Glossary of RTI/PLC Terms
advertisement

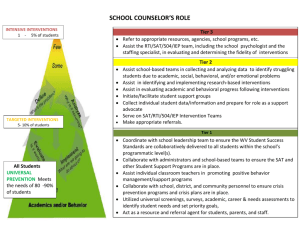
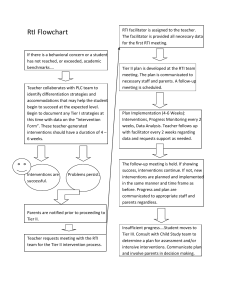
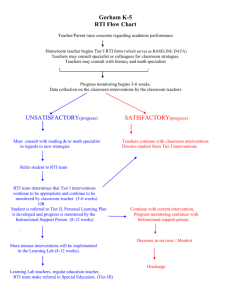
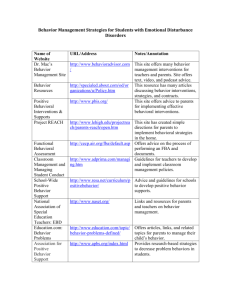
Glossary of RTI/PLC Terms Benchmarks (As related to standards) A subset of a standard designed to bring more specific targets or benchmarks for student performance. (sample at end of Glossary) Benchmark Indicators (As related to standards and benchmarks) A subset of the benchmark that describes specific grade level performance targets. (sample at end of Glossary) Behavior Intervention Plan A behavior plan is based on a Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA). It is developed and implemented by a collaborative team, which includes the student and parent. The plan includes positive behavior supports (PBS), identified skills for school success, and specific strategies for behavioral instruction. Common Assessment Any assessment used by more than one teacher to commonly assess student learning. Curriculum-Based Measurement (CBM) A precise tool for directly measuring student competency and progress in the basic skill areas of reading, spelling, math, and written language, using simple tests called “probes.” Data-Based & Data-Driven Decision Making The process of planning for student success (both academic and behavioral), by collecting and analyzing information to guide instruction or to develop, implement and evaluate an action/intervention. Differentiated Instruction The process of designing lesson plans that meet the needs of the entire range of learners in the classroom; such planning includes objectives, grouping practices, teaching methods, varied assignments, and varied materials chosen based on student skill levels and learning preferences. Duration Duration is the length (number of minutes) of each session multiplied by the number of sessions. “Sufficient duration” is dependent on a number of factors including the program or strategy being used, age of the student, and severity of the deficit involved. Some programs offer guidelines or recommendations for duration. Essential Learning The critical concepts, skills, knowledge, and dispositions each student must acquire as a result of each course, grade level, and unit of instruction that are embedded in standards.. They are the highest priority for instructional time, attention, and resources. They establish instructional priorities and are taught to mastery, not “covered”. They have Endurance, Leverage, and provide Readiness for the next level or course. Essential learnings may also be referred to as essential outcomes or power standards. Essential Standards .PSD’s efforts to organize state standards by grade level with more specific targets/benchmarks and specific grade level performance indicators. Endurance The knowledge, skills, and dispositions that students are expected to retain over time as opposed to merely learning something for a test. Equity The practice by which educators will ensure that all students have a fair and equal access to a high-quality education regardless of the students’ race, color, national origin, culture or linguistic difference, sex, age, marital status, sexual orientation or disability Fidelity Fidelity refers to the accuracy, loyalty and attentiveness with which an intended research design for instruction and/or intervention is implemented. To ensure standardization, intervention specialists must generally follow a prescribed protocol in order to attend to a program’s or strategy’s fidelity. Flexible Grouping Groups are formed according to specific student needs. Prescriptive, focused, researchbased interventions are provided to these groups by any trained or skilled staff member, regardless of special or general education categorization of the students or the educator’s special or general education job description. Students move in and out of groups according to need. Formative Assessment An assessment for learning created collaboratively by a team of teachers responsible for the same grade level and/or content area. Used frequently throughout the year to identify (1) individual students who need additional time and support for learning, (2) the teaching strategies most effective in helping students acquire the intended knowledge and skills, (3) program concerns-areas in which students generally are having difficulty achieving the intended standard- and (4) improvement goals for individual teachers and the team An assessment for learning used to advance and not merely monitor each students learning. Formative assessments are used to guide instruction. Formative assessments are used to ensure any student who experiences difficulty reaching or exceeding proficiency is given additional time and support as well as additional opportunities to demonstrate his or her learning. Formative assessments are also used to help students monitor their own progress toward an intended standard of proficiency. Frequency Documented how often an intervention or behavior occurs. It is an important element of a student’s prescribed intervention and should be monitored as an element of implementation fidelity. Functional Behavior Assessment (FBA) This is the process of determining the cause (or function) of behavior before developing an intervention or Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP). The intervention/BIP is based on the hypothesized cause (function) of behavior. Gap Analysis A method of measuring the difference between a student’s or group’s current level of performance and benchmark/targeted expectations. It is also used to determine progress of learning over time. Intensity The adjustment of duration, length and teacher-to-student ratio for a student’s academic or behavioral needs within an intervention. Intervention The systematic and explicit instruction provided to accelerate growth in an area of identified academic and/or behavioral need. Interventions are provided by both general and special education teachers and are based on training, not titles. They are designed to improve performance relative to a specific, measurable goal. Interventions are based on valid information about current performance, realistic implementation, and include ongoing student progress monitoring. Leverage Knowledge and skills that will be of value across contents. Mission The primary purpose of an organization. Multi-tiered Model School resources/interventions provide differing levels of intensity. Tier I is the universal or core academic and behavioral instruction that all students receive. Tier II are targeted/supplemental strategies. Tier III are intensive interventions. All are based on student responsiveness, with ongoing progress monitoring and focused assessment. See definition of Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3. Norms Rules or commitments developed by a team to clarify expectations on how to work together to achieve mutual goals. Outcomes Academic and social/emotional/behavioral targets that are endorsed and valued by students, families, and educators, and aligned with district goals. Positive Behavior Supports Establishes and maintains effective school environments that maximize academic achievement and behavioral competence of all learners. Behavior supports are provided for individual students in Tiers 2 and 3. It is data driven. Practices Interventions and strategies for all students that are evidence based. Problem Solving Process The problem solving process is an interdisciplinary, collaborative team process which is based on a multi-tiered model and includes data-driven decision making, parent-school partnerships, progress monitoring, focused assessment, flexible service delivery, and prescriptive, research based interventions for behavior and/or academics. Student Success Team (aka Problem Solving Team) Interdisciplinary teams composed of general and special education staff members who plan prescriptive interventions for students at risk for school failure or underachievement by completing targeted assessments, collecting and reviewing data, making data-driven decisions, partnering with parents, and participating in ongoing problem solving. Professional Learning Community (PLC) The essence of a PLC is a focus on and a commitment to the learning of every student. A PLC is composed of collaborative teams whose members work interdependently to achieve common goals linked to the purpose of learning for all. Inherent to a PLC are a persistent disquiet with the status quo and a constant search for a better way to achieve goals and accomplish the purpose of the organization: Educating All Children. Educators dedicated to working collaboratively in a process of collective inquiry and action research to achieve greater gains for students. Progress Monitoring The ongoing process that involves collecting and analyzing data to determine student progress toward benchmark or attainment of specific skills. The data generated is essential to determine effectiveness of the instruction/intervention and for making instructional decisions. Readiness Essential skills and knowledge that students need to be ready for the next grade level or course. Research-Based Instruction/Intervention/Practice Found to be reliable and valid based on evidence to suggest that when the program is used with a particular group of students, the students can be expected to make adequate gains in achievement. Ongoing documentation and analysis of student outcomes helps to define effective practice. In the absence of evidence, it must be considered “best practice” based on available research and professional literature. Response to Intervention (RtI) RtI is a school wide, systematic, collaborative process in which all school resources are aligned and matched to student’s academic and/or behavioral needs. Progress is monitored frequently in order to make important educational decisions. The outcome is to ensure that all students learn at high levels. Scaffolding: An instructional technique of breaking a complex task into smaller, more manageable components, providing support as students learn the task. Schoolwide PBS Team A team that develops the PBS structures within the school building. They train and support the teachers in implementing the PBS process. Schoolwide RtI Team A team that develops the RtI structures within the school building. They train and support the teachers in implementing the RtI process. SMART Goals Goals that are strategic & specific, measurable, attainable, results-oriented, and time bound. Focused on specific needs of students and linked to school district goals. Specific Learning Disability (SLD) Is an identifiable category of disability in both the federal law, Individuals with Disabilities Education Act of 2004 (IDEA 2004), and Colorado law, Exceptional Children’s Education Act (ECEA). This disability category was previously referred to in Colorado law as Perceptual/Communicative Disability or PCD. Specific, Measurable Outcomes A specific desired result from an academic and/or behavioral intervention. It should be written in observable and quantifiable terms to be measurable. Standard Protocol Interventions Refers to the implementation of a specific academic and/or behavioral intervention that is supported by research to be effective with students with similar needs/deficits. There are usually well defined entry criteria and clear progress monitoring tools. They are often chosen as an initial intervention for struggling students with similar problems. The standard protocol can be implemented in any tier, but is most commonly applied at the universal or targeted levels. When students are unresponsive to the intervention trial, more intensive ore individually designed interventions might be necessary. Summative Assessment An assessment of learning designed to provide a final measure to determine if learning goals have been met. It measures students’ level of learning after a unit of study. They yield a dichotomy: pass or fail, proficient or not proficient. CSAP and Final exams are an example of summative assessments Systems Supports that are needed to enable adults to implement evidence based practices with accuracy and consistency. Systematic Data Collection Monitoring student progress through setting a baseline and regularly monitoring student progress through the use of appropriate assessments. Tier 1 (Universal/Core) Interventions Research-based core instruction provided to all students in the classroom, regardless of individual needs. Appropriate differentiation of instruction in content, process, and product may occur. Tier 1 must meet the needs of 80-90% of the student population. Tier 2 (Targeted) Interventions Targeted interventions are to be implemented when data analysis indicates that a student is not making adequate gains from universal/core instruction alone. Generally, these are small group interventions with other students with similar needs. Progress monitoring is ongoing, thus the groups are fluid. It is intended to remediate deficits and promote continuous participation with universal instruction. Tier 3 (Intensive) Interventions Intensive interventions offer a student highly individualized, systematic and explicit instruction in the area of need. Progress monitoring happens more frequently than at Tier 2. Universal Screening The process of assessing all students in a school in specific content areas to determine performance in relation to the benchmarks and standards. Universal Assessments in use in PSD are CSAP (grades 3-10), NWEA’s MAP-Measure of Academic Progress (grades 2-9), DRA2 (grades K-6) SRI (grades 7-12) Validity An indication that an assessment accurately measures what it is designed to measure. Sample of Standard, Benchmark & Indicator Hierarchy PSD Essential Standards for Language Arts State Standard 1: Reading Students read and understand a variety of materials 1.1 Comprehension Skills (BENCHMARK) Students will use a variety of comprehension skills in reading (e.g., preview, predict, compare and contrast, self-monitor, summarize) 1.1.a Paraphrase, summarize and synthesize information from a variety of texts & genres with support (INDICATOR) 1.2 Prior Knowledge (BENCHMARK) Make connections between texts and prior knowledge and identify knowledge needed before reading about topics 1.2.a Make connections between texts and the world (INDICATOR) 1.3 Reading Purpose (BENCHMARK) Adjust reading strategies for different purposes 1.3.a Determine reading purpose and use strategies appropriate to that purpose (INDICATOR) 1.3.b Use text structures (e.g., cause and effect, problem/solution and compare/contrast) to locate and recall information (INDICATOR) 1.4 Word Recognition Strategies(BENCHMARK) Use a variety of word recognition skills and resources 1.4.a Locate definitions of unfamiliar words using dictionaries, glossaries and other sources (INDICATOR) 1.5 Vocabulary (BENCHMARK) Use information from reading to increase vocabulary and enhance language usage 1.5.a Select appropriate definitions from the dictionary to determine appropriate word meaning (INDICATOR)