Statistics 101 Name: Exam 4 ID#
advertisement

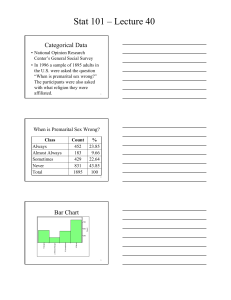
Statistics 101 Exam 4 May 10, 2002 Name: ID# INSTRUCTIONS: Read the questions carefully and completely. Answer each question and show work in the space provided. Partial credit will not be given if work is not shown. When asked to explain, describe, or comment, do so within the context of the problem. 1. [15 pts] Does regular exercise lead to lower resting pulse rates? A random sample of 20 college students was selected. Each student was asked whether or not they exercised regularly (at least 30 minutes of aerobic exercise 3 times a week). The resting pulse rate for each student was also taken. Below are the summarized data. Number Mean Std. Dev. No regular Exercise 8 72.0 9.13 Regular Exercise 12 65.0 7.01 (a) [4] Is this an observational study or an experiment? Explain briefly. (b) [11] Determine whether the mean resting pulse rate for college students who exercise regularly is lower than that of college students who do not exercise regularly. Be sure to include all the steps of a test of hypothesis. 1 2. [18 pts] For each of the following indicate: (1) whether it is an observational study or an experiment, (2) what statistical method you would use: two sample or matched pair and (3) the formula you would use. (a) [6] A pretest is given to students to assess their knowledge of the frog’s anatomy prior to covering this topic in class. The teacher wishes to see if boys are different from girls in terms of their mean pretest score. (b) [6] Students are then assigned at random to two groups. One group of students do simulated frog dissection using a computer program. The other group dissects actual frogs. A posttest on the frog’s anatomy is given after the dissection. The teacher wishes to estimate the difference in mean posttest scores for the two groups. (c) [6] The teacher also wants to see if students who did the computer dissection have a higher mean score on the posttest when compared to the pretest. 2 3. [15 pts] A business woman owns two fast food franchises in the same town. She wants to compare the average daily sales of the two. She chooses 5 days at random. On each day she records the daily sales for each franchise. Below are the data. Day Franchise 1 Franchise 2 Difference 1 1112 996 116 2 1212 1238 −26 3 1481 1385 96 4 2017 1867 150 5 2406 2212 194 Std. Dev. 551.4 492.4 82.6 (a) [3] Explain why this is a matched pairs problem. (b) [5] Construct a 95% confidence interval for the mean difference in franchise daily sales. (c) [4] Based on the confidence interval in (b), do the two franchises differ in terms of mean daily sales? Explain briefly. (d) [3] What conditions should be satisfied in order for the procedure in (b) to be valid? 3 4. [22 pts] The 1996 General Social Survey obtained information on religious preference and opinion on when premarital sex might be wrong. Below are the data. Religious Preference Catholic Protestant Other None When is premarital sex wrong? Almost Never Sometimes Always Always 226 120 37 62 384 227 117 355 74 37 16 15 147 45 13 20 831 429 183 452 Total 445 1083 142 225 1895 (a) [3] What proportion of the entire sample feels premarital sex is always wrong? (round your answer to 3 decimal places). (b) [4] Construct a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of the population that feels premarital sex is always wrong. (c) [3] Among only Catholics, what proportion feel premarital sex is always wrong? (round your answer to 3 decimal places). (d) [3] If religious preference and opinion on when premarital sex might be wrong are independent, what is the expected number of Catholics who feel premarital sex is always wrong? 4 (e) [3] What is the contribution to the χ 2 test statistic for the cell Catholic and feel premarital sex is always wrong? (f) [1] How many degrees of freedom will be associated with the χ 2 test statistic? (g) [3] The value of the χ2 test statistic is 147.0 with an associated P-value < 0.0001. What does indicate about the independence of religious preference and opinion on when premarital sex is wrong? (h) [2] Based on this survey, does religious preference cause people to hold a particular opinion on when premarital sex is wrong? Explain briefly. 5. [5 pts] You are planning a survey and want to determine how many people to sample. (a) [3] If you want to estimate a population proportion and have a maximum margin of error of 2.2%, how many people should you have in your sample? (b) [2] Once you get your sample you discover you have 948 males in it. What is the maximum margin of error for estimating the male population proportion? 5