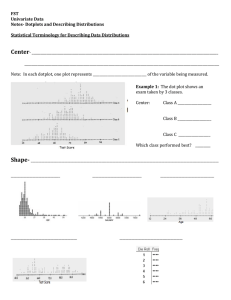
GRAPPLING WITH DATA Variability in observations Visualizing the sample data •
advertisement

GRAPPLING WITH DATA Variability in observations • Sources of variability • measurement error and reliability Visualizing the sample data • Frequency distributions – Plotting frequency distributions – Types of distributions FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONS skewed normal bimodal truncated GRAPPLING WITH DATA Reducing and describing the sample • Measures of central tendency – Mode: the most common score(s) – Median: the middle score – Mean: the “center of gravity” – sum / n • Measures of dispersion – Range: largest minus smallest score – Variance: average squared deviation from mean USING EXCEL FOR DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS • Entering data into a spreadsheet – Formatting numerical cells • Generating frequency distributions – Scores go in “data array” – Categories go in “bins array” – Select cells adjacent to bins + 1 – Select Frequency formula, data and bin arrays – Press CTL+SHIFT+ENTER USING EXCEL FOR DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS • Obtaining measures of central tendency – “by hand” – By using Excel formulas • Obtaining measures of variability – Variance and standard deviation TABLE ASSIGNMENT • Obtain data file from web or lab • Use Excel to calculate means, SD’s • Construct table with those data for – Three tasks (simple form, color, complex form) – X four array sizes (4, 8, 16, 32) • Format according to APA Style guide Signal Detection Analysis “no” “yes” Target absent (noise) Target present (signal+noise) Response Criterion SIGNAL DETECTION ANALYSIS Response: “YES” “NO” Stimulus Present hits misses Stimulus Absent false alarms correct rejections Deriving d’ d’ = NORMSINV(prob hit) - NORMSINV(prob FA) In effect, the difference in “distance” of the mean of the normalized distributions for hits versus false alarms (!) Signal Detection Analysis Vary % of trials with targets: 10% 50% 90% p(hit) .24 .66 .94 p(FA) .06 .36 .77 NormSI(h) -0.71 0.41 1.55 NormSI(fa) -1.55 -0.36 0.74 d’ 0.85 0.77 0.82 Conclusion: likelihood of a “signal” affects response criterion (or “bias”), not “sensitivity” to the signal. FIGURE ASSIGNMENT • Derive d’s from Hits & False alarm rates in Lab 5 • Construct an APA-formatted Figure with: – Mean d’ for 2 durations x 2 frame stimuli – Error bars indicating standard deviations – Figure caption on a separate page