WARMUP 1. Determine the quadratic function that has the
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
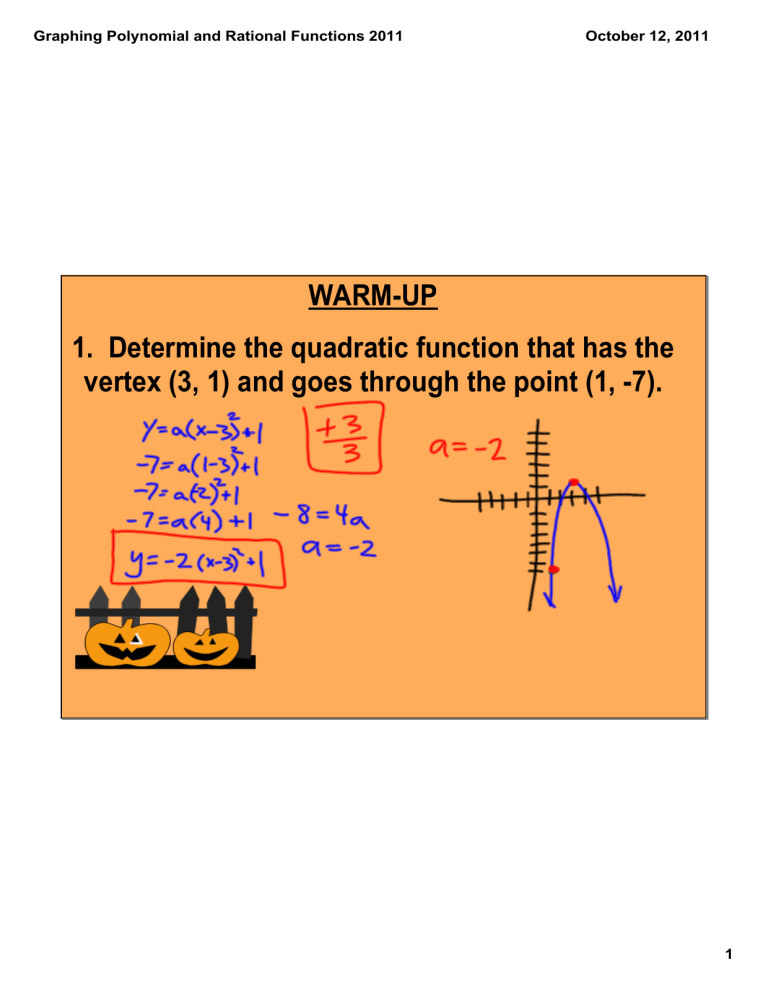
WARMUP
1. Determine the quadratic function that has the vertex (3, 1) and goes through the point (1, 7).
1
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
3.4 Graphing Polynomial
&
Rational Functions
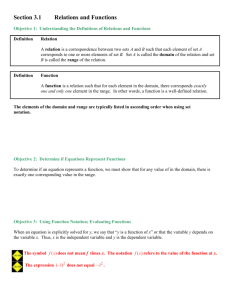
Objective
:
Graph polynomial and rational functions.
2
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
a. State the degree.
b.
Find the yintercept.
c.
Find each xintercept and state whether the graph bounces
or crosses at each xintercept.
d.
Determine the end behavior of the function.
e.
Find f(2).
f. Using the information from parts a e, make a sketch of the
graph.
3
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
a. State the degree.
b.
Find the yintercept.
c.
Find each xintercept and state whether the graph bounces
or crosses at each xintercept.
4
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
d.
Determine the end behavior of the function.
WHAT IS END BEHAVIOR??
5
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
End Behavior direction of the far left and far right portions of the graph.
Four types of end behavior:
up & up
down & down
down & up
up & down
6
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
7
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Determine the end behavior by looking at the coefficient and degree of the leading term of a polynomial function.
Right:
•
If the leading coefficient is positive, then the graph rises to the right.
•
If the leading coefficient is negative, then the graph falls to the right.
Left:
•
If the degree of the polynomial is even, then the left behavior is the same as the right behavior.
•
If the degree of the polynomial is odd, then the left behavior is the opposite of the right behavior.
8
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example: Describing End Behavior
Determine the end behavior of the graph of each polynomial.
a. y = 4x
3
3x
The leading coefficient 4 is positive, so the graph rises to the right.
The degree of the polynomial is 3, which is odd.
The left behavior is opposite the right behavior, so the graph falls to the left. b. f﴾x﴿ = 2x
4
+ 8x
3
8x
2
The leading coefficient 2 is negative, so the graph falls to the right.
The degree of the polynomial is 4, which is even. The left behavior is the same as the right behavior, so the graph falls to the left.
The end behavior is .
The end behavior is .
9
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
d.
Determine the end behavior of the function.
OK...NOW FIND THE END BEHAVIOR!
10
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
e.
Find f(2).
11
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #1:
Given the function f(x) = (x 1) 2 (x + 1)(x + 3), find the following information.
f. Using the information from parts a e, make a sketch of the
graph.
12
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #2:
2
Given the function f(x) = , find the following x 2 4 information.
a. State the domain.
b.
Find the vertical asymptote(s).
c.
Find the xintercept(s).
d.
Find the yintercept.
e.
Find the xvalue of the "hole" and the location of the "hole".
f. Find the horizontal or oblique asymptote.
g.
Find f(4).
h.
Using the information from parts a g, make a sketch of the
graph.
13
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #2:
2
Given the function f(x) = , find the following x 2 4 information.
a. State the domain.
b.
Find the vertical asymptote(s).
c.
Find the xintercept(s).
14
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #2:
2x 2 5x + 2
Given the function f(x) = , find the following x 2 4 information.
d.
Find the yintercept.
e.
Find the xvalue of the "hole" and the location of the "hole".
15
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #2:
2x 2 5x + 2
Given the function f(x) = , find the following x 2 4 information.
f. Find the horizontal or oblique asymptote.
g.
Find f(4).
2(4)
2
5(4) + 2
(4)
2
4
2(16) + 20 + 2
16 4
32 + 20 + 2
12
54
12 f(4) = 4.5
16
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Example #2:
2x 2 5x + 2
Given the function f(x) = , find the following x 2 4 information.
h.
Using the information from parts a g, make a sketch of the
graph.
17
Graphing Polynomial and Rational Functions 2011 October 12, 2011
Homework: page 240 (35, 40, 55, 56)
For #s 35 and 40 complete all parts a h.
For #s 55 and 56 follow all 8 steps on page 198 and find the
"hole" in the graph. Show the
"hole" when you graph by hand .
18