Practice 8-4, 8-5, 8-6
advertisement

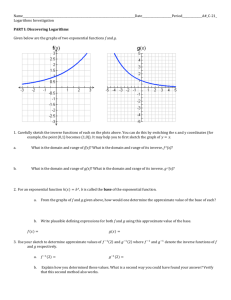
Name _____________________________ Class ___________________Date ____________ Practice 8-4, 8-5, 8-6 8-4 Assume that log 3 0.4771, log 4 0.6021, and log 5 0.6990. Use the properties of logarithms to evaluate each expression. Do not use a calculator. 1. log 12 2. log 16 3. log 3 5 Write each logarithmic expression as a single logarithm. 4. log54 + log53 5. log625 – log65 8. log2 6. log24 + log22 – log28 9. log 6x3y Expand each logarithm. 7. log xyz x yz 8-5 Use the Change of Base Formula to evaluate each expression. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 10. log212 11. log340 12. log48 Solve each equation. Check your answer. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 13. 2x = 243 14. 8n+1 = 3 15. 4n–2 = 3 Solve each equation. Check your answer. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 16. log 3x = 2 17. 4 log x = 4 18. log (3x – 2) = 3 19. 2 log x – log 5 = –2 8-6 t The formula P 50e 25 gives the power output P, in watts, available to run a certain satellite for t days. Find how long a satellite with the given power output will operate. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 20. 10 W The formula for the maximum velocity v of a rocket is v = c ln R, where c is the velocity of the exhaust in km/s and R is the mass ratio of the rocket. A rocket must reach 7.8 km/s to attain a stable orbit. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 21. Find the maximum velocity of a rocket with a mass ratio of about 18 and an exhaust velocity of 2.2 km/s. Can this rocket achieve a stable orbit? Use natural logarithms to solve each equation. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 22. ex = 15 23. 4ex = 10 24. ex+2 = 50 Solve each equation. Check your answer. Round answers to the nearest hundredth. 25. 4 ln x = –2 26. 5 ln (4x – 6) = –10 27. 3 – 4 ln (8x + 1) = 11 28. ln x + ln 3x = 14 Write each expression as a single natural logarithm. 29. ln 16 – ln 8 30. 3 ln 3 + ln 9 31. a ln 4 – ln b 32. 4 ln x + 3 ln y