Construction Engineering 221 Probability and statistics Normal Distribution
advertisement

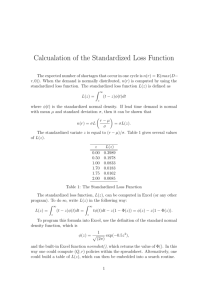
Construction Engineering 221 Probability and statistics Normal Distribution Normal distribution • Normal distribution is continuous (X can assume any value- measurement) • Binomial was discrete distribution (X can assume only certain values, usually integer values representing counts) • Binomial is the most common counting distribution (probability) • Normal distribution is the most common measurement distribution (classification) Normal distribution • Normal distribution is described by two parameters, mean μ and variance σ2 • The shape of the graph (distribution) varies for each population or sample based on the mean and variance, but each normal distribution has the same equation as noted on page 67 in the book Normal distribution • Normal distributions are symmetrical about the mean, and the curves never intercept the X-axis, • Normal distribution describes a great number of natural phenomena (height, weight, intelligence, measurement errors of materials, test scores) occurring in a population Normal distribution • Standardization- set the mean to 0 and the standard deviation to 1, a simple transformation • X-μ/σ is the standardization equation. • Example ACT is a normalized test with a mean of 18 and a sd of 6. If you scored an 18, you would have a standardized score of 0 (0-0/6) or the mean of a standardized distribution Normal distribution • If you had a score of 30, you would have a standardized score of 30-18/6, or 2, meaning two standard deviations above the mean. • When variables are standardized in this manner (an ACT score of 30 is transformed to “2”), they are denoted by the letter z Normal distribution • Using standardized (z) values allows for the production of standard normal tables to define areas under the curve (probabilities or percentages) • Need to keep track of 1-tail versus 2-tail probabilities • Can also calculate areas under the curve between values • Review normal distribution tables on page 180181- note the rule of 9’s and 5’s