax Unit2: JavaScript and HTML Unit3: Control Flow Unit4: Java Script Methods Unit5: Forms Unit6: Introduction to VB Script Unit7: Variant Data Type, Subtypes, and Literals Unit8: Arithmetic Operations Unit9: Variable Declaration and Assignment Statement Unit10: Array Data Type and Related Statements Unit11: Conditional and Loop Statements Unit12: Function and Sub Procedures Course7- (BMG 207) -Video-Production Basics (TH) Unit1: Handling Video Camera Unit2: Video Camera Functions Unit3: Video Camera Tripods Unit4: CCU (Camera Control Unit) Operations Unit5: Video Chrome—Green Screen Unit6: Shooting Events Unit7: Streaming Video Unit 8: Introduction to Video Editing Unit9: Embedding Streaming Video in a Web Page Unit10: Introduction to Video Formats Course8: BMG 208: Story Boarding (TH) Unit1: Introduction to Storyboard Unit2: Creating and Using Storyboards for CBT Unit3: Storyboarding for Multimedia Unit4: Interactive Storyboarding Unit5: Storyboarding Design Process Unit6: Storyboard for Website Design Unit7: Storyboard Presentation Course9: BMG 209: Visual Communication (TH) Unit1: Basic Visual Elements Unit2: Oral and Visual Culture: A Dominant Form of Communication Unit3: Classical Philosophical Theories of Perception Unit4: Photographic Composition Unit5: Types of Photography Course10: BMG 210: Audio-Editing: Sound Forge (TH+PR) Unit1: Digital Audio Unit2: Digital Audio Formats Unit3: Creating MP3 Files Unit4: Editing Sound Files Unit5: Sound Editing with Audacity Unit6: Audacity Menu Unit7: Toolbar and Tracks Unit8: Working on Sound Forge Course11: BMG 211: Video-Editing: Adobe Primer (TH+PR) Unit1: Digital Audio Unit2: Digital Audio Formats Unit3: Creating MP3 Files Unit4: Editing Sound Files Unit5: Sound Editing with Audacity Unit6: Audacity Menu Unit7: Toolbar and Tracks Unit7: Working on Sound Forge Course12: BMG 212: Advanced Video Effects (TH) Unit1: Final Cut Pro Interface Unit2: Organizing Media Unit3: Timeline Unit4: Capturing Audio and Video Unit5: Three-Point Editing* Unit6: Working with Audio* Unit7: Transitions* Unit8: Creating Titles* Unit9: Exporting to Media* THIRD YEAR Course1: BMG 301: Animation Principles (TH) Unit1: What is an Animator’s Job? : An Animator’s Job Unit2: The tasks of animation: Tasks of Animation Unit3: What equipments will be necessary? : Equipments Necessary in Animation Unit4: How do leading animation programs like Maya and 3ds Max work? : Maya and 3ds Max Course 2: BMG 302: Introduction to Maya (Th+Pr) Unit1: User interface: User interface Unit2: Polygonal Modeling Unit3: Organic Modeling Unit4: Basic NURB Modeling Unit5: Advanced NURB Modeling Unit6: Preparing Models for Animation Unit7: Deformers Unit8: Joints and Skeletons Course3: BMG 303: Character Set up and Animation in Maya (TH) Unit1: Skinning and Advanced Deformers: Skinning and Advanced Deformers Unit2: Connecting Attributes: Connecting Attributes Unit3: Character Controls: Character Controls Unit4: Animation Basics: Animation Basics Unit5: Character Animation: Mechanics of Walking Unit6: Animation Tools: Animation Tools Course 4: BMG 304: Advanced Maya (Th+Pr) Unit1: Texture Basics: Texture Basics Unit2: Texturing in Practice: Texturing in Practice Unit3: Lights and Camera: Lights and Camera Unit4: Lights and Camera: Lights and Camera Unit5: Particles and Fields: Particles and Fields Unit6: Maya Hair: Maya Hair Unit7: Maya Hair: Maya Hair Unit8: Rendering for postproduction: Rendering for postproduction Unit9: Composting for postproduction: Composting for postproduction Course5: BMG 305: Introduction to 3Ds Max (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction: 3Ds Max: An Unit2: The 3Ds Max Production Pipeline: The 3Ds Max Production Pipeline Unit3: Starting Simple, Creating Shapes and Primitives: Starting Simple, Creating Shapes and Primitives Unit4: Managing and Manipulating 3D Space: Managing and Manipulating 3D Space Unit5: Building with Sub-Objects: Building with Sub-Objects Unit6: Building the Water Tower: Building the Water Tower Unit7: Building the Elastics-Powered Atmospheric Transporter Unit8: Complex Modeling: Creating a Skull: Complex Modeling: Creating a Skull Course6: BMG 306: Advanced 3DS Max (Th+Pr) Unit1: Building a Character: Building a Dolphin Character Unit2: Basic Hierarchies and Parametric Animation: Basic Hierarchies and Parametric Animation Unit3: Rigging and Animating: Rigging and Animating Unit4: Material Basics: Basics of Materials Unit5: Materials Unwrapped: Materials Unwrapped Unit6: Lighting and Atmospherics: Lighting and Atmospherics Unit7: Rendering-Getting to Pixels: Rendering Unit8: Particle Flow for Modeling and Effects: Particle Flow for Modeling and Effects Course7: BMG 307: Character Animations (Th) Unit1: Basics: Basic Unit2: Character Modeling Unit3: Preparation for Modeling Unit4: Animation of Biped (Two-Legged) Character Unit5: Animation of Quadruped (Four-legged) Character Unit6: Animation of Expressions Unit7: Preparing Biped with Character Studio Unit8: Animating Using Character Studio Course 8: (BMG 308) CG Film making (Th) Unit1: Story Ideas: Story Ideas Unit2: Production: 3DS Max and the Animation Pipeline: Production: The Animation Pipeline Unit3: Scriptwriting: Story and Character through Dialogue: Scriptwriting: Story and Character through Dialogue Unit4: Art Direction: Designing the Animation: Art Direction: Designing the Animation Unit5: Storyboarding: Cinematic Planning: Storyboarding: Cinematic Planning’ Unit6: Sound: Your Film’s Sonic Identity: Sound: Your Film’s Sonic Identity Unit7: Layout: Preparing the Scene: Layout: Preparing the Scene Unit8: Facial Animation: Key-framing Expressions: Facial Animation: Key-framing Expressions Unit9: Bringing the Background to Life: Bringing the Background to Life Unit10: Lighting and Rendering: Crafting an: Lighting and Rendering: Crafting an Unit11: Composting and Video Editing: finishing Touches: Composting and Video Editing: finishing Touches V30: B.Sc(Interior Design) Program Structure - First year Sr No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Course Name Theory of Materials Services - I Interior Construction - I Graphic Design Basic Design Interior Design - I BID101. Course Credit Examination Code Points Theory 4 100 Marks 4 100 Marks 8 -8 -4 100 Marks 8 -- THEORY OF MATERIALS Detailed Contents Chapter No1. CLAY Bricks a) Types, Qualities & Properties b) Manufacturing (not for examination) c) Application Teracota a) Types, Qualities & Properties b) Manufacturing (not for examination) c) Application Ceramic a) Types, Qualities & Properties b) Manufacturing (not for examination) c) Application Chapter No2. STONES a) Types, Qualities & Properties b) Processing c) Application Chapter No3.MORTAR LIME CEMENT a) Types, Qualities & Properties b) Processing c) Application (like Terrazzo, Mosaic, Cast Stone etc) Concrete Practical --100 Marks 100 Marks -100 Marks a) Types of concrete b) Types of coping/ shapes of coping c) Concrete Blocks d) RCC- Introduction & Concept for lintels & chajja Chapter No4.TIMBER Types of Timber Used for furniture or interiors Used for construction/ structure Properties & defects in timbers Introduction & purpose of seasoning Timber Product Plywood, Block-Board, Particle Board, MDF, Fire Boards v) Laminates - types & textures, thickness etc. Chapter No5.GLASS a) Qualities, Properties & Types b) Manufacturing c) Processing & Application Chapter No6.FIXTURES & FINISHES a) Paints b) Polishes c) Textured finishes d) Wall Papers e) Cladding materials f) Types of plastering & finishes g) Upholstery, fabrics, curtain, Venetian blinds, vertical blinds h) carpets, Vinyl flooring, rubber, plastic, nylon etc Chapter No7. Metals Ferrous & Non-ferrous metals like Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Mild Steel, Galvanized Iron, Stainless Steel etc. a) Quality, Properties & Types b) Surface treatments like anodizing, powder coating, specialized coating etc. c) Applications Chapter No8. Artificial Materials a) Acrylic plastic, polycarbonate, polyurethane b) Artificial woods, Eco-friendly and Recycled materials Chapter No9. Materials for Lighting a) Types for wires, conduits, distribution boards, mini circuit breakers, earth leaked circuits breakers specifications b) Light fittings c) Decorative fittings d) Special effect lightings like neon, fiber optics, flash etc. Chapter No10. Materials Specialty a) Water Proofing b) Fire Fighting & Fire Prevention c) Acoustical d) Thermal Insulation e) Light weight construction materials/ reuse of materials Chapter No11. Materials for Sanitation and Plumbing Different Plumbing Materials, Properties, Uses, Fittings Different Sanitation Materials & Fixture Applications REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr.No. Author D.N.Ghosh 1 Gurucharan Singh 2 S.C. Rangawala 3 4 K.P Roy Choudhary S.C. Rangawala 5 William Rupp 6 M.V. Naik 7 BID 102 Title Materials of constructions Building Materials Engineering Materials Engineering Materials Water Supply & Sanitary Engineering Construction Materials of Interior Design Building Construction materials Publication Tata McGraw Hill Standard Pub, & Dist Charottar Pub. Anand (India). Oxford Press, New Delhi Charottar Pub. Anand (India). Whitney Library Nirali Publication SERVICES - I Detailed Contents Chapter No 1. Lighting Terms like lumen, candle, wring systems & their suitability, types of lighting, types of light fittings & fixtures Chapter No 2. Telephone & Telecommunication and LAN system Different types of electronic (sound equipments) Chapter No 3. Environmental considerations like energy efficiency, solar energy etc Study pertaining to energy efficiency, solar energy etc. Chapter No4. Ventilation & Air Conditioning- Change in Temperature & Heating 1.1) Principles of Heating 1.2) Principles of Air-conditioning 1.3) System like window units, Split and central air conditioners 1.4) Principles of ducting & distributing REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. Author Title Publication F. Hall Plumbing technology 2 Shubhangi Bhide 3 H. L. Ohri 4 A. C. Panchdhari 5 Sandeep Mantri 6 7 B. Raja Rao Norbert Lechner Building services & equipments Water Supply and Sanitary Engineering Water Supply and sanitary installations Practical Bldg. Const. & its mgmt Electricity for Architects Heating, cooling, lighting Design British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data Rudra offset No. 1 Charotar Publishing House Bureau of Indian Standards, N Delhi Mantri proj. & consultancy Pvt. ltd Technical Book publisher Library of congress Cataloguing in Publication Data BID 103 INTERIOR CONSTRUCTION - I Detailed Contents Chapter No1: MASONARY Brick Masonry Different types of Bonds in various thickness/ corners Submission : Sketches and notes in journal Stone Masonry a) Various types of stone masonry b) Dry Rubble c) Random Rubble d) Ashlars fine e) Ashlars chamfered Submission : Sketches and notes in journal Structures - framed and load bearing structures a) Basic concept, differentiations and limitation for construction special care to be taken while demolition (without damaging existing structure) b) Introduction of foundation Submission: Sketches and notes in journal Chapter No2: Opening in Masonry work Lintels - various types a) Timbers b) Brick c) Stone d) Steel e) RCC (lintels with projections (chajja) Arches in bricks & stones - various shapes and section Practice oriented exercise Chapter No3: Joinery Details Timber Construction - with consideration of environment i) Various joints in Timber and their applications ii) Introduction to various fastners: nails, screws, nuts and bolts rivets etc. iii) Various methods of fasterning: wielding, brazing, gluing & pasting etc. Doors & Windows Chapter No3. Types of Doors a) Battened b) B V Ledged c) B L and Braced d) B L, B & Framed e) Paneled Door f) Flush Door g) Partly Glazed Door h) Sliding/ Folding Door Accordion type i) Bathroom Door Sliding/ folding type Submission: (a,b,c & d) - 1 plate each, e-1 plate, f-1 plate, h&I - 1 plate each REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. Author No. Title Publisher & Address 1 2 3 Joseph De Chaira Jullius Panero Martin Zelnik John Pile Ahmed Kasu Time Saver Standard for Interior Design & Space Planning Interior Design Interior Design Mcgraw Hill New York Harry N. Adry Publishers TWAIN Pub. Bombay 4 5 Jullius Panero Martin Zelnik Phillis Sleen Allen 6 Shirish Bapat 7 Shirish Bapat 8 9 Francis D K Ching V. S. Parmar Human Dimensions and Interior Spaces Beginning of Interior Environment Basic Design of Anthropometry Living Area (Interior Space) Interior Design Illustrated Design Fundamental in 1st Whitney Library New York New York Bela books Publishers Bela books Publishers Van Norstrund, New Delhi Somaiya Pub. Pvt. Ltd. architecture BID 104: GRAPHIC DESIGN Detailed Contents Chapter No1: a) Study of lines b) Study of surfaces c) Study of volumes with various gradations d) Lettering techniques Practice oriented exercise: 1 plate Chapter No2: Solid Geometry a) Cube b) Rectangle c) Cone d) Prism etc e) Pyramids f) Polygon g) Tetrahedrons Practice oriented exercise: 1 plate Chapter No3: Scale Drawing a) Use of scales & proportions b) measure drawing Practice oriented exercise: 1 plate Chapter No4: Study of Orthographic projections a) Plans b) Elevations c) Sections Chapter No5: Views Isometric view Axonometric view Chapter No6. a) Perspective View b) One Point (measuring point method) c) Two Point (measuring method) Practice oriented exercise: minimum 3 plated Chapter No7. Study of Sciography Chapter No8. Presentation Techniques a) Pencil Rendering b) Color Rendering c) Plain d) Pencil (B&W) e) Pen & Ink f) Color Pencil g) Water Color h) Photo/ Fuji color Chapter No9. Model Making a) Models of various Geometrical forms b) Study of Doors & Windows in mount board models with wall finishes REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. No. Author N.D. Bhatt 1 S. C. Rein Koff 2 4 Robert W. Gill Graphic Shaw 5 Shankar Mulik 6 7 F D K Ching Title Engineering drawing- Plane & Solid Geometry Interior Graphics and Design Standards The Thames and Hudson Manual of Rendering with pen and ink Interior Perspectives to Architectural Designs A Text Book of perspectives and graphics Perspective Drawing Publisher & Address Charottar Pub. Anand, Gujrat Whitney Library, New York Thames & Hudson ltd. London Graphic Shaw Allied Pub. Bombay BID 105 :BASIC DESIGN Detailed Contents Chapter No1: Introduction & Importance of Interior Design Chapter No2: Principles of Design a) Srructural Design, Decorative design with characteristics and examples b) Symmetry, Balance, Harmony, Scale & Proportions, Rhythm, Colour, Emphasis etc Chapter No3: Elements of Design a) Line, Form, Texture, Light, Space, Pattern, Colour Practice oriented exercise: 2 plates Chapter No4: Drawing Presentation a) Presentation of various Furniture items including plants in Plan & Elevation Practice oriented exercise: 1 plates Chapter No5: Ergonomics & Anthropometrics a) Introduction to Ergonomics b) Introduction to Anthropometrics Practice oriented exercise: 2 plates Chapter No6: History of Interior Design a) Classical Period b) Medieval Period c) 19th Century d) Modern Period e) Oriental Period f) Indian Interior Design REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. No. Author Joseph De Chaira Jullius Panero 1 Martin Zelnik 2 John Pile 3 Ahmed Kasu Jullius Panero 4 Martin Zelnik 5 Phillis Sleen Allen 6 Shirish Bapat 7 Shirish Bapat 8 9 Francis D K Ching V. S. Parmar 10 M. Prataprao 11 Sudhir Diwan Title Time Saver Standard for Interior Design & Space Planning Interior Design Interior Design Human Dimensions and Interior Spaces Beginning of Interior Environment Basic Design of Anthropometry Living Area (Interior Space) Interior Design Illustrated Design Fundamental in 1st architecture Interior Design Principles & Practices Sanskruti a manual of Interior Design Vol-1 Publisher & Address Mcgraw Hill New York Harry N. Adry Publishers TWAIN Pub. Bombay Whitney Library New York New York Bela books Publishers Bela books Publishers Van Norstrund, New Delhi Somaiya Pub. Pvt. Ltd. Standard Publisher & Distributor, New Delhi Interior Affairs, Mumbai BID 106 :INTERIOR DESIGN - I Detailed Contents Chapter No1. Basic Design for Living Units (with built-in-Environmental Consideration) a) Living Room b) Dining Room c) Living-cum-Dining room d) Kitchen-cum-Dining room e) Kitchen f) Master, Children’s, Guest Bedrooms g) Toilets Practice oriented Exercise: 9 plates REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. No. Author 1 Thames & Hudson 2 Aurora Cuito 3 Ruth Pretty 4 Stephen Crafti 5 J Grayson Trulove 6 Shenzen Nanhair Art Design Co. Title Living large in small spaces New small homes The Ultimate Interior designer Making the most of small spaces Studio Apartments Publisher & Address Thames & Hudson Design 02 Residential Space I Design 09 Residential Space III RS 03 Residential Space III Juzhu Kongjan Loft Publications. S.L. Ward Lock Images Pub. Group, Pvt. Ltd James Grayson Trulove Juzhu Kongjan Juzhu Kongjan Program Structure - Second year Sr No 1 2 3 4 5 6 BID 201 : Course Name Services - II Interior Construction-II Interior Design - II Professional Pct & Estimation CAD 2D & 3D 3D Studio & Photoshop Course Credit Examination Code Points Theory 100 Marks 4 -8 -8 100 Marks 4 -8 -8 Practical -100 Marks 100 Marks -100 Marks 100 Marks Services II Detailed Contents Chapter No1. Water Supply & Plumbing Anthropometrics data Client’s needs/ utilities Service Utilities Aesthetics Feasibility in construction Chapter No2. Landscaping - Elements of Landscaping, Principles of Landscaping Terrace gardening, types of plants, selection of plants Plant care Technical details like water proofing, sanitation, lighting etc Aesthetics Chapter No3. Sound Acoustics- Study of different systems of insulations & sound proofing, use and methods of applications Chapter No4. Fire Fighting- Types of fire, Fire fighting equipments and systems Chapter No5. Security System - Detection of alarm, close circuit TV Study pertaining to Anthropometrics data clients needs/ utilities Service Utilities Aesthetics Feasibility in construction REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. Author No. 1 Madan Mehta & James Johnson 2 Frank and John Walk 3 Norbert Lechner 4 Donald Hoff 5 Ernest Tricomi Title Publication Architectural Acoustics, Principles and Design Noise and vibration Library of congress Cataloguing in Publication Data British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data Library of congress Cataloguing in Publication Data Library of congress Cataloguing in Publication Data D. B. Taraporevala & sons Heating, cooling, Lighting Design Building services and equipments ABC of Air-conditioning BID201 :Interior Construction II Detailed Contents Chapter No1. Staircase Types & Materials Chapter No2. Floors Types & Materials Chapter No3. False Ceiling Types- suspended ceilings with concealed lighting arrays & ducting Various materials - metals, POP etc Chapter No4. Specialty partition & paneling a) Insulating material b) Thermal Material c) Acoustical d) Other Insulating Materials Submission: 2 plates Chapter No4. Study of Furniture along with costing a) Fixed & Moveable (Residential & Commercial) Chairs, Bed (single & double), sofa, space dividers, built in furniture, wardrobe, Dining table, wall units, curtain types, counters of bars, bank executive tables, Conferences etc. Submission: 10 Plates along with costing (abstract sheet) REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. Author No. Joseph De Chaira Jullius Panero 1 Martin Zelnik 2 John Pile 3 Ahmed Kasu Jullius Panero 4 Martin Zelnik 5 Phillis Sleen Allen 6 Shirish Bapat 7 Shirish Bapat 8 Francis D K Ching V. S. Parmar 9 Title Time Saver Standard for Interior Design & Space Planning Interior Design Interior Design Human Dimensions and Interior Spaces Beginning of Interior Environment Basic Design of Anthropometry Living Area (Interior Space) Interior Design Illustrated Design Fundamental in 1st architecture Publisher & Address Mcgraw Hill New York Harry N. Adry Publishers TWAIN Pub. Bombay Whitney Library New York New York Bela books Publishers Bela books Publishers Van Norstrund, New Delhi Somaiya Pub. Pvt. Ltd. BID 203 :Interior Design II Detailed Contents Chapter No1. Complete Design Project with Floor Plans, Sectional Elevation & Views 1.1) Design for Handicapped/ disabled person 1.2) One small residential space up to area 35 sqm 1.3) One large Residential space with Terrace Chapter No2. Project (I) small (Minor) like Shop, Office, Clinic, Cyber Café, Consulting room, office, Window display including study of energy saving techniques Drawing Requirements Measurement Sheet Plans - furniture layout flooring layout false ceiling layout Plumbing & Sanitation layout Sections, Sectional Elevation Perspective views Façade design, awning along with display window Rendering in any medium REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. No. Author Stafford Cliff 1 Vilma Barr Katherine 2 Field 3 Carles Broto Rolshoven 4 Martin Jeong JI 5 Seong ed. Nanuelli Sara 6 Jeong JI Seong 7 8 Carles Broto Title Publisher & Address The best exhibition Roto vision Sa Switzerland Stand Design 2 Stores: Retail Display PBC International Inc. and Design New shop Design Exhibition Design Arian Mostaedi Rockport Publishers Interior Design Bar and Restaurant Design for Shopping New Retail Interiors Interior design boutique, hotel & spa (Motel & hotel) New shop Design Jeong JI Seong Laurence King Publishing Ltd. Jeong JI Seong Arian Mostaedi BID 204: Professional Practice & Quantity Estimation Detailed Contents Chapter No1. Introduction 1.1) Professional Ethics 1.2) Code of Conduct & Responsibility 1.3) Responsibility towards clients 1.4) Responsibility towards Contractor 1.5) Professional Responsibility Chapter No2. Specification 2.1) Specification & Schedule writing 2.2) Mode of work & Units of Measurement 2.3) Color Chart & Material Chart Chapter No3. Tenders Tenders, types of tenders, tenders forms, terms & condition, NIT (Notice Inviting Tenders) Composition of Tender Document (Tender Notice BOM, General Condition Sheet, Contract Document Specification, Acceptance letter etc. Set of working drawings) Preparation of Tender Documents Process of Tendering (Floating, Receiving, Opening & Tabulation, Acceptance of Tender & further formalities) Criteria for contemporary tenders Pre tender qualifications & Pre Bid meetings Chapter No4.Office Management Working of an Interior Designs office Scale of fee Chapter No5.Career Opportunities How to enter the profession and types of avenues open Advantages and limitations of different options/ avenues Latest Trends in Professional Practice for eg Super-specialization, acquisition, mergers, tie-ups, collaborations, take over Chapter No6. Project Management Introduction to Project Management Principles of Management Establishment & Financial Implications Maintenance & Refurbishment Introduction to Site Management Project Resourcing Time Management Chapter No7. Study of Services along with Estimation & Costing 7.1) Plumbing 7.2) Wiring & Lighting 7.3) Futuristic Orientation Lifts Escalators Submission: 02 Plates minimum (along with costing) REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr.No. Author 1 Roshan Namavati 2 Roshan Namavati 3 C M Pitrowski Harry Siegel, CPA, Alan Sigel 4 5 6 7 William R. Hall William Rupp Title Professional Practice (Estimation & Valuation) Architectural Detailing in Residential Interiors Professional Practice in Interior Design A Guide to Business Principle and Practices for Interior Designers Contract Interior Finishes Construction Materials of Interior Design Publication Lakhani Book depot Lakhani Book depot Van Nostrand Reinhold Whitney library of design Whitney library Whitney Library BID 205: CAD 2D & 3D Detailed Contents Introduction to AUTOCAD - 2D Starting & Closing AutoCAD Screen Layout and Mouse operation Pull Down Menu, Tool Bars, Command Window Drawing file operation Creating Entities - Line - Arc - Circle Erase - Redraw Entity Selection Draw Toolbars Hatch Patterns Working with Text & Fonts Stiles Modify Tool Bar Editing with Grips Ply line and Editing of Plotline Entity Tools Using Arrays Zoom options Making Blocks and Insertion of objects Specifying Units and Limits Understanding Scale factors Using Grip and Snap Modes Standard and Properties Bar Creating Assigning, Controlling, working with Layers and Line Types Dimension Menu Enquiry Printing/ Plotting the Drawings Creation of sample drawing Introduction to AUTOCAD - 3D Concept of Evaluation/ Thickness Use of 3D view point, Tri pod and view option Top, Side, Front view Hide & Shade option Dynamic 3D viewing - Perspective View Use of 3D Face/ 3D plotline/ 3 dimensions Use of Ucs & U csicon Edge surface, Ruled surface, Revolution Surface & Tabular Surface Wire Frame and Solid Modeling Boolean Functions Rendering Concept of Slides and Scripts Model Making Use of Layers and Colors in 3D Adding Shadows and Materials Background Scenes & light effects Insertion Landscape & people Export and Import of 3D model to and from 3D Studio Sample Project BID 206: 3D Studio & Photoshop Detailed Contents Chapter 1: 3D Studio & Photoshop Getting Started Using 3D studio The Pull down Menus The Icon Panel The 2D Sharper Creating Shapes for Lofting in 3D lofter The 3D Lofter Importing 2D Shapes for lofting & exports lofted objects into 3D editor The 3D Editor Creating 3 D Models Importing AutoCAD Models/ 3 D lofted objects Understanding Vertex/ face/ Elements/ Objects Applying materials to objects Fixing of lights and use of colors Setting Cameras & understanding view ports Rendering the image Saving & Color prints of Rendered Image The Key Framer Understanding Selection sets The Material Editors Sample Projects Photoshop Basic Chapter 2: Walk Through 3 D Animation Introduction to Animation Animation- The Illusion movement Key Framer Commands Selection Geometry Hierarchy/ Links/ Unlinks Object Commands Light & Camera Commands Setting Animation Path Rendering Animation Display & Time Commands The Materials Editors Surface Color Mapping Shading Models Creating Materials Using Materials Editor Material Color Monitor Material Property Control Sample Project Submission: One Sample Project to be completed Program Structure - Third year Sr No 1 2 3 4 5 Course Name Interior Design - III Interior Construction - III Design Elective (Techno Seminar) Environmental Design Design Dissertation (Project Work) Course Credit ExaminatIon Code Points Theory -8 -8 -8 -8 -8 Practical 100 Marks 100 Marks 100 Marks 100 Marks 100 Marks BID301: Interior Design III Detailed Contents Chapter No 1. Major Projects Large Project6 (300 sqm to 500 sqm) like Banks, Restaurants, Corporate offices, Exhibitions, Bars, Pubs & Casinos, Hotels, Motels, Supermarkets, Hospital etc including Landscape & special considerations/ & provision for handicapped persons for circulation & facilities Practical/ Field/ Project work etc. All the works in Interior Design - II are related to project work with emphasis on practice and practical approach Drawing Requirements a) Measurement Sheet b) Plans Furniture layouts Flooring layouts False ceiling Air-conditioning ducting layout Electrical layout Layout indicating security system c) Landscape Layouts d) Sectional Elevations c) Perspective views d) Rendering in any medium (Pencil, Ink, Water color, Poster color etc) REFERENCE MATERIAL Sr. No. Author Thames & 1 Hudson 2 Aurora Cuito Ruth Pretty 3 Stephen Crafti 4 J Grayson 5 Trulove 6 Shenzen Nanhair Art Design Co. Title Living large in small spaces New small homes The Ultimate Interior designer Making the most of small spaces Studio Apartments Publisher & Address Thames & Hudson Design 02 Residential Space I Design 09 Residential Space III RS 03 Residential Space III Juzhu Kongjan Loft Publications. S.L. Ward Lock Images Pub. Group, Pvt. Ltd James Grayson Trulove Juzhu Kongjan Juzhu Kongjan BID302: Interior Construction III Detailed Contents Chapter No.1. Modular, knockdown and foldable furniture Kitchen furniture, platforms etc Furniture for handicapped person Sr. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Author F D K Ching William P. Spence L. Duane Griffith Mario Dal Fabro William P. Spence L. Duane Griffith D.A.C.A. Boyne D.A.C.A. Boyne D.A.C.A. Boyne Title Building Construction Illustrated Publisher & Address Van Nortrand How To Build Modern Furniture Prentice Hall Inc. New Jersey McGraw Hill Book Company, New York Cabinet making, design & construction Prentice Hall Inc. New Jersey Furniture & Cabinet Construction Architects’ Working Detail Vol. I The Arch. Press Ltd. London The Arch. Press Ltd. London Architects’ Working Detail Vol. III The Arch. Press Ltd. London Architects’ Working Detail Vol. IV 8 9 D.A.C.A. Boyne D.A.C.A. Boyne The Arch. Press Ltd. London Architects’ Working Detail Vol. V The Arch. Press Ltd. London Architects’ Working Detail Vol. VIII BID303: Design Ellective Detailed Contents Chapter 1: Introduction to Design Electives 1.1 Introduction to the Design Elective 1.2 Scope and Objective of the Design Elective 1.3 History of Design Elective Related Assignment: 1 Report Presentation Chapter 2: Design Elective Theory 2.1 Principles of the Design Electives 2.2 Elements of Design Elective 2.3 Materials and components of Design Elective 2.4 Systems and techniques of Design Electives Related Assignment: 1 Report Presentation Chapter 3: Elective Design & Management 3.1 Specialty of Design Elective 3.2 Management of the Design elective 3.3 Designing the Elective Furniture, Product or Theme Related Assignment: 1 Design Project Presentation NOTE A student is offered any one of the Elective Design Programme Elective Design Programmes offered are A) Furniture/ Product Design B) Set Designing C) Visual; Merchandising REFERENCE MATERIAL Books on Furniture Design Books on Visual Merchandising Books on Set Design BID 304: Environmental Design Detailed Contents Chapter No.1. Relative Study of Earth 1.1) Earth in the universe Earth & solar system, delineation & seasons, climatic zones (tropical, temperate, polar, desert, highland, etc.) & classification, influence of ocean currents, prevailing winds and solar radiation on the earth’s climate, region-wise distribution of fauna and flora 1.2) Geographical Factors Effecting climate & Indian Climatic Classification Latitude, Altitude, Aspect, Nearness to Sea Six climatic zones & their characteristics, study of Indian subcontinent & its historical origins 1.3) Global & Local environmental problems Global warming & climate change, ozone depletion, deforestation, degrading oceans, shelter, urban heat island effect, urbanization, availability of energy and natural resources, air, noise, land and water pollution 1.4) Study of Ecosystems & their components Forest, Oceans, Rivers, Ponds, Deserts, Natural cycles such as Hydrological, Carbon, etc. Interdependence of ecosystems CHAPTER NO.2.THERMAL COMFORT & PASSIVE DESIGN 2.1) Thermal Comfort Definition, Variables, Tools to measure such as bioclimatic chart, Meteorological instruments, Psychometric chart, standards for comfort – day-lighting & ventilation 2.2) Climate Analysis Solar path diagram, wind rose & wind square, Mahoney tables, solar radiation chart, plotting of bio-climatic chart, , analysis of design strategies, study of vernacular architecture 2.3) Bio-climatic design of architectural elements Design of fenestrations, heat gain calculations, azimuth & altitude, Design for day-lighting 2.4) Study of materials and passive design strategies Properties of materials, principles and definitions of natural heat transfer, passive design strategies such as solar chimney, wind towers, courtyards, etc, Case studies & application CHAPTER NO.3.ENERGY EFFICIENCY IN INTERIOR DESIGN 3.1) Energy Efficiency & Conservation Need for energy conservation, ways to conserve energy, basic concepts, carbon credits, Kyoto protocol, renewable sources of energy 3.2) Energy Efficient Lighting Systems Lighting design principles, equipment, LPD, CCT, Color Rendering Index, Definitions – lumen, Lux, candela, efficacy, etc., circuits, NBC, IESNA, LEED & Eco-housing guidelines 3.3) HVAC Reduction of heat load, efficient air conditioning, natural systems, CFC free refrigeration systems, ASHRAE/ ISHRAE guidelines CHAPTER NO.4.EFFICIENT & ECO-FRIENDLY BUILDING MATERIALS 4.1) Eco-friendly Interior materials Parameters such as local, renewable, recyclable, non-toxic, etc., Life Cycle Analysis, Cradle to Grave assessment, study of alternate and non-conventional materials, embodied energy of materials 4.2) Efficiency of existing interior materials LEED & Eco-housing guidelines, Case study of use of efficient materials, properties of materials, assessment with case based studies CHAPTER NO.5.DESIGN PROJECT Introduction to Design Brief Case Study, Analysis, Research, Empirical studies, Results & Recommendations, Presentation of Report IMPLEMENTATION STRATERGY Focus on applicative knowledge about the subject. Discussion by way of market surveys, site studies and critical analysis of existing designs trends & solutions. Stress on understanding and depicting the trend and research basis for the future environments. REFERENCE MATERIAL Books on Building Environment Indian Environment Directory Books on Environment Design Books on Environmental Interiors capes Books on Eco friendly Environment Books on Natural & Manmade comforts Books on Waste Management Books on Build ability & Sustainability Books on Energy Efficiency BID 305: Design Dissertation Detailed Contents Chapter 1: Preliminary Study 1.1 Introduction to the concept of Dissertation 1.2 Finalization of the Thesis Topic & Thesis Guide 1.3 Setting the Scope and Objective 1.4 Establishing the feasibility and viability Related Assignment: 1 Report Presentation Chapter 2: Report Presentation 2.1 Identification of the Case Study 2.2 Data Collection and Research 2.3 Conduction of Critical Analysis 2.4 Synthesis and Evaluation Related Assignment: 1 Report Presentation Chapter 3: Subjective Study 3.1 Formation of a rough draft 3.2 Finalization of subjective dissertation Related Assignment: 1 Presentation of Subjective Dissertation. IMPLEMENTATION STRATERGY Focus is on individualistic approach to problem and one-to-one discussion with competent guide resulting in a professionally satisfying presentation of the thesis that would put to test the individual strength and caliber of the student. NOTE Students are required to submit two hard copies of the subjective dissertation at the end of the term REFERENCE MATERIAL Individual sourcing for self study Individual case study Information could be collected through Internet as well as books, as per the guidance given by the concerned Guide School of Continuing Education B.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester I Subject Credits BFD 101: Elements of Design And Fashion Theory Total hours Marks 4 Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1) To develop understanding of elements of design (point, line, pattern, shape, texture, color form & space). 2) To develop understanding of principles of design (balance, rhythm, harmony, proportion, emphasis & variety). 3) To understand & analyze the effective use of elements / principle of design & fashion in the garment design process. CONTENT: Block Topic/Content Objective Method of No Analysis Teaching 1 Importance of Elements of Design and Fashion To develop a basic understanding about the elements of design & Fashion. Class room lecture and discussion 2 Line – To understand the application of line in the design. And the interpretation of mood created by the line -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations To understand the application of shape in the design and To develop the ability to evaluate the use of shape in the apparel -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations To understand the application of line in the design. And the interpretation of mood created by the texture -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations i) ii) iii) iv) v) 3 4 Directing Dividing Psychological effects of line Optical Illusion Analysis of use of line in fashion Shape – i) Geometric ii) Natural iii) Non-objective iv) Silhouettes v) Analysis of use of Shapes in fashion Texture – i) Visual ii) Tactile iii) Audible vi) Analysis of use of Textures in fashion 5 Value & Colour – i) Colour wheel ii) Colour schemes iii) Colour psychology 6 7 Principles of Design i) Rhythm, ii) Balance, iii) Emphasis iv) Harmony, Scale v) Proportion, Variety Elements of Fashion – i) Skirts ii) Dresses iii) Trousers iv) Tops v) Jackets vi) Coats vii) Necklines viii) Collars ix) Sleeves x) Cuffs xi) Pockets xii) Yoke To understand the application of shape in the design and To develop the ability to evaluate the use of shape in the apparel -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations To understand the application of principles of design and to develop an ability to evaluate them in the apparel -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations To understand the application of elements of fashion and to develop an ability to evaluate them in the apparel -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book Elements of Design – Space & Form 1 Elements of Design –Line 2 Basic Principles of Design (Vol. 1-4) Basic Design: The Dynamics of visual 3 form 4 Principles of Color 5 Clothing Technology Author Albert W. Porter Manfred Maier Sansmarg Birren & Fabersvan Hannelore Eberle, Hermann Hermeling Marianne Horaberger, Dieter Menzer Warner Ribng School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester I Subject Credits BFD 102: Fashion Model Drawing 4 Total hours Marks Practical Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1) To understand the importance of anatomical studies as the basis of fashion model drawing. 2) To realize the need for understanding, clarity & confidence in drawing of the Human body as a mode of visual communication in fashion. 3) To develop skill in fashion model drawing (drawing from a live model). CONTENT: Block Topic/Content Objective Method of No Analysis Teaching 1 Perspective To understand Presentation -Objective Developing your Demonstration -Figurative object or any drawing Practice and Human Anatomy in perspective view. Corrections. - Kids, Female and Male Studies of Human Body - Kids, Female and Male 2 Proportion of the Croquis: To understand Presentation Kids, Male, Female Proportion of all types Demonstration -Stick croquie croquis. Practice and -Flesh out croquie Corrections. (front, back, side and 3/4th view) 3 Draping of garments on kids, male ,female figure for Skirts Dresses Trousers Tops Jackets Coats REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Fashion Design Manua 2 Fashion Sketch Book 3 Fashion Deisgn Illustration 4 Fashion Illustration Today 5 9 Heads 6 Fashion Illustration Techniques To develop skill in garment and figure drawing. Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections Author Pamela Stekar Bina Abling John Turnpenny Nicholas Drake Nancy Riegelman Julian Seaman School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester I Subject BFD 103 :Pattern Making and Construction - I Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Practical) OBJECTIVES: 1) To understand basics of pattern making and construction. Block Topic/Content Objective No Analysis Introduction to industrial To understand basics of 1 sewing Machine sewing machine Hand Seams and Machine To acquire the skills of seams stitching and understanding 2 Selection of seams for different the use of it. fabrics To acquire the skills of Pockets stitching pocket, placket and 3 Plackets necklines Necklines Basic Block Adult and Children To acquire the skills of 4 drafting the kids and adult basic block Skirts and variation To acquire the skills of drafting and stitching the Straight basic basic skirt & its variations. A-line Dirndl skirt 5 Gypsy skirt Tiered skirt Balloon Skirt To acquire the skills of Sleeves and variation 6 drafting and stitching sleeve & its variations. Term Garments 7 REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Metric Pattern Cutting for children’s wear 2 Patternmaking for Fashion Designers 3 Flat Pattern Design 4 Complete Guide to Sewing 5 Complete Book of Sewing 6 Singer Sewing Book Internal External Method of Teaching Lecture, discussion and power point presentation Lecture & demonstration Lecture & demonstration Lecture & demonstration Lecture & demonstration Lecture & demonstration Lecture & demonstration Author Winifred Aldrich Lori A . Knowles Nora M. MacDonald Readers Digest DK Gladys Cunningham Total School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester I Subject BFD 104: Communication skills Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Theory) Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1. To equip the students with effective communication tools required in the fashion business. 2. To develop their skills for the effective communication. Block No 1 Topic/Content Analysis Introduction to communication i. Meaning & Definition of communication ii. Characteristics of communication Objectives Method of Teaching To equip the students with effective communication tools 2 Objectives of communication To impart the aims of communication 3 Written Business Communication Emails, Reports, Minutes of Meeting, Proposal, Notes, Letters, elements of resumes. To impart the students with processes of communication 4 Presentation skills related to Communication To impart knowledge about the methods of communication 5 Etiquettes and manners To understand the barriers of communication REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Business communication 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. Author Dr. Rodrigue School of Continuing Education B.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester II Subject BFD 105: Introduction to Textiles Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Theory) Internal OBJECTIVES: 1) To educate students about the various stages from fibre to fabric. 2) To familiarize the fabric properties to enable better design skills.. 3) To aid the fabric choice as per the design, budget and client. CONTENT: Block Topic/Content No Analysis 1 Introduction to Textile Industry 2 Classification of Fibers Characteristics of Fibers pertaining to performance - Fiber blends and its performance Objectives To learn about the basic segments of textile industry To understand characteristics of fibers for its right application for its products. External Method of Teaching -Class room lecture and discussion -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations. 3 Yarns – - Types of yarn - Yarns properties To learn about various types of yarns, their classification, their formation and uses -Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations -Industry visit 4 Fabric Construction -identification and application of woven fabrics and knitted fabrics - Application of non woven’s in Fashion Study of fabric performance pertaining to fabric finishes - Preparatory - Aesthetic - Functional To understand the major classification of fabric construction techniques - Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations -Industry visit To develop an understanding about the importance, types of finishes given to the textile products Class room lecture and discussion -Computer assisted presentations 5 REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. Title of the Book 1 Textile from fibre to fabric 2 Understanding Textiles 3 J.J. Pizzuto’s Fabric Science 4 Clothing Technology 5 Textiles Total Author Berard Cobman Phyllis Toratora Arthur Price Europa Lehrimittal Wayne,A,Macmillan,London School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester II Subject Credits Total hours Marks BFD 106: Surface Ornamentation 4 Techniques Theory Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1) To understand the different types of textile and surface ornamentation designs and techniques and to use them effectively and designing the garments. 2) To know the various methods of surface ornamentation & to select the appropriate method of ornamentation for a specific product or fabric. CONTENT: Block No 1 2 3 4 5 Topic/Content Analysis Objective Method of Teaching Families of Textile Design Floral Geometric Conversational/Traditional Ethnic Repeat and its types - Directional - Non-Directional - One way - Two way - All over - Half Drop Vertical - Half-Drop Horizontal. Print s techniques - Block Printing - Stencil Printing - Fabric Printing - Lithography - Screen Printing Machine Embroidery To understand the different types and techniques in textile Designing. Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections. To understand the different types repeats and use them to according to your concept. Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections. To understand deferent types of printing methods and try out virus styles. Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections. To understand different types of machine embroidery Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections. Presentation Demonstration Practice and Corrections. Hand Embroidery To understand different types of handembroidery REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Textile Design 2 Encyclopedia of embroidery stitches including crewel 3 Quilters work book Author Susan Meller & Joost Q. Elffers Marion Nicholas Pam Lonttot & Rosemary School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester II Subject BFD 107: Pattern Making and construction - II Credits 1 Topic/Content Analysis Design detailing through Dart manipulation and fullness techniques 2 Salwaar And Churidar 3 Ladies Shirt 4 Ladies Trouser 5 Kid’s wear Marks 4 (Practical) Block No Total hours Internal Objectives REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Metric Pattern Cutting for children’s wear 2 Patternmaking for Fashion Designers 3 Flat Pattern Design 4 Complete Guide to Sewing 5 Complete Book of Sewing 6 Singer Sewing Book External Method of Teaching Author Winifred Aldrich Lori A . Knowles Nora M. MacDonald Readers Digest DK Gladys Cunningham Total School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester II Subject BFD 108:Computer Application - I Credits H o ur s Marks 4 (Practical) OBJECTIVES: Internal External Total 1. To introduce the basic principles of computer hardware and software 2. To familiarize with core elements of Windows, Spread Sheets and basic applications in the areas of word, and presentation with computers. 3. To familiarize students with the scope and utility of the Internet Block No 1 2 3 Topic/Content Analysis Window - Using window Explorer - Managing files and folders - Using Paint Brush, WordPad & Notepad - Network Neighborhood Word Processor (Microsoft Word) - Introduction to Word Processor - Overview of Word Processor Packages - Use of word in different areas - Document concept – (Creating, Saving, Opening, Closing Document) - Formatting document (Bold, Italic, Underline, Justification, fonts, colors of fonts, format painter) - Copy, cut and paste - working with margins and page setup - Tables - Uses of drawing toolbar - Columns, header & footers - Printing procedure - Spell Check & Thesaurus - Adding a chart to the report - Mail Merge Spread Sheets(Microsoft Excel) - Introduction to spread sheet - Overview of spread sheet packages - About Excel (Role of Excel in day to day life) - Understanding Excel Sheet - Inserting, deleting and hiding columns / rows - Manipulating formulas and functions - working with charts - Printing a sheet Objectives To introduce them with principles of windows Method of Teaching Practical exercises, and interactive sessions. To familiarize with core elements Microsoft Word Lecture and practical work. To Understand the Spreadsheet Format in EXCEL, including graphs Lecture and practical work. - Sort & Filter Presentation Package (Microsoft powerpoint) - What is presentation? Explain its need - Overview of presentation packages - Use of powerpoint - Making Presentation - Different types of slide layouts - Slide view, slide sorter view and slide show buttons - Setup show - Applying design templates and backgrounds - Transitions & custom animation effects - Recording voice in presentation - Electronic presentations Internet - What is internet? And its advantages and disadvantages - Minimum hardware and software requirement for internet connection - Role of modem in internet - Websites & ISPN - Browsing and Surfing - Search Engines - Downloading Pictures and Text - E-mailing - Downloading pictures and Text - Creating Accounts - Attachments - Chatting 4 5 For professional presentations Lecture, practical exercises, and interactive sessions. For information search and collection . Lecture and practical work. REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Title of the Book “Mastering word 2000” “Mastering Excel 2000” “Mastering Powerpoint 2000” “Mastering Fox Pro 2000” “The internet in 24 hours” “Internet 101 A Beginner’s Guide to the internet and the world Wide Web” Author Ronthansfield, J.W.Oslen,BPB Publication Mindy C.Martin, Steven M.Hansen,Beth Klingher BPB Publication Katherine Murray BPB Publications Charles Siegal Ned Shell: SAMS Publishing Wendy G.Lehnert School of Continuing Education B.Sc in Fashion Design Semester III Subject Credits BFD 201: Fashion Studies Total hours Marks 4 (Theory) Internal External Total Objectives: Develop an understanding of the Elements and Principles of Design with reference to Apparel Develop an understanding of Aesthetic aspects Understand market influences on Fashion designers, Fashion centers and brands. Block No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Objectives Topic/Content Analysis Method of Teaching Fashion Terms Fashion Categories Fashion Evolution- Fashion Cycle Adoption of fashion Economic influence on fashion Technological influence on fashion Global influence on fashion International fashion centers Fashion Promotion REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 2 Title of the Book Dynamics of Fashion – Promotstyle / Here & There, Apparel View, Author Ellaine Stone View on color 3 Inside Fashion Business Jeanettle Jernow & Kitt Dickeson WWD School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester III Subject Credits BFD 202: Fashion Illustration Total hours Marks 4 Practical Internal External OBJECTIVES: 1) To acquire the skills to use different mediums: - pencil, water color, poster color, etc. 2) To understand the texture of fabric and render it. 3) To develop types of rendering. 4) To analyze variety of pictures and sketch and render them accordingly (body & garments). CONTENT: Block Topic/Content No Analysis 1 Rendering Techniques Croqui Styling using hand movements, leg movements and features Objective Method of Teaching To understand various types of medium and developed your own rendering style. Presentation Demonstration, Practice and Corrections. Analysis fabric texture and render them suitable medium. Presentation Demonstration, Practice and Corrections. Presentation Demonstration, Practice and Corrections. Presentation Demonstration, Practice and Corrections. 2 3 Photo Analysis Different garments of Kids, Male and Female Analysis figure salute, fabric, texture and feel and render them. 4 Development of Costumes on Croquis using elements of fashion Develop your own rendering style. Fabric Rendering - (30samples of different Varieties of fabric) REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Advance Fashion sketch book 2 Fashion Illustration 3 The Fashion guide 4 The Snap Fashion sketch book 5 Figure Drawing for Fashion I & II 6 Fashion Illustration Today 7 Fashion Illustration Now 8 Fashion Art for the Fashion Industry 9 Fashion Design in Vouge Author Bina Abling Colin Barnes / Steven Stipelman Haurent Hartung Bill Giazer Isao Yajima Nicholas Drake Laird Borrelli Rita Gersten William Packer School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Total Semester III Subject BFD 203:Computer Application II Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Practical) Internal External Total Objectives: To incorporate in design students the ability to represent and create visuals using image editing and object creation / manipulation capabilities of Adobe Photoshop, Corel draw And Page maker Block Topic/Content Method of Objectives No Analysis Teaching 1 Coreldraw To familiarize Demonstration and - About CorelDraw with the corel Practical - Using the menus, standard toolbar, property bar and draw and to diglog boxes used it - Drawing rectangle, ellipses, polygons, stars, spirals effectively in and graph paper making - Drawing lines of all shapes and size presentation - Creating and manipulating text - Selecting and transforming objects - Shaping objects - Filling and outlining objects - Viewing, zooming and ordering - Combining, breaking apart, grouping, ungrouping, separating and converting to curves - Weld, intersection and trim - Aligning, coping, pasting, and cloning - Lens, perspective and power clip - Fitting Text to a path - Page setup - Uses of Corel draw 2 Photoshop To familiarize Demonstration and - About Photoshop with the photo Practical - Using toolbox, palettes and Context menus shop and to - Creating, Operating and closing files used it - Changing canvas size, color modes and resolutions effectively in - Understanding and working with layers making - Selecting areas presentation - Picking and selecting colors - Paining and selecting colors - Creating text -Resizing and Reshaping image - Scanning - Filter effects - Manipulating focus with blur, sharpen, and smudge - Adjusting tone with dodge - Morphing images - Cloning and pattern creation with the rubber stamp - Creating special images effect REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. Title of the Book Author 1 Respective software manuals (Adobe Photoshop, Corel Trace) 2 Photoshop Retouching Techniques 2 “Teach Yourself Access for Windows 95, Version 7.0” 1999, BPB Publications, New Delhi School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester III Eismann, Katrin, Simmon – Steve Publisher Siegel, Charles Subject Credits BFD 204:Machinery and Equipment 4 Total hours Theory Marks Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1) To create an awareness of the types of garments machinery available in the industry 2) To develop an understanding about the selection of the right machinery for production of the required garment. CONTENT: Block No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Topic/Content Analysis Overview of the Garment mass production setup Marker making Spreading Cutting Ticketing Bundling Sewing Finishing Quality Checking Classification and application of cutting machines in garment industry Classification of Sewing Machines and their applications i. Horizontal bed Machines ii. Vertical bed machines Stitch type analysis, classification and their applications i. 100 Class ii. 200 Class iii. 300 Class iv. 400 Class v. 500 Class vi. 600 Class Feed Mechanisms i. Drop Feed ii. Differential Feed iii. Unison Feed iv. Compound Feed v. Roller Feed Classification of Finishing Equipments and their applications i. The purpose of pressing ii. Categories of pressing iii. Pressing Equipments and methods iv. Stain removal Objective To familiarize with the various process in garment mass production Method of Teaching Class room lecture and discussion - Industry visit To get knowledge on various types of cutting machines and their operation. To get knowledge on various types of sewing machines and their operation. To understand various types of stitches Class room lecture and discussion Computer Assisted Presentation Class room lecture and discussion To understand the importance and types of feed mechanism Class room lecture and discussion To get knowledge on various types of pressing equipments and their operation. Class room lecture and discussion Class room lecture and discussion Computer Assisted Presentation v. Packaging 7 Introduction to Sewing Machines attachments and their applications. To get knowledge about sewing machine attachment used in the garment industry Class room lecture and discussion REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. 1 2 Title of the Book Clothing Technology Technology of Clothing Manufacture Author Europa Lehrmittel Harold Carr and Barbara Latham School of Continuing Education B.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester IV Subject BFD 205:Fundamentals of fashion marketing and merchandising (Theory) Credits Total Hours Marks 4 Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: To familiarize with marketing mechanisms that affects and governs Apparel Trade To make students understand the basic concepts of merchandising and its importance in the Apparel industry. To make students understand the basic concepts of merchandising and its importance in the Apparel industry. Blk Topic/Content Method of Objectives No Analysis Teaching 1 - Marketing concept To conceptualize marketing 1. Lecture and discussion strategies and selling. 2. Guest Speaker. - Marketing and Selling 3. Case Studies 2 - 4 P's of marketing - Developing Marketing Strategy and Tactics 3 - Product strategy. - Pricing strategy 4 - Distribution Policy - Promotion policy 6 Merchandising in Apparel Industry Merchandising Process Responsibilities Merchandising Techniques 7 8 Merchandising terminology and concepts Sampling Pricing and product Costing Product Line Development Assortment planning Inventory Control Global Sourcing Import and Exports Fashion Promotion and images Fashion Calendar and event planning To familiarize the basic principles of marketing and various tactics and strategies involved. 1. Lecture. 2. Small Group Discussion. 3. Case Studies To conceptualize the strategies and tactics involved in product and pricing. 1. Lecture and discussion 2. Guest Speaker. 3. Case Studies To understand the tactics of getting the product to the customer and various promotion measures. To understand the concept of merchandising 1. Lecture. 2. Panel of Experts. 3. Case Studies. To understand the work of merchandiser To understand merchandising terminologies and concepts and buyer responsibilities. 1. Class-room teaching. 1.Classroom teaching. 2. Case Study and role-play. 1. Class-room teaching. 2. Case Study and role play. 9 Customer vendor Relation a) Responsibilities of the buyer To understand the buying concept 1. Class-room teaching. 2. Case Study and role-play 1. Class-room teaching. 2. Case Study and role-play. b) Working with Vendors To understand the vendoring concept 10 Organizing buying / selling activity To understand merchandise and buying and selling activities. 1. Class-room teaching. 2. Case Study and role-play. REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Title of the Book Author Principles of Marketing Philip Kotler Relevant business & trade journals, magazines, and Govt. Publications Fashion Buying & Merchandising Packard, S., Winters, A. & Axelrod, The Business of Fashion Burns, David L Fashion: From Concept To Consumer Frings, Gini S School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester IV Subject Credits BFD 206:Traditional Textiles & Embroideries of India 4 Theory Total hours Marks Term Work TP / Pr. Total Objectives: To acquire knowledge of different textiles produced in different states of India To acquaint the students with the different motifs, colour and weaving techniques used in textiles along with their significance. To acquire knowledge of various embroideries done in India with the historical background of each. To learn different types of stitches, motifs, colour and material used in the embroideries and their significance. To acquaint the student with the work of handloom board, khadi board and cottage industries in India. CONTENT: Block Topic/Content Method of Objectives Analysis No Teaching To acquire knowledge of various embroideries done in 1 Introduction Class-room teaching India with the historical background of each Textiles Of The Following States regarding the fiber used, weave, motifs, colors and their significance and descriptive terms used- Unit 1: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Saurashtra, Kutch, Rajasthan, To acquaint the students with Jammu & Kashmir, the different motifs, colour Punjab, Class-room teaching 2 and weaving techniques used Uttar Pradesh, and LCD presentation in textiles along with their Assam, significance Orissa, Manipur, West Bengal, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamilnadu Andhra Pradesh. 3 Class-room teaching Embroidery Of Different States. To learn different types of stitches, motifs, colour and and LCD presentation material used in the Unit 1: History of embroidery embroideries and their Unit 2: Embroidery of the following significance states, regarding history, colors, motifs, threads, materials and stitches used. Kasuti of Karnataka, Embroidery of Sindh, Kutch & Kathiawar, Kashida of Kashmir, Kantha of Bengal, Chikankari of Uttar Pradesh, Embroidery of Manipur, Chamba Rumal, Phulkari of Punjab, Gold and silver embroidery, Applique work of Bihar and Orissa. 4 Handloom Industry Of India 5 Khadi Board 6 Cottage Industry To acquaint the student with the work of handloom board, khadi board and cottage industries in India. To acquaint the student with the work of handloom board, khadi board and cottage industries in India. To acquaint the student with the work of handloom board, khadi board and cottage industries in India. Class-room teaching and LCD presentation Class-room teaching and LCD presentation Class-room teaching and LCD presentation REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Title of the Book Indian Embroidery Traditional textiles of India Kasuti of karnataka Karnataki Kashida Colourful textiles of Rajasthan Carpets and floor covering of India Ikat textiles of India 8 Sari of India 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 The sari style Masterpiece of Indian textile Needlelore Costumes and textiles of India Appliqué work of Orissa Indian Embroidery Textiles and Embroidery of India Handicrafts of india Author Irwin and Hall Shailji naik Indira joshi Ahilya kirloskar Kothari Gulab Chattopadhayya kamaladevi Chelna Desai Kapur Chishti and Amba sanyal Linda Lynton Rustom J Mehta Neelam Garewal Jamila brij Bhushan Mohanti Vijay Chandra Savitri Pandit Marg publication Chattopadhayya kamaladevi School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester IV Subject Credits BFD 207:Garment Construction Total hours 4 (Practical) Block No 1 2 Marks Internal Topic/Content Analysis Torso foundation Semi fitted Fitted Stylelines Classic princess Armhole princess Panel styleline Objectives To acquire the knowledge & skills to develop torso block for various garments To acquire the knowledge & skills to develop garments with stylelines External Total Method of Teaching Description & Demonstration Description & Demonstration Gents Shirt To acquire the knowledge & skills to develop gents shirt Description & Demonstration Gents Trouser To acquire the knowledge & skills to develop gents Trouser Description & Demonstration 3 4 REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr No. 1 2 Title of the Book Dress Pattern Designing Author Natalie Bray Patternmaking for Fashion Design Helen Joseph Armstrong School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester IV Subject BFD 208:History of fashion Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Theory) Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: 1) To develop an understanding of world costumes and their contemporary interpretations 2) To understand the characteristics of the costumes of various parts of the world. CONTENT: Block Topic/Content No Analysis 1 Study of historical fashion from Ancient Egypt to modern age Fashion development Fashion in France Effect of industrial revolution on fashion 2 Objectives Method of Teaching Class room lecture and discussion Computer assisted presentations Class room lecture and discussion Computer assisted presentations Mass production of clothing Retailing during 19th century Changes caused by communication Effect of world war I and II on fashion 3 Influential designers and trends from 17th century onwards 4 Study of Indian Designers and Their Brands 5 Study of Indian Retail Brands -Class room lecture and discussion -Demonstration -Industry visit Class room lecture, discussion Computer assisted presentations Class room lecture, discussion Computer assisted presentations REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 Title of the Book A history of costume in the west Author Francots Boucher 2 Costume The Pepin press 3 Historic costumes Karen Baclawski 4 The chronicle of western costume John Peacock 5 Costume And Fashion Jack Cassin – Scott 6 Survey of historic costumes Phyllus tortora 7 The Complete Costume History Auguste Racinet 8 Clothing Technology 9 Indian Costume-II – Patkas Hannelore Eberle, Hermann Hermeling Marianne Horaberger, Dieter Menzer Warner Ribng B.N.Goswamy 10 Indian Costume B.N.Goswamy 11 Indian Costume G.S.Ghurye 12 Traditional Indian costume and textiles Parul Bhatnagar School of Continuing Education B.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester V Subject Credits BFD 201: Principle of Management Total hours Marks 4 (Theory) Internal External Total Objectives: To expose students to management creativity. To acquaint the participants with Business organization and to familiarize them with basic management concepts, applications & processes. To Provide experiential learning for the students in the area of decision making, motivation, leadership and communication Bk Topic/Content Objectives Method of No Analysis Teaching 1 Definition, Nature, Purpose and Social To understand the basic 1. Class-room teaching. responsibility of Management. management Evolution of Management, Managing is Fundamentals & an art or Science concepts. 2 Types and Levels of Organization, To get a clear vision of 1. Class-room teaching. Managerial Functions, Process of organizational structure Management- Planning, Organizing, and its Leading and Controlling Function. 3 Planning – Types, Steps and Process. Clear vision of business 1. Class-room teaching. SWOT Analysis planning and implementation of 2. Case Studies processes. 4 Organizational Structure, Types, StaffTo understand various 1. Class-room teaching. line of authority, Delegation of work and organizational structure 2. Case Study decentralization. and their functioning. 3. Role play for delegation-n of Process of Decision making, Evaluation work. and selection of alternatives 5 Motivation,Leadership, Communication 6 Finance-functions, goals, source, breakeven analysis and profitability. Ethics and Social responsibilities in management. To understand Importance of HR practices in the industry keeping in mind their future roles. To familiarize with the concepts and their implementation 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. 2. Case studies REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. 1 2 3 Title of the Book Management Essentials of Management – 5th edn Strategic management concept and cases Author Stoner & others Koontz & Weihrich – Part1 S.C. Bhattacharya School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester V Subject BFD 306:Women’s Wear Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Practical) Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: To develop an understanding, Analysis and Development of women’s wear Block No 1 Topic/Content Analysis Market survey Objectives 2 Conceptualization To analyze the concept and to develop concept through mood board and story board 3 Design Development To develop various designs reflecting the concept (partially rendered) Lecture and Discussion method 4 Final Presentation To utilize presentation skills for the final presentation of women’s wear on paper Lecture and Discussion method 5 Product Development To develop the product 6 Product presentation To understand the process of promotion Description & Demonstration Lecture and Discussion method To understand the present trends Method of Teaching Lecture and Discussion method Lecture and Discussion method School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester V Subject Credits BFD 307: Textile & Garment Quality Analysis Assurance (Theory) Total hours Marks 4 Internal External Total OBJECTIVES: This course is intended to impart the knowledge of quality analysis and assurance and its importance in textile industry. CONTENT: Block Topic / Content No. Analysis 1 Introduction What is quality? Why quality is important? 2 Inspection - Objectives To understand the meaning and importance of quality To develop an understanding about the importance of inspection at various level and the standards related to garment industry -Raw material inspection -In process inspection -Final inspection -How much to inspect -Definitions of fabric defects -British standards of interest garment manufacturers - ISO standards of interests to garment manufacturers -Class room lecture and discussion -industry visit to 3 Textile Testing & Product Evaluation 4 Precision & Accuracy of Test Methods -Atmospheric conditions for testing -Strength properties of apparel -Fabric stretch properties -Dimensional changes in apparel due to laundering, dry-cleaning, steaming & pressing. -Needle cutting / yarn severance -Sew-ability of fabrics -Bow and skew ness (Bias) in woven and knitted fabrics -Soil and stain release testing -Fabric thickness -Abrasion resistance -Color fastness Method of Teaching -Class room lecture and discussion To impart knowledge about the tests and standards set in the garment industry on which products are evaluated. To understand the Process and importance of different tests used in industries. -Class room lecture and discussion -Class room lecture and discussion -Industrial visit Textile labs visit, -Testing of fusible interlinings -Testing of zippers -Elastic waistband testing -Yarn strength and elongation -Yarn number -Yarn twist -Sewing Threads -Wear testing Care labeling of apparel and textiles 5 Class room lecture and discussion Objective evaluation of fabric hand To familiarize students with various symbols and their meaning. To study the evaluation of fabric hand Quality cost To impart knowledge about the quality cost Class room lecture and discussion Quality management To gain knowledge about the quality management Class room lecture and discussion 6 7 8 Class room lecture and discussion REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 2 Title of the Book Managing quality in the apparel industry Author Pradip V Mehta, Satish K. Bharadwaj Quality Assurance for textiles and apparel Sara J.Kadolph School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester V Subject Credits BFD 308: Draping Total hours 4 (Practical) Block No 1 2 3 4 5 6 Marks Internal External Topic/Content Analysis Introduction to Draping Terminology Dummy preparation Muslin preparation Basic Bodice Block Front Back Dart Manipulation Single dart series Double dart series Objectives To acquire the knowledge & skill of draping Bodice Block standard size # 8 To acquire the knowledge & to develop skill for dart manipulation by draping method Description & Demonstration Basic Skirt Block Single dart Double dart Dart Equivalents Skirt variations Flared Gathered Skirts with yokes Neckline & Armhole variations To acquire the knowledge & skill of draping Basic skirt Description & Demonstration To acquire the knowledge & skill of skirt variations by draping method. Description & Demonstration To acquire the skill of draping Description & Demonstration To acquire the basic knowledge of Draping. Method of Teaching Description & Demonstration Description & Demonstration REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 Total Title of the Book Draping for Apparel Design Author Helen Joseph Armstrong School of Continuing Education Bachelor of Science in Fashion Design Semester VI Subject Credits BFD 303: Range Development Total hours Marks 4 (Practical) Internal External Total Objectives: 1. To understand the requirement of domestic brands through research 2. To develop a range suitable to the selected domestic brand. Bk No 1 2 3 Topic/Content Analysis Selection of themes for the collection Market Research Development of mood boards Roughs Work on Textures Collect swatches & Trimmings Experimenting and creating a storyboard The final sketches Fabric swatches Trimmings Ornamentation Textures Making of toils (muslin pattern) for the selected collection. Objectives To develop the skill to choose an appropriate themes and implementation of the same Method of Teaching Discussion and Guidance To develop the final sketches, fabric swatches, trimmings, ornamentation, textures by experimenting. Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Experimentation Discussion and Guidance 4 -Presentation & Feedbacks -Co-ordinate accessories To develop the toils in order to bring out perfection in final garments. To develop the accessories according to the selected theme 5 -Final collection -Client Presentation using CAD. To present the final presentation in front of external jury REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. 1 2 Title of the Book Concept to Consumer Sewing for Apparel industry, Author Fringes. Claire Shaeffer School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester VI Subject BFD 304: Men’s Wear Credits Total hours Marks 4 (Practical) Internal External Total Block No 1 Topic/Content Analysis Market survey Objectives 2 Conceptualization To analyze the concept and to develop concept through mood board and story board Method of Teaching Lecture and Discussion method Lecture and Discussion method 3 Design Development 4 Final Presentation To develop various designs reflecting the concept (partially rendered To utilize presentation skills for the final presentation of women’s wear on paper Lecture and Discussion method Lecture and Discussion method 5 Product Development To develop the product 6 Product presentation To understand the process of promotion Description & Demonstration Lecture and Discussion method To understand the present trends School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester VI Subject Credits Total hours Marks BFD 302: Recent Advances in Apparel Industry Practical) Internal External Total Each student has to select a topic, collect information from literature, industry and library and present report in the class, on the topics such as weaving, wet processing, readymade garment industry, household textiles, printed design analysis, advertisements of textiles and clothing and such more topics. School of Continuing Education B.Sc. (Fashion Design) Semester VI Subject Industrial Project Credits Total hours Marks 4 Internal Block No 1 2 3 4 5 6 External Total Topic/Content Analysis Objectives Method of Teaching Introduction Industry project concept notes Concept- research and methodology To understand the concept of the industry project Guidance, disscussion To analyze the concept and to develop concept through research Guidance, discussion and practical Identification of research topic Objectives, Introduction, Planning Methodology, review of literature, planning - Preparation of tools, progress of project Presentation of tools Finding and analysis presentation To understand the objectives, introduction and planning about the topic Guidance and disscussion To understand the method employed, its review of literature, planning Guidance and disscussion Interpretation of the findings Guidance discussion and practical Final presentation Computer assisted Presentation in front of jury Guidance, discussion, Name of Programme: M.Sc. in Hospitality and Tourism Studies – (M.Sc HTS) V-77 FIRST YEAR Course 1: MTH101: Corporate Communication (TH) Unit1: Principles of Communication Unit2: Listening Skills Unit3: Oral Skills Unit4: Non-verbal Communication Unit5: Public Speaking, Interview Skills Unit6: Meeting and Conference Course 2: MTH102: Front Office & Public Relations (Th+Pr) Unit1: The Growth of Hospitality Industry Unit2: Reservation and Registration Management and Handling of Complaints Unit3: Front Office Responsibilities and Operations Unit4: Evolution of Public Relations Unit5: Public Relations in Hotels Course 3:MTH103: Cultural Tourism Management (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Cultural Tourism Management Unit2: Cultural Tourism in India Unit3: Managing Tourism at the Places of Heritage and their Significance Unit4: Heritage Tourism-Concepts, Practice and Challenges Unit5: Cultural Tourism Management Course 4: MTH104: Accommodation & Leisure Management (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction to the Housekeeping Department Unit2: Linen and Uniform Room Unit3: Laundry Services Unit4: Flower Arrangement Unit5: Housekeeping Control Desk and Public Area Unit6: Economics of Travel Agency Business Course 5: MTH 105: Travel Agencies Operations (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Tourism and Travel Products: Introduction to Tourism and Travel Products Unit2: Organization and Working of a Travel Agency: Organization and Working of a Travel Agency Unit3: Approval and Recognition of Travel Agencies: Establishment, Approval and Recognition of Travel Agencies Unit4: Organizational Setup and Planning Patterns in Tourism Industry: Organizational Setup and Planning Patterns in Tourism Industry Unit5: Economics of a Travel Agency Business: Economics of a Travel Agency Business Course 6: MTH 106: Supervision in Hospitality (Th) Unit1: Supervisor and Supervisory Management : Supervisor and Supervisory Management Unit2: Leadership and Communication: Leadership and Communication Unit3: Create Positive Work Climate: Create Positive Work Climate Unit4: Job Expectations: Job Expectations Unit5: Recruitment and Selection Procedure: Recruitment and Selection Procedure Course 7: MTH 107: Food and Beverages Operations and Control (TH+PR) Unit1: Place of Catering in Hospitality Industry: Place of Catering in Hospitality Industry Unit2: Staff Organization: Staff Organization Unit3: Attributes of Service Staff: Attributes of Service Staff Unit4: Planning Organization and Supervision: Planning Organization and Supervision Unit5: Fundamental of Food and Beverage Control: Fundamental of Food and Beverage Control Course 8: MTH 108: Food Production Technique (Th+Pr) Unit1: Introduction to Production Management: Introduction to Production Management Unit2: Fish/ Meat/ Vegetables Cookery: Fish/ Meat/ Vegetables Cookery Unit3: Cooking Materials: Cooking Materials Unit4: Patisserie: Patisserie Unit5: International Cuisine: International Cuisine SECOND YEAR Course 1: MTH 201: German (TH) Unit1: Introduction to German: Alphabet, Greeting and Nouns Unit2: Days, Dates and Months of the Year: Colors, Months and Verbs Unit3: Drei Personen – Three People: Vocabulary, Seasons and Grammar Unit4: How to Order Food in a Restaurant: Conversation in German and Grammar Unit5: Glossary Re4lated to Food and Cooking: Vocabulary of Food and Drinks Course 2: MTH 202: Air Travel Operation (Th) Unit1: Tourism and Travel Products: Tourism and Travel Products Unit2: Air Travel and World Airlines: Air Travel and World Airlines Unit3: Approval and Recognition: Establishment, Approval and Recognition Unit4: Economics for a Travel Agency Business: Economics for a Travel Agency Business Unit5: Air Ticketing Techniques: Air Ticketing Techniques Course 3: MTH 203: Bakery and Confectionary (Th+Pr) Unit1: Wheat and Wheat Milling: Wheat and Wheat Milling Unit2: Commercial Baking Technology: Commercial Baking Technology Unit3: Partially Prepared Bakery Products: Partially Prepared Bakery Products Unit4: Breakfast Cereals and Snack Foods: Breakfast Cereals and Snack Foods Unit5: Icing and Sugars: Icing and Sugars Course 4: MTH 204: Advance Food Production (Th+Pr) Unit1: Kitchen Management: Kitchen Management Unit2: Pasts and Rice-Manufacture, different types: Cereals, Fish and Meat Preparations Unit3: Modern techniques in preparation: Modern Techniques in Food Preparation Unit4: Larder Organization: Larder Organization Unit5: Non-Edible Display: Non-Edible Display Course 5: MTH 205: Tourism Economics (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Economics: Introduction to Economics Unit2: Demand Analysis: Demand Analysis Unit3: Supply and Cost Analysis: Supply and Cost Analysis Unit4: Market Structure: Market Structure Unit5: The Hotel Industry and Economic Development: The Hotel Industry and Economic Development Course 6: MTH 206: Team Management (TH) Unit1: Team Formation and Its Psychological Dimensions: Team Formation and Its Psychological Dimensions Unit2: The Team and the Group Processes Unit3: Principles of Team Building and Team Balance Unit4: Team Management System Unit5: Implementing Team Work Course 7: MTM 207: Alcoholic Beverages (TH) Unit1: Wines: Wines Unit2: Wines Equipment and Service: Wines Equipment and Service Unit3: Spirits: Spirits Unit4: Menu Terminology: Menu Terminology Unit5: Cocktails: Cocktails Name of Programme: M.Sc. in Food Science Degree Programme (M.Sc FS) V-78 FIRST YEAR Course1: MFS 101: Food Chemistry (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Water: Introduction to Water Unit2: Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates Unit3: Lipids: Lipids Unit4: Proteins and Amino Acids: Proteins and Amino Acids Unit5: Minerals: Minerals Course2: MFS 102: Food Preservation (Th) Unit1: Introduction: Introduction to Food Preservation Unit2: Refrigeration and Freezing: Refrigeration and Freezing Unit3: Drying: Refrigeration and Freezing Unit4: Curing and Preservation: Curing and Preservation Unit5: Preservation by Heat and Vacuum: Preservation by Heat and Vacuum, Irradiation Course3: MFS103: Microbiology of Food (Th) Unit1: Introduction: Introduction to Food Microbiology Unit2: Contamination: Contamination Unit3: Microbiological Organism of Foods: Microbiological Flora of Foods Unit4: Food Poisoning: Food Poisoning Unit5: Preservation of Microorganisms: Preservation of Microorganisms Course4: MFS 104: Food Packaging (Th) Unit1: Packaging of Fresh Foods: Packaging of Fresh Foods Unit2: Packaging of Dairy Products: Packaging of Dairy Products Unit3: Packaging of Cereal and Snack Foods: Packaging of Cereal and Snack Foods Unit4: Packaging of Beverages: Packaging of Beverages Unit5: Packaging of Microwavable Foods: Packaging of Microwavable Foods Course5: MFS 105: Principles of Management (Th) Unit1: Nature And Functions Of Management Unit2: Co-ordination, Planning and Decision Making Unit3: Directing: Motivating People at Work Unit4: Nature and Importance of Organizing Unit5: Social Responsibilities of Business Course6: MFS 106: Food Processing 1 (Th+Pr) Unit1: Operation in Food Processing: Operation in Food Processing Unit2: Process Technology of Cereals, Legumes & Oil Seeds: Process Technology of Cereals, Legumes & Oil Seeds Unit3: Process Technology of Baking & Baking Products: Process Technology of Baking & Baking Products Unit4: Baking Technology of Tea and Coffee: Baking Technology of Tea and Coffee Unit5: Special Foods: Special Foods Course7: MFS 107: Food Packaging Materials (Th) Unit1: Function of Packaging: Function of Packaging Unit2: Paper Containers: Paper Containers Unit3: Metal Packaging Materials: Metal Packaging Materials Unt4: Glass Containers: Glass Containers Unit5: Safely and Legislative Aspect of Package: Safely and Legislative Aspect of Package Course 8: MFS 108: Food Processing and Preservation (Th) Unit1: Food Colour and Flavour: Food Colour and Flavour Unit2: Food Additives and Micro-Organisms Associated with Foods: Food Additives and Micro-Organisms Associated with Foods Unit3: Fermented Food and Food Chemicals: Fermented Food and Food Chemicals Unit4: Food Borne Diseases: Food Borne Diseases Unit5: Food Preservation: Food Preservation Course 9:MFS 109: Dairy Technology (Th) Unit1: Market Milk: Milk Unit2: Butter: Butter Unit3: Cheese: Cheese Unit4: Ice Cream and Related Products: Ice Cream Unit5: Indian Dairy Products: Indian Dairy Products Course 10: MFS 110: Fermentation Technology (Th) Unit1: Introduction to Fermentation: Introduction to Fermentation Unit2: Designing and Operation of Fermentation: Designing and Operation of Fermentation Unit3: Fermentation Technology of Different Products: Fermentation Technology of Different Products Unit4: Immobilization: Immobilization Unit5: Unfermented Product: Unfermented Product SECOND YEAR Course 1: MFS 201: Food Processing II (Th+Pr) Unit1: Fruits: Processing of Fruits Unit2: Vegetables Unit3: Structure of Meat Unit4: Egg and Fish Unit5: Miscellaneous Foods Course 2: MFS 202: Bakery and Confectionery (Th) Unit1: Wheat and Bread: Wheat and Bread Unit2: Bread Making Process: Bread Making Process Unit3: Cakes, Pastries, Biscuits and Cookies: Cakes, Pastries, Biscuits and Cookies Unit4: Cake Faults: Cake Faults Unit5: Pastry: Pastries, Biscuits and Cookies Unit6: Partially Prepared Bakery Products: Partially Prepared Bakery Products Course 3: MFS 203: Marketing Management (Th) Unit1: Basics in Marketing Management Unit2: Marketing Environment Unit3: Buyer Behavior – Consumer and Industrial Buyers Unit4: Personal Influence Unit5: Basics of Strategic Marketing Unit6: Marketing Research Approach Unit7: Product Unit8: Pricing Methods and Pricing Strategies Unit9: Promotion and Promotion Mix Unit10: Distribution and Distribution Channels Course 4: MFS 204: Sensory Evaluation (Th) Unit1: History of Sensory Science: Sensory Evaluation: Introduction and History Unit2: Central Nervous System: Central Nervous System Unit3: General Laboratory Set-up for Sensory Evaluation: General Laboratory Set-up for Sensory Evaluation Unit4: Sensory Analysis: Tests of Sensory Analysis and Evaluation Unit5: Tests of Sensory Evaluation Unit6: Sensitivity Test, Sensitivity Threshold Test: Sensitivity Test, Sensitivity Threshold Test Unit7: Sensory Evaluation Personnel: Sensory Evaluation Personnel Unit8: Panel Screening, Selection and Training: Panel Screening, Selection and Training Unit9: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Important Definitions: Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point Unit10: Control of Microorganisms: Control of Microorganisms Course 5: MFS 205: Rules and Regulations of Foods (Th) Unit1: Food Adulteration and Quality Control: Food Adulteration and Quality Control Unit2: Prevention of Food Adulteration Act: Prevention of Food Adulteration Act Unit3: Legislative Control: Legislative Control Unit4: The Fruit Product Order 1955: The Fruit Product Order 1955 Unit5: Food Law and Standard 2: Food Law and Standard 2 Unit6: Food Legislations: Food Legislations School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester I Subject Credits Aesthetic in Design - I Total hours Marks 4 Theory Internal External Total CONTENT: Block No Topic/Content Analysis Introduction to aesthetics- 1 2 3 Defining aesthetics Factors influencing aesthetics Elements and principles of design in apparel Visual elements of design Principles of design organization Aesthetic related skills and apparel industry 4 Creative activities and skills Applications of aesthetics Body and apparel Trend forecasting Objective Method of Teaching Period Hours School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester I Subject Credits Fashion Art Appreciation Total hours Marks 4 Theory Internal External Total CONTENT: Block No 1 2 Topic/Content Analysis Introduction to fashion art Study of any 5 international designers and 5 Indian designers Study of their specialty in fashion Study of one design collection each in terms of fashion art Acceptance to the international and Indian market Objective Method of Teaching Period Hours School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester I Subject Design Management Practical Credits Total hours Marks 4 Internal External Total School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester II Subject Credits Fashion Studies Total hours Marks 4 Theory Internal External Total CONTENT: Block No Topic/Content Analysis 1 Industry Study 2 Fashion Environment Fashion According to Culture Fashion According to Geographical Location Fashion According to Gender Fashion According to Economics Fa,shion Psychology 3 4 Study of designer and brand for history, style, Range, Costing, Special Contribution Objective Method of Teaching Period Hours School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester II Subject Credits Surface Ornamentation Technique Total hours Marks 4 Practical Internal External Total CONTENT: Block No Topic/Content Analysis Objective Method of Teaching 1 Selection of themes for the collection Market Research Development of mood boards Roughs Work on Textures Collect swatches & Trimmings Experimenting and creating a storyboard The final sketches Fabric swatches Trimmings Ornamentation Textures To develop the skill to choose an appropriate themes and implementation of the same Discussion and Guidance To develop the final sketches, fabric swatches, trimmings, ornamentation, textures by experimenting. To develop the toils in order to bring out perfection in final garments. Experimentation Discussion and Guidance 2 3 Making of toils (muslin pattern) for the selected collection. Experimentation Discussion and Guidance 4 -Presentation & Feedbacks -Co-ordinate accessories To develop the accessories according to the selected theme Experimentation Discussion and Guidance 5 -Final collection -Client Presentation using CAD. To present the final presentation in front of external jury Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Period Hours School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester II Subject Design Development Process Credits Total hours Marks 4 Practical Internal External Total CONTENT: Block No Topic/Content Analysis 1 Research on previous fashion forecast. Discussion and Guidance 2 Inspiration research (for developing concept) Experimentation Discussion and Guidance 3 Directional process Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Color Objective Method of Teaching Silhouettes Proportions Fabrics Trims Prints Textures 4 Construction techniques Inspiration boards Mood board Fabric development board (surface ornamentation techniques) Developing DDS (design development sheets) Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Period Hours Final line up of garments 5 Specs and flats (technical drawing) Developing prototypes (samples) Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Designing accessories Promotion of the product (ex. designing a window display or designing a brochure or designing a bag etc.) School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester II Subject Research Methods and use of Statistics Theory Credits Total hours Marks 4 Internal External Total School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester III Subject Fashion Forecasting Credits Total hours M ar ks Internal External To tal 4 Practical Objective: 1. To understand the forecasting techniques to determine market demands 2. To be able to make use of the forecast to design collections. Objectives Method of Bloc Topic/Content Analysis Teaching k No Introduction To understand the . Class-room i. Meaning of Fashion concept of fashion teaching ii. Meaning of Forecasting and forecasting Discussions iii. The role of a forecaster To understand the iv. The precision of the forecast various stages of 1 v. The fashion industry’s components forecasting. vi. The structure of the fashion industry o vii. viii. 2 3 The fashion timetable Information Network ix. ix. The selling strategy Research Process in Forecasting i. Primary sources ii. Secondary sources iii. Tertiary sources iv. Tracking sales v. Competition vi. Demographics vii. Value & life style viii. Publication ix. Forecasting services x. Plethora influences xi. Observation posts xii. The new technology xiii. Fashion of involvement xiv. New uses of products xv. Old neighborhoods xvi Related industries Processes of Reporting i. Process of implementation ii. Promotion iii. Making the fashion happen To acquire the skills in research process in forecasting . Class-room teaching Discussions To acquire the skills in the processes of reporting . Class-room teaching Discussions Hr REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr No. Title of the Book 1 Fashion Forecasting 2 Fashion Forecasting Author Evelyn L. Brannon Rita Perna School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester III Subject Advance Styling 1 2 Total hours M ar ks Internal External To tal 4 Prctical Bloc k No Credits Topic/Content Analysis Introduction i. Meaning of Fashion ii. Meaning of Forecasting iii. The role of a forecaster iv. The precision of the forecast v. The fashion industry’s components vi. The structure of the fashion industry vii. The fashion timetable viii. Information Network ix. The selling strategy. Research Process in Forecasting i. Primary sources ii. Secondary sources iii. Tertiary sources iv. Tracking sales v. Competition vi. Demographics vii. Value & life style viii. Publication ix. Forecasting services x. Plethora influences xi. Observation posts xii. The new technology xiii. Fashion of involvement xiv. New uses of products xv. Old neighborhoods xvi. Related industries Objectives Method of Teaching Hr 3 Processes of Reporting i. Process of implementation ii. Promotion iii. Making the fashion happen School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester III Subject Brand Design Credits Total hours M ar ks Internal External To tal 4 Theory CONTENT Block No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Topic/Content Analysis Nature of the fashion industry, the structure of fashion company, merchandise process & timing & the inter-relationship of players and their roles. Fashion marketing & buying at industry trade shows Fashion Marketing Strategies, Consumer analysis and trade forecasting. Fashion Marketing Strategies, Competitive Marketing Strategies of luxury fashion companies, distribution and communication. Fundamentals in Brand Management the designer as brand. Developing brand image, advertising and promotion in the fashion industry and international flagship stores of luxury brand. Brand management – focus on public relations, event and media planning. The fashion system and its most important brands – designs, consumers and quality. Presentation and research on 3 completely different brand as case studies, for target, Objectives Method of Teaching Hr customers, style & quality. 10. Brand research project 11. Presentation of brand research project. 12. Collection design for a brand (group project). 13. Presentation of the design collection (group project). School of Continuing Education M.Sc. in Fashion Design Semester III Subject Aesthetic in Design – II Practical Credits Total hours M ar ks Internal External To tal 4 School of Continuing Education Bachelor in Fashion Design Semester IV Subject Range Development Credits M Total hours ar ks 4 (Practical) Internal External To tal Objectives: xvi. To understand the requirement of domestic brands through research xvii.To develop a range suitable to the selected domestic brand. Bk Topic/Content Method of Objectives No 1 Analysis Teaching Selection of themes for the collection Market Research Development of mood boards Roughs Work on Textures Collect swatches & Trimmings 2 3 Experimenting storyboard and creating a x. The final sketches xi. Fabric swatches xii. Trimmings xiii. Ornamentation xiv. Textures Making of toils (muslin pattern) for the selected collection. To develop the skill to choose an appropriate themes and implementation of the same Discussion and Guidance To develop the final sketches, fabric swatches, trimmings, ornamentation, textures by experimenting. Experimentation To develop the toils in order to bring out perfection in final garments. Experimentation Discussion and Guidance Discussion and Guidance 4 -Presentation & Feedbacks To develop the accessories according to the selected theme -Co-ordinate accessories 5 -Final collection Experimentation Discussion and Guidance To present the final presentation in front of external jury -Client Presentation using CAD. Experimentation Discussion and Guidance REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. Title of the Book Author 1 Concept to Consumer Fringes. 2 Sewing for Apparel industry, Claire Shaeffer School of Continuing Education Bachelor in Fashion Design Semester VI Subject Dissertation 4 Credits Total hours M ar ks (Practical) Internal External To tal School of Continuing Education M.A in Fashion Administration Semester I Subject Economics For Managers Credits Hours Marks 4 Term Work (Theory) Theory Paper OBJECTIVES: - To introduce economic concepts relevant to modern business management; - To perform various forms of economic analysis extracting useful information from economic data. - To develop the analytical skills of the students and familiarize them with the statistical methods. CONTENT: Block No. Topic / Content Objectives Method of Analysis Teaching 1 -Macro and Micro economics To develop an 1. Lecture and - The nature of economic understanding of discussion decisions economic concepts. 2. Guest Speaker. 2 - Demand analysis - Production and Costs Analysis - Pricing and Output Decisions 3 -National economy, Budgets & Fiscal policy. - Grouping and Displaying Data 4 Measures of Central Tendency, Dispersion, Variation, Skewness. - Introduction to Probability theory - Probability Distributions and sampling distribution 5 Correlation, Regression Analysis and Applications. - Standard error, Testing of Hypothesis, Chi-square test. - Index Numbers REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. Title of the Book 1 Business Economics To develop skills on various forms of economic analysis. 1. Lecture. 2. Small Group. 3. Case Studies To develop skills on budgetary control and data analysis. To familiarize the students with various statistical methods. 1. Lecture and discussion 2. Guest Speaker. 1. Lecture. To familiarize the students with various statistical methods. 1. Lecture. 2. Case Studies 2. Case Studies Author Perman, Roger 2 An Introduction toPositive Economics Lipsey Chrystal 3 Microeconomics Mankiv 4 Statistical Methods S.P.Gupta 5 Business Statistics Gupta & Gupta 6 Business Statistics Chandan, Singh & Khanna Total Hours 7 Business Statistics Bhatia and Gupta 8 Statistics for Management Richard Levin & David Rubin School of Continuing Education MBA in Fashion Management Semester I Subject Fashion Retailing Credits Total hours 4 64 (Theory) Marks 25 75 100 Term Work Theory Paper Total OBJECTIVES: This course is designed to provide an overview of retailing in India and abroad and to make the students understand the evolution of retailing as an emerging sector of importance. This will build basic retail knowledge and skills will familiarize the students with various retail formats, and locational considerations. It will also expose students to the organizational structure of retail company. CONTENT: Block No 1 2 3 4 5 Topic/Content Analysis Evolution of Retailing Retailing role in Marketing System Store formats Store Organization Franchising and product labels Site selection and Layout Trade area analysis and siteselection SPF calculation Store Interior and Design Departmentalization Objectives Layout Planning & Space Allocation Promotion Calendar Signage policies To understand retail promotions To have an overview of retailing Method of Teaching 1. Class-room teaching. 2.Educational visits To understand retail functioning To understand the process of establishing retail. 1. Class-room teaching. 1. Class-room teaching. To understand the process of store functioning 1. Class-room teaching. 2.Educational visits. 3.Projects and submissions 1. Class-room teaching. 2.Educational visits 3.Projects and submissions REFERENCE BOOKS: Sr. No. 1 Title of the Book Retail Management Author Davidson, Sweeney, Stamp Period Hours 2 3 4 5 Effective Retailing Images Retail Journal of Retailing Fashion Retailing ( A multi channel Approach ) Fashion from Concept to Consumer Bolen & William Ellen Diamond Fringes School of Continuing Education MBA in Fashion Management Semester I Subject Credits Introduction to Fashion Business Hours Marks 4 Term Work (Theory) Theory Paper Total OBJECTIVES: - To introduce the concepts of management in today’s fashion business context. - To establish various management thoughts and discuss the styles of leading management thinkers. CONTENT: Block No. 1 2 3 4 5 Topic / Content Analysis Overview of Fashion Business Sector: National and International Planning the Business: the nature and purpose, objective of planning premises. Planning the Business: Policies, procedures and methods Organizing the business organization: The nature and purpose of internal organization, principles of organization. Organizing the business organization: Span and structure of organization, line and staff organization Objectives To develop a thorough understanding of the basics of fashion business To establish the strategies of fashion business To develop the skills for business planning and procedures To familiarize to students the fundamentals of business organization To attain thorough understanding of organizational structures and to establish various management thoughts Method of Teaching 1. Lecture and discussion 2. Guest Speaker. 1. Lecture. 2. Small Group Discussion. 1. Lecture and discussion 2. Case Studies 1. Lecture and discussion 1. Lecture. 2. Panel of Experts. 3. Case Studies. Hours REFERENCE BOOKS: Sl No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Title of the Book Principles of Management Management and Organization Management of Tomorrow The Practice of Management Management Fashion Marketing Marketing Today’s Fashion Fashion: A Marketing Approach Fashion Innovation & Marketing How to Sell Fashion Author Koontz and O, Donnell Allen Louis Allen Louis P.F. Drucker Stoner Gardon Wills & David Midgley Helena De Paola & Carol Stewart Mueller Dorothy S. Rogers & Lynda R. Gaman Catterine Moore Annalee Gold M.Sc. II (Environmental Science) Second Year Paper. MES 201 Environmental Monitoring and Energy Studies. Marks : 100. Lectures : 45. 1. Environmental Quality Assessment and Monitoring. What is environmental quality? Quality of environment for life on earth and man. Deterioration of environmental quality with reference to anthropogenic impact, methods of assessment of environmental quality, short term studies / surveys rapid assessment continuous short and long term monitoring. (5) 2. Environmental Impact Assessment. Need of EIA, scope and objectives, types of environmental impacts, steps involved in conducting the EIA studies. Environmental Impact Assessment Techniques – Ad – hoc method, checklist method, overlay mapping method, network method, simulation and modeling technique, matrix method, and system diagram technique, matrix method, and system diagram technique, Merits and Demerits of EIA studies. (4) 3. Principles of remote sensing, its applications in Environmental Monitoring. Concept of remote sensing. EMR & its interaction with matter, aerial photography types, camera, elements of photo interpretation (Aerial photography/ image recognition ), sensors & platforms, IRS satellites & their sensors, application of remote sensing in environmental studies. (5) 4. Geographical Information System (GIS) Concept of GIS, types of geographical data, data structure, vector and raster data, their advantages and disadvantages, Input, verification, storage and output of geographical data. Importance of geographical information system in environmental studies. (4) 5. Present status of energy use patterns in India. Population and energy demand, energy use pattern in rural and urban area, impact of growing population on energy use, changing life style and energy use, energy profile of oil and natural gas, Indian production and reserves, nuclear option, role of IRDA & MEDA in energy generation. (5) 6) Conventional and non – conventional energy sources. Concept and classification of energy sources, renewable and nonrenewable energy resources, coal, oil and natural gas, hydropower as conventional energy resources, environmental imparts of conventional energy resources, need of nonconventional energy resources, geothermal energy, oceanic energy, wind energy, biomass energy, nuclear energy, merits, demerits and environmental issues of these energy resources. (5) 7) Solar Energy. Measurement of solar radiation, collection, conversion, and storage, solar pond, solar energy collectors, solar heaters, concentrating collectors, solar water heating systems, solar cookers, solar agricultural product dryers and other applications of solar energy. (6) 8) Biomass Energy Concept of biomass energy, biomass energy conservation technologies wet & dry processes, concept of energy plantation, thermal gasification of biomass, biogas generation, factors affecting bogas production, types of biogas plants, their merits and demerits. (5) 9) Wind energy Introduction to wind energy, basic principles of wind energy conservation, wind energy for electrical energy generation, criteria for site selection, major components of wind Energy Conservation system, types of wind energy conservation systems, applications of wind energy, merits and limitations of wind Energy Conservation System. (5) Paper – MES 202 Natural Resources and Instrumentation. Marks : 100. Lectures : 45. 1) I) Internal Structure of the Earth: Structure and composition of the earth, concept of natural resources, their classification, review of natural resources with special reference to fossil fuels and radioactive minerals. (2) II) Natural Resources of India : Mineral Resources: With special reference to their occurrence distribution and utilization of metallic minerals ( Iron, Aluminum and Manganese) and nonmetallic minerals ( Mica, asbestos, common salt ). (5) 2. Land resources: General account (2) 3. Soil resources: Types and classification. (2) 4. Water resources: Concept of hydrological cycles, monsoons distribution of surface and ground water resources, utilization for various purposes. (5) 5. Energy resources: Non – renewable energy resources. (2) 6. Marine resources: food, Mineral and Energy. (3) 7. Floral and faunal resources: Biological diversity and concept. (2) 8. Forest resources: forest cover and types, major and minor forest products. III) Instrumentation: (2) 1. Fundamentals of Environmental Chemistry: Stoichometry, Gibb’s energy, chemical potential, Chemical equillibria, solubility product, solubility of gas in water, Carbonate System. (3) 2. Classical Methods: Basic concepts and techniques, titrimetric analysis – Primary standards acid base titration, oxidation – reduction methods, iodometry. (3) 3. Electro- analytical Methods: Basic electronic and instrumentation, conductometry, potentiometry (Glass – electrode, Ph, Ion selective electrode). Voltametry- Polarography and Dropping Mercury Electrode. (4) 4. Colorimetry and spectrophotometry: Components and working of spectro photometer, Beer (2) Larnbert’s Law. 5. Flame techniques: Flame photometer and Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer. (2) 6. Separative Techniques: Solvent extraction, Ion Exchange Chromatography, Gas chromatography, High pressure Liquid Chromatography, Thin Layer Chromatography. (6) References: 1. A Handbook of techniques by Sachs H. (1982) 2. Statistical methods for Engineers and Scientists by Bethea, R. M. Duran, B. N. and Bonlion, T. L. (1975). 3. Applied Regression Analysis by Draper A. and Smith G. (1981). 4. Elements of practical statistics by S. K. Kapur. 5. Chemistry for Environmental Engineering by Sawyer, Mc Carty and Parkin. 6. Vogel’s Textbook of quantitative chemical Analysis, 5th edition by basett, J. nendham and Denny. R.C. 7. Handbook of Analytical Instruments by khandur R.S. 8. Environmental pollution Analysis by Khopkar S. M. 9. Instrumental methods of chemical analysis by B. K. Sharma. 10. Instrumental methods of analysis by Willard, Meritt, Dean and Settle. 11. Mineral Resources by Krishna Swamy 12. Environmental Geology by KS Valdiya 13. Energy Resources and Science by Kirwan 14. Environmental Resources by Mathur 15. Handbook of Minerals, IBM (1993) 16. Fundamentals of Soil Science by Henry De. Foth 17. Principles of Photo geology by Singh 18. Principles of Remote Sensing by Currain 19. Fundamentals of Photo geology by SN Pandey 20. The Atmosphere by Turback and Lutgen 21. Agrwal, V. P., : Forest in India, Oxford and IBH, New Delhi. 22. Sagreiya, K. P. : Forest and Forestry, National book Trust India 23. Puri, G. S. et al : Forest ecology, Oxford IBH, Bombay 24. Sarma, P. K. : Forest resources and their Utilization in India, Mittal Publishers, New Delhi 25. Hydrology by Todd 26. Ground water hydrology by Hiremath Paper MES 203 Environmental Education, Policies and Legislation Marks : 100. Lectures: 45. I. Environmental Education: Definition and background of environmental education, need and objectives of environmental education. Status of environmental education in new education policy – Role of various II. institutions (Govt. and Non Govt.). (6) Environmental Policy: Government policies in the protection and development of environment- environmental NCEP and district considerations in economic planning and development in India. environmental committee. Emerging environmental concerns in India – Case study of silent environmental concerns in India – case study of silent valley, sardar sarovar. Tehri Garwal dams, Carbon credits, Carbon trading, etc. (7) III) Environmental Awareness: Pollution trading, Stockholm conference (UNCHE), World commission on Environment and Development (WCED)“Our Common Future”, Rio – Conference (UNCED). IV) (5) Global Environment Conservation Strategy: United Nations environmental Programme (UNEP). International Union for conservation of Nature and Natural Resources. (IUCN) World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) v) (5). Environmental Acts: The wild life (protection) Act, 1972. The Water (Pollution and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974. The Air ( Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981. Forest ( Conservation ) Act, 1980. The environment ( protection ) Act, 1986. Public Liability Insurance At, 1991. Industrial wastes and Law, Sec. 12 of Factories Act, (1948) and rules framed there under. Noise pollution and Law, Sec. 119 and 120 of the Motor Vehicles Act (1989) and rules framed there under. (22) Note: Any amendment to the act impinged time to time is to be covered. Paper MES 204 Environmental Microbiology, Toxicology and Chemistry Marks: 100. Lectures:45. 1. Environmental Microbiology: a) Introduction to Microbiology b) Microbial diversity and Metabolism: Microbial structure, classification according to nutrition, anaerobiosis, chemolithotrophy, photosynthesis and Nitrogen Fixation. c) Determination of microbial numbers, biomass and activities: (1) (5) Microbial numbers: Direct and viable count procedures, biochemical methods; microbial biomass. (3) d) Microbial activities: Photosynthesis, respiration, hetrootrophic potential, specific enzyme assays. e) (3) Microbial population and community dynamics: Microbial growth in closed and open environments. (2) f) Methods for enriching, isolationg and analyzing microbial communities in laboratory system (3) e) Effects and measurement of environmental determinants: Tempreature, radiation, salimity, moisture activity, redox potential, magnetism, etc (2) f) biological interactions; Int eractions between microorganisms, interactions of microorganisms with plants and animals. (2) 9) Recombinant DNA Technology II) Environmental Toxicology: a) Toxicology – scope, Definition. (1) (1) b)Evaluation of toxicity – routes of exposure; acute, sub-acute, chronic toxicity. (2) c) LC 50 /LD 50 / NOEL – Concepts and significance, their estimation. (4) d) Chemical / Pharmacological basis of toxicity. (2) e) Toxic effects at cell, tissue, organ level. (2) f) Some organ specific toxicit y studies – Neurotoxicity, Nephrotoxicity, Hepatotoxicity, Radioactive toxicity (4) g) Genotoxicity – Mutations, mutagenic agents, mechanism of mutagenesis.(2) h) Detection of genotoxicity – DNA, GENE, CHROMOSOME LEVEL, CARCINOGENESIS – Relation between mutagenesis and carcinogenesis, Environmental carcinogens. (2) i) Toxic agents in environment pesticides, agrochemicals, industrial chemicals, drugs, food additives, chemical structure – function relationship. (2) j) Safety regulations, legal control, population monitoring for toxic end points. (2) Concept and scope of environmental chemistry. (10) Introduction to environment Concept of environmental chemistry Chemistry of lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere Chemical cycles of the environment – O2, N, S, P, C. Environmental pollution 1. Chemistry of air pollutants (9) Chemical composition of air Chemical composition of air pollutants Sources, sink of air pollution Classification of sources of air pollution Effects of air pollution on living and non-living 2. Chemistry of water pollutants Water and water quality parameters Industrial waste pollution Sources and classification of water pollutants Effect of water pollution on living and non-living 3. Chemistry of soil pollutants (8) Chemistry and composition of soil Chemical factors affecting the soil quality (8) Sources of soil pollution Effect of modern agro-technology on quality of soil 4. Environmental monitoring (10) Sampling of air and water pollution Monitoring techniques and methodology pH, Dissolved oxygen (DO), Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD), Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) Analysis of CO, NOX, CO2, SOX, pesticide residue, phenols, And petrochemicals Reference Books: 1. Agarwal, S. K. and Dubey, P.S. 2002: Environmental controversies, APH publishing corporation, New Delhi. 2. Radheshyam Doria, 1990 : Environmental Impact on Narmada Sagar Project, Ashish Publishing House, New Delhi. 3. Diwan, S and Rosencranz, A. 2001: Environmental Law and policy in India, Oxford University press Singh, H. , Environmental policy and Administration, Printwell, Jaipur. 4. Shekar singh: Environmental policy in India, PA, Delhi. 5. Environmental protection and the Laws by C. N. Mehta, 1991. 6. Indias forests, Myth and Reality by J.B. Lal 1989. 7. Legal aspects of Environmental pollution and its Management by Ed. S.M. Ali, 1992. 8. Man – Nature and Environmental Law by G. S. Nathwal, S. Shari and J.P. Vyyar, 1998. 9. International Environmental policy, Emergence and Dimentions by L.K. Caldwell, (1990). 10. Lal’s commenteries on water, air pollution laws along with the Environmental (protection) Act, and rules, 1986, 3rd Ed., 1992 Law Publisher- India. 11. The wildlife (protection) Act, 1972 (with amendment – 1991) 12. Our common future – WCED, 1991. 13. Universal’s Environment and Pollution law Manual by S. K. Mohanty, 1998. 14. Microbiology By; Michael J. Pelezar, Jr; ECS Chan & NR. Krieg. Tata Mcgraw- Hill Edition New Delhi. (1998). 15 Principles of Microbiology By: Ronald M. Atlas 2nd Edition, Wcb McgrawHill, Boston (1997). 16. General Microbiology By: R. Y. Stanier, J. L. Ingraham, M. L. Wheelis & P.R. Painter 5th Edition Macmillan press Ltd., London. (1995) 17. Microbial Ecology-Fundamentals and Application By: Ronald M Atlas and Richard Bartha 4th Edn. An Imprint of Addison Wesley Longman, Inc. California(1998). 18. Microbiology: Fundamentals and Applications By: S.S.Purohit 6th Edn. Agro Botanica(1997-98) 19. General Microbilogy By : SB Sullid & S Shantharam.Oxford & IBH publishing(o.pvt.Ltd,New Delhi(1998)). 20. Microbiology-Diversity, Disease & Environment By: Abigail & A Salyers & Dixie D klhitt,Fitzgerald science press, Maryland(2001). 21. Industrial Microbiology-An Introduction By : Michel J. Waites, Neil L Morgan, John S Rockey & Gary Higton. Blackwell science, London(2002). 22. Microbiology- A Laboratory Manual(International Students Edition)By: James G (appuccina & Natalie Sherman Addison-Wesley Longman, Inc, Calforia(1990). 23. Environmental Microbiology – A Laboratory Manual By:Jan L pepper, Cp Gebra & JW Brendecke, Academic press, New York(1965). 24. Harish Kumar,2001: Environmental Health Hazards,Ivy publishing House,Delhi. Paper MES 206 Environmental Geo-science Marks: 100. Lectures:45. 1. Origin and evolution of the Earth (8) Introduction to universe, planets, comets, asteroids, meteorites. Theories of origin of the earth Origin and evolution of life – Spontaneous generation of life, chemical prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellular evolution. Brief outline of crust, mantle and core 2. Dynamic Aspects of the earth (10) Earthquake Volcano Mountain geotectonic Continental drift and plate tectonics Introduction of structural geology – fold, fault, joint. 3. (a) Atmosphere (12) Vertical structure and formation of earth crust (b) Lithosphere Cross section and formation of earth crust Generation of rocks – Rock cycle, study of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks Generation of minerals – Study of physical characters, origin, use of rock, forming and ore minerals (c) Hydrosphere Physicochemical characteristics Hydrological cycle, river water, ground water 4. Bio-geo chemical cycle (7) Carbon Cycle Nitrogen cycle Phosphorous cycle Oxygen cycle Gaseous and sedimentary cycle 5. Environmental geology (8) Concept, objectives scope and significance of environmental geology Major relief features of earth surface – the external and internal Process responsible for the modification of earth’s surface References: 1. Sharma B. K., Environmental Chemistry 2. Santra S. C., Environmental Science 3. T. C. Baruah and A. P. Barthakur, Text book of soil analysis 4. Vogel’s text book of quantitative chemical analysis 5. Trivedy R. K. and Goel P. K., (1994), Chemical and biological method for water pollution studies, Enviromedia Publication, Karad. 6. APHA, (1992), Standard methods for water and wastewater, 18th edition, APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington. 7. Rangwala S.C., (1987), Water supply and sanitary engineering, 18th edition, Charotar Publishing House, New Delhi. 8. Engineering of general geology – Prabin Singh 9. Introduction of petrology – G. W. Tyrreu 10.Elements of mineralogy – H. H. Pens 11.Environmental Geology – K. S. Valdia 12.Environmental Geology – Edward A. Keuer Paper – MES 205 Environmental Management – Land, Soil and Water Marks : 100. Lectures:45. a. Land and Soil Land classification on the basis of topography, climate, soils and utilization of agricultural land use pattern (03) b. Land productivity, capability and capacity c. Degradation of land, causes and effect d. The problem of waste land, wet land, khar land, dry land. (02) (03) (02) e. Desertifecation with special references to India. Reclamation of waste lands . (06) f. The methods of soil conservation (04) g. The use of remote sensing in land management (02) a. Water b. Classification and sources of surface and groundwater (01) c. Exporation and exploitation of water resources (01) d. Concept of water balance and significance in water use policy (01) e. Quality of irrigation water (01) f. Consequences of unskilled irrigation practices: Water logging salinity: causes consequences and control measures (03) g. Planning, execution and effect of man-made reservoirs (02) h. Utilization of water resources for energy production, sanitation, drinking, navigation, industries and agriculture. (03) i. Water management strategies and problems: Watershed concept and classification: watershed characteristics, multi-disciplinary water management. (03) j. Water resource economics (02) k. Quanitative Techniques of water resources planning and management (02) l. Regional water quality management (02) m. Use of Remote sensing in water management (01) n. Integrated approached towards water, soil and land Management (01) Practical – MES 207 Natural Resources Marks: 100 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Study of minerals Study of rocks. Scale of aerial photography Stereoscopic interpretation of aerial photography. Measurement of sound level and smoke density. Preparation of windrose diagram. Study of meteorological equipments Rain gauge, Thermometer, Hygrometer. Environmental Education, Policy Microbiology and Toxicology and Legislation and Environmental 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Isolation of microbes by serial dilution of waste-water Isolation of microbes by serial dilution of given soil sample Preparation of microbial media. Cultural character of microbes Identification of Gram+ve and Gram-ve bacteria. Enrichment of cultural technique for the isolation of degrading chemical pollutants. 7. Effect of pollutants on O2 consumption in aquatic animals. 8. Effect of microbial determinants on microbial growth. 9. Estimation of MPN from clean water and polluted water. 10.Effect of pollutant on enzyme activity Environmental Chemistry & Environmental Geosicence (1) Determination of pH, Electrical conductivity and alkalinity of water sample. (2) To determine the bulk density, moisture content and water holding capacity of soil. (3) To determine chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) from the given waste sample. (4) Determination of Dissolved Oxygen (DO) from given sample. (5) Determination of Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) from given water sample. (6) To identify the zooplanktons present in the given water sampl (7) Study of physical properties of rock forming minerals. a. Silicate minerals (Silica, feldspar, Amphibole, Mica, Olivine, etc.) b. Non-silicate minerals (8) Study of Igneous rocks (9) Study of sedimentary rocks (10) Study of metamorphic rocks (11) Study of ore minerals Educational visit from environmental geology point of view Journal – Consisting record of practical’s. Environmental Management – Land, Soil and Water, Aquaculture and Agriculture 1. Mathematical calculation in energy. 2. Caloric value of fuel. 3. Database Management system (DBMS). 4. Study of crop disease and pest management practices. 5. Study of different irrigation systems in agricultural area. 6. To study fresh water fish culture. 7. Visit to fish farms. 8. To study establishment of freshwater aquaculture. PROJECT WORK MES 208 Marks : 100 1) Dissertation Marks : 80 2) Study Tour and Industrial Training Marks : 20