October 3, 2007 PHY2053 Quiz 4 (Section 4.6, 5.1-5.3)
advertisement

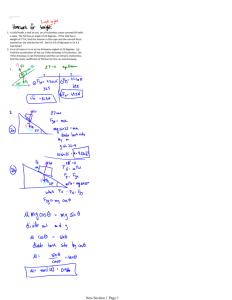
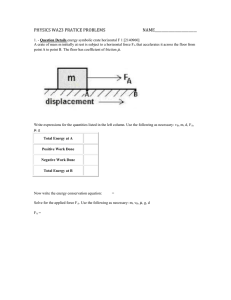
October 3, 2007 PHY2053 Quiz 4 (Section 4.6, 5.1-5.3) Name: UFID: 1. (5 pts) A 5.00 kg block is resting on an incline of 30.0º. When you push the block vertically down with 30.0 N, it starts to slide down. Find the acceleration of the block. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the incline and the block is 0.400. Taking +x direction downhill and +y perpendicular to the incline, we express each force acting on the block in components: Fex = (30sin30º, -30cos30º) = (15N, -26.0N) Fg = (mgsin30º, -mgcos30º) = (24.5N, -42.4N) n = (0, mgcos30º+30cos30º) = (0N, 68.4N) f = (-μn, 0) = (-27.4N, 0N) ΣFx = 15+24.5-27.4 = 12.1N, a = ΣFx/m = 2.42 m/s² You only need x-components of the forces to solve the problem, but it’s important to write down the y-components and make it sure they add up to zero. 2. (5 pts) A crate of mass 5 kg rests on a horizontal table and is connected to a light string that passes over an pulley and is then fastened a hanging object with mass 10 kg. The hanging object is 0.5 m above the floor. When you let the object drop, the crate on the table slides 1 m and stops. What is the kinetic coefficient between the crate and the table? (Hint: Do this algebraically, without substituting values until you get an expression for μ.) We first calculate the speed of the block when the hanging object hits the ground (m = 5kg, M = 10kg, L = 0.5m): (m+M)a = Mg – μmg, a = (M-μm)g/(m+M), v² = 2aΔx = 2L(M-μm)g/(M+m) After the hanging mass hits the ground, only the friction is exerted on the block and the block slides another 0.5m. ma’ = -μmg, a’ = -μg Use Vf² - Vi² = 2aΔx and solve for μ: 0²-v² = -2μgL, -2L(M-μm)g/(M+m) = -2μgL, μ = M/(M+2m) = 10/(10+2×5) = 0.5 I hope you guys are interested in this problem, for it gives a practical way to measure μ. 3. (5 pts) A crate of mass 15.0 kg is pushed up a rough incline of 20.0º. The pushing force is horizontal and 200 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.300. The crate is pushed 5.00 m. Determine the work done by the net force on the crate. Calculate the work done by each force and add (take uphill as +x): Wex = 200cos20º×5 = 940J Wg = -mgsin20º×5 = -251J Wf = -0.3(mgcos20º+200sin20º)×5 = -310J Wnet = 940-251-310 = 379J 4. (5 pts) A 100 g stone is thrown upward from the top of a building at an angle of 45.0º to the horizontal with an initial speed of 20.0 m/s. The point of release is 50.0 m above the ground. Find the change in kinetic energy of the stone during the projectile motion. During the projectile motion, only the gravity does work, thus ΔKE = Wg = mgΔh = 0.1×9.8×50 = 49J You can calculate the final velocity first, and then plug the result into the definition of ΔKE.