Monetary Policy and Recent Economic Developments Teacher and Student Guide May 2016
advertisement

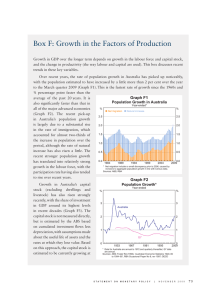
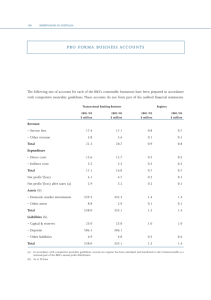
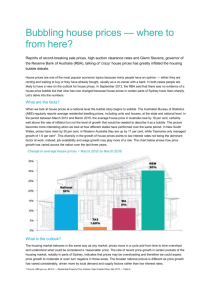
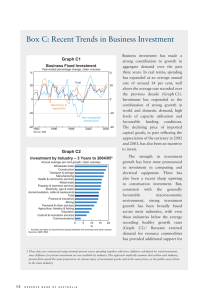
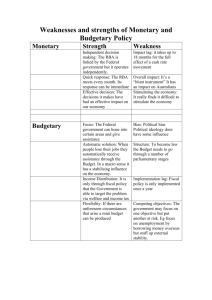
May 2016 Teacher and Student Guide Monetary Policy and Recent Economic Developments Reserve Bank of Australia Responsible for: • Monetary policy and market operations • Payments system stability & efficiency • Financial system stability • Issuing Australia’s currency notes • Banker to the government • Managing foreign exchange reserves The objectives specified in the Reserve Bank Act (1959) are: • Stability of the currency • Maintenance of full employment • Economic prosperity and welfare of the people of Australia Reserve Bank Board • Responsible for monetary and banking policy • Nine members: Governor, Deputy Governor, Secretary to the Treasury, and six external members • Meets first Tuesday, except January How the RBA achieves its objectives • Inflation targeting regime since 1993, agreed with the government since 1996, and which was most recently updated in 2013 • Objective is to keep annual inflation between 2 and 3 per cent, on average, over the cycle • CPI inflation is the target, but underlying measures – which abstract from temporary large price increases and decreases – help show future trends in ‘headline’ inflation • RBA sets the policy interest rate (termed the cash rate – the rate banks charge each other for overnight funds) • The RBA uses liquidity operations (altering the supply of overnight funds) to ensure the cash rate remains at target • Changes in the cash rate affect private mortgage and other lending and deposit rates that, along with any exchange rate response, affect the amount of private consumption and investment spending • Inflation will remain steady and low when total spending is kept close to the level of potential output over time Cash Rate* % % 7 7 6 6 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 2000 1 * 2004 2008 2012 2016 Data from June 2016 onwards are expectations derived from interbank cash rate futures Sources: ASX; Bloomberg Consumer Price Inflation % % 5 5 Year-ended 4 4 3 3 2 2 1 1 0 0 Quarterly (seasonally adjusted) -1 2004 Source: ABS 2008 2012 -1 2016 Measures of Underlying Inflation Year-ended % % 5 5 Weighted median 4 4 3 3 Trimmed mean 2 2 Trimmed mean (quarterly) 1 1 0 2004 Source: ABS 2008 2012 0 2016 Non-tradables and Tradables Inflation* % % Non-tradables** 4 4 Excluding utilities 2 0 2 0 % 1996 2001 Tradables*** 2006 2011 4 % 2016 4 Year-ended 2 2 0 0 Quarterly (seasonally adjusted) -2 1996 * ** 2001 2006 2011 Adjusted for the tax changes of 1999–2000 Excluding interest charges prior to the September quarter 1998 and deposit & loan facilities to June quarter 2011 *** Excluding volatile items (fruit, vegetables and automotive fuel) and tobacco Sources: ABS; RBA -2 2016 Labour Costs Year-ended growth % % Wage price index 4.5 4.5 Other states 3.0 3.0 WA and Qld 1.5 1.5 % % Average earnings per hour 10 10 5 5 0 0 -5 -5 1995 1999 Sources: ABS; RBA 2003 2007 2011 2015 Trimmed Mean Inflation Forecast* Year-ended % % 3 3 90 per cent interval 2 2 1 1 70 per cent interval 0 0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Confidence intervals reflect RBA forecast errors since 1993 * Sources: ABS; RBA 2018 Labour Market % % 7 65 Participation rate 6 64 Employment to working-age population ratio 5 63 Unemployment rate 4 62 3 61 2 60 2008 Source: 2012 ABS 2016 2008 2012 2016 Unemployment Rate Forecast* Quarterly % % 90 per cent interval 7 7 5 5 70 per cent interval 3 1998 2002 2006 2010 2014 Confidence intervals reflect RBA forecast errors since 1993 * Sources: ABS; RBA 3 2018 GDP Growth % % Year-ended 4 4 2 2 0 0 Quarterly -2 -2 1999 Source: 2003 ABS 2007 2011 2015 State Final Demand Year-ended growth % % WA and Qld 10 10 5 5 0 0 Rest of Australia -5 1999 -5 2003 Sources: ABS; RBA 2007 2011 2015 Household Income, Consumption and Wealth* % % Real, year-ended growth 10 10 Consumption 5 5 0 0 Disposable income % % Saving ratio 10 10 5 5 0 0 % % Net wealth** 650 650 550 550 450 450 350 350 1990 * 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 Household sector includes unincorporated enterprises; disposable income is after tax and interest payments; income level smoothed with a two-quarter moving average between March quarter 2000 and March quarter 2002; saving ratio is net of depreciation ** Per cent of annual household disposable income, before the deduction of interest payments Sources: ABS; RBA Private Residential Building Approvals Monthly ’000 ’000 18 18 Total* 15 15 12 12 Detached 9 9 6 6 Higher-density* 3 3 0 0 2008 2010 2012 * Smoothed lines are ABS trends Source: ABS 2014 2016 Employment and Non-mining Business Investment m Business investment* Employment $b Current prices NSW 3 45 Vic Qld 2 30 WA 1 15 0 0 2006 2011 2016 2006 * Refer to footnote 1 in the text Sources: ABS; RBA 2011 2016 GDP Growth Forecast* Year-ended % % 90 per cent interval 4 4 2 2 70 per cent interval 0 0 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 * Confidence intervals reflect RBA forecast errors since 1993 Sources: ABS; RBA 2018 Housing Price Growth Six-month-ended annualised % % 20 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 -5 -5 -10 -10 2004 2007 Sources: CoreLogic RP Data; RBA 2010 2013 2016 Housing Credit Growth* Year-ended % % 8 8 Housing credit 7 7 6 6 5 5 Net housing debt 4 4 3 3 2010 2012 * Seasonally and break adjusted Sources: ABS; APRA; RBA 2014 2016 Australia’s Trading Partner Growth* Year-average % RBA forecast % 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 -2 1981 1987 1993 1999 2005 * Aggregated using total export shares Sources: ABS; CEIC Data; RBA; Thomson Reuters 2011 -2 2017 China – Activity Indicators Year-ended growth % GDP by sector % Retail sales Tertiary 15 20 Secondary Nominal 10 15 Real 5 10 Primary 0 5 2008 2012 Sources: CEIC Data; RBA 2016 2008 2012 2016 Chinese Steel and Iron Ore Spot Prices US$/t US$/t 200 800 Chinese steel* (RHS) 150 600 100 400 Iron ore** (LHS, fines) 50 200 0 0 2008 2010 2012 2014 * Average of hot rolled steel sheet and steel rebar prices ** Free on board basis Sources: Bloomberg; RBA 2016 Terms of Trade 2013/14 average = 100, log scale index Forecast index 120 120 100 100 80 80 60 60 40 40 2018 1978 Sources: ABS; RBA 1988 1998 2008 Major Advanced Economies – GDP Growth % United States % % (LHS) %% Euro area (LHS) % Japan (RHS) Year-ended 3 33 63 6 0 00 00 0 -3 -3 -6 -3 -6 Quarterly -3 -6 2009 Source: -6 -6 2016 2009 Thomson Reuters -12 -6 2016 2009 -12 2016 Major Advanced Economies – Inflation Year-ended % United States* Euro area % Japan** 4 4 Headline 2 2 0 0 Core -2 -4 -2 -4 2009 2016 2009 2016 2009 * Personal consumption expenditures (PCE) inflation ** Excluding the effects of the consumption tax increase in April 2014 Sources: RBA; Thomson Reuters 2016 Australian Dollar US$ index US$ per A$ (RHS) 80 1.00 70 0.80 TWI (LHS) 60 0.60 50 0.40 2008 2010 Sources: Bloomberg; RBA 2012 2014 2016 For more information Visit the Reserve Bank website: • Chart Pack • Education • Statistics (updated monthly)