MICROBIOLGOY FIELD TRIP SUMMARY FORM GRAM STAINING
advertisement

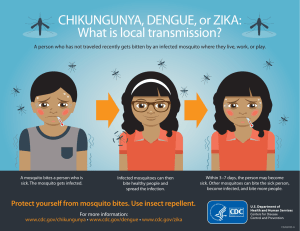
Name: __________KEY____________ Period:_____ Date:__________ MICROBIOLGOY FIELD TRIP SUMMARY FORM GRAM STAINING 1. List the steps of Gram Staining (in order): (5 – need at least five BOLD items) 1. Smear bacteria on slide 2. Allow to air dry. 3. Heat fix bacteria 4. Add 1o stain (Crystal Violet) 6. Add mordant (Iodine) 8. Add decolorizer (Acetone) 10. Add 2o stain (Safranin) 5. Rinse with water 7. Rinse with water 9. Rinse with water 11. Rinse with water 12. Dry slide & view cells 2. What was a positive aspect of this experience? (1) 3. What was a negative aspect of this experience? (1) 4. How could this experience have been improved? (1) SPEAKER TOPIC #1 (Tuberculosis) BLACK = Mr. Sonnenberg’s Research BLUE = things heard from speakers/presentation 1. Describe Tuberculosis (5 – have @ least five things listed) TB = Tubercle Bacillus, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Spread by coughing/sneezing; Human to Human transmission “A disease of the poor”; In normal body – macrophages attack TB (CD4/T-cell tell macrophage to destroy TB), in AIDS/Immuno-compromised body = T-cells are destroyed, TB is allowed to grow 2. What organism(s) does this disease affect and how? (2) Immune Disease; affects the lungs (pulmonary TB) of humans, can affect CNS, Lymphatic, Circulatory, Genitourinary systems, as well as bones & joints; Two types: Latent TB I – infected, show no symptoms (~ 95%) Active TB II – infected, disease symptoms (TB disease) (~5%) Not infected = (~ 45%) Symptoms = ongoing cough & tiredness, weight loss, loss of appetite, fever, bloody sputum, night sweats 3. What are some ways to prevent and/or treat this disease? (2) D.O.T.S. program – World Health Organization Drugs – a cocktail = Isoniazid (“INH”) [‘52], Pyrazinamide [‘52], Ethambutol [‘58], Rifampicin [‘72] most widely used Drugs are taken for 6-9 months = Non-compliance with drug therapy results in drug resistant TB (mutated); newer drugs are aimed at stopping the bacterial cell wall synthesis Drugs MUST: 1. Inhibit growth 2. Be non-toxic 3. Be orally available 4. Stay around long enough 5. Work quickly Surgery to remove TB infected lung tissue; proper medical practices & scientific research can help; Penicillin not effective against TB 4. What was a positive aspect of this experience? (1) 5. What was a negative aspect of this experience? (1) 6. How could this experience have been improved? (1) Name: __________KEY____________ Period:_____ Date:__________ SPEAKER TOPIC #2 (Dengue Fever) BLACK = Mr. Sonnenberg’s Research BLUE = things heard from speakers/presentation 1. Describe Dengue Fever (5 – have @ least five things listed) DF (Dengue Fever), one of 4 serotypes of viral infections; Flavivirus genus (Flaviviridae); RNA genome (10 genes) Disease of the tropical/sub-tropical areas; an obligate intra-cellular parasite An Arbovirus (Arthropod-borne Virus); Disease & mosquito occur in >100 countries Human to Mosquito to Human transmission; Mosquito (Aedes aegypti) DHF (Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever) 2. What organism(s) does this dies disease affect and how? (2) Affects humans; Symptoms = flu-like, high fever, rash, severe headache, retro-orbital pain (pain behind the eyes), muscle/joint pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite; DHF = blood vessels start to leak – bleed out of mouth, gums, anus, bruise easily DHF may lead to DSS (Dengue Shock Syndrome) 3. What are some ways to prevent and/or treat this disease? (2) Blood test required to detect infection; NO specific treatment, blood transfusions can help (esp. for DHF individuals) NO specific drugs – a tetravalent vaccine is being tested (similar to a vaccine for Yellow Fever that is already available) DF & DHF: Incubation= 5-8 days, Duration= 3-14 days (ave. of 7 days) A majority of viral infections DON’T lead to disease Viruses = only organisms known to have RNA genome Most arboviruses cycle of transmission= Arthropod vector Human Host (incidental host) ↓↑ Bird (vertebrate) Reservoir 1. Reservoir host usually doesn’t get sick 2. Incidental host usually DOES get sick Great question is = Are Arboviruses arthropod or vertebrate originated? Female mosquitoes are the only ones that bite (NOT males) – blood needed for development of eggs; Male mosquitoes feed on plant nectar Mosquito control Habitat reduction & Chemical/Biological pesticides Novel Strategies for Controlling Dengue Virus Diseases: 1. Genetic manipulation of mosquitoes 4. What was a positive aspect of this experience? (1) 5. What was a negative aspect of this experience? (1) 6. How could this experience have been improved? (1)