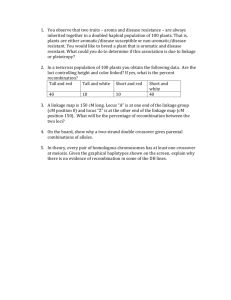
Review Questions Polyploid Segregation Q1.
advertisement

Review Questions Polyploid Segregation Q1. (5) What are the differences between disomic and tetrasomic inheritance in tetraploids? (20) Determine the proportion and types of gametes produced by the duplex AAaa, if: • The individual is a disomic polyploid: i. Homologues are homozygous ii. Homoelogues are heterozygous. • The individual is a polysomic polyploids. Draw chromosomes to show the segregation of genes among different gametes considering random chromosome segregation. Q2. (12) Molecular mapping in polysomic polyploids can be achieved by single dose restriction fragments. Explain this mapping strategy for polysomic polyploids by considering a hypothetical example of segregation of DNA bands/fragments among the progeny. (8) What are the requirements for this mapping strategy? Is it really different from diploid mapping? If not, why not? Q3. (20+5) Using a simplex quadrivalent diagram show the segregation of two loci, one (Aaaa) is next to the centromere, and the other (Bbbb) away from the centromere. Why do you see the double reduction in tetraploid segragation not in diploid segregation? Questions 2 Q4. (25) What is a double reduction? Explain double reductions with a suitable diagram. What are the requirements for double reduction to happen? What are the biological significances of double reduction? Q5. (30) Describe the three models of segregation in autopolyploids. Draw segregating chromosomes or chromatids to explain these models. Segregation of an either simplex or duplex may be considered to explain these models. Genome Organization: Q6. (20) What do we know about the following from the sequences of the Arabidopsis genome? i) Organization of genes in the genome; ii) telomeres; iii) centromeres; iv) transposable elements. Q7. (20) A possible question from the Heslop-Harrison paper. Linkage Detection and Estimation Q8. (20) In peas round seed shape is dominant over wrinkled shape and red flower color is dominant over white. Both traits are governed by single genes. The following data were obtained from a cross between two parents. 1. P1 (Round seed, red flower) x P2 (Wrinkled seed, white flower); F1 (round, red) F2 segregation: Round seed and red flower = 450 plants Round seed and white flower = 80 plants Wrinkled seed and red flower = 75 plants Wrinkled seed and white flower= 115 plants Questions 3 Carry out the suitable statistical analysis to test if there are any linkages between these two traits. Q9. (25) The following F2 segregation data are provided by your major professor for statistical analysis. He does not know about the mode of inheritance of genes that control plant height and nematode resistance in a cross between two tomato lines. He wonders if these two traits are linked. F2 segregation Tall plant and resistant to nematode = 550 Tall plant and susceptible to nematode = 100 Dwarf plant and resistant to nematode = 80 Dwarf plant and susceptible to nematode= 150 Carry out a suitable statistical analysis to determine if there is any linkage between plant height and nematode resistance. Q10. (5) Considering θ as the recombination fraction between two genes that are in a repulsion phase linkage (Ab/aB) write the frequency of gametes that will be produced in a double heterozygous plant. (5) What will be the frequencies of gametes in terms θ, if the genes are in repulsion phase linkage? (5) How about if they are in coupling phase? Q11. (30) In a dihybrid segregation between resistance to powdery mildew disease and seed shape in peas the following classes were observed. • Round and resistant = 203 • Round and susceptible = 65 • Wrinkled and resistant = 60 • Wrinkled and susceptible = 5 Round is dominant over wrinkle. Questions 4 Resistance is dominant over susceptibility. Both traits are governed by single genes. (10) Is there any linkage between these two traits? (2) Write the genotypes of both parents. (18) Develop a suitable maximum likelihood equation to determine the recombination fraction between these traits. Determine the extent of linkage between these two traits. What could be the error variance for this estimate? Q12. (30) Using the available information from the Allard’s paper [Allard 1956] determine the recombination fraction and its standard error between flower color and plant height in peas. Red flower and tall plants = 990 plants Red flower and dwarf plants = 400 plants White flower and tall plants = 375 plants White flower and dwarf plants = 80 plants Apply Newton-Raphson Interaction in calculating the best recombination fraction estimate. Q13. (5) List advantages and disadvantages of using: • maximum likelihhod, • product method for determining the extent of linkage between two traits. (20) Your friend suspects that one of the traits he is studying has reduced viability in recessive homozygous condition. He found the following classes in the study of leaf color and male fertility. Questions Green leaf and male fertile = 805 Green leaf and male sterile = 305 Albino leaf and male fertile = 105 Albino leaf and male sterile = 8 What method of linkage determination would you apply if these two traits are linked in repulsion? Calculate the recombination fraction and its standard error. Q14. (10) It was found that an albino lethal mutant is linked to flower color in repulsion phase. Flower color red is dominant over white, and normal green leaf is dominant over albino. Both traits are governed by single genes. In one experiment he noticed that there were no albino plants survived to the flowering stage. He, however, collected following data. Red flower and green leaf = 1400 White flower and green leaf = 450 How would you analyze these data to obtain the best possible estimate of linkage between these two traits? Develop a suitable maximum likelihood equation to determine the map distance between these two traits. Assume that the recombination fraction is θ. Q15. (15) Describe G and Z statistics that are applied to test the significance of linkages between two loci. Write the formulae and null hypotheses for each statistic. (10) What are the similarity and differences between the two approaches? 5 Questions 6 Q16. (5) Preliminary data indicate that the crossing over % increases with water stress in maize. Design an experiment to investigate if there is any significant effect of water stress on the recombination fraction between the two linked traits that were studied previously under water stress and normal growing conditions. (15) Describe in detail the statistical analysis to use in investigating if there is any significant effect of water stress on the recombination fraction in maize. Q17. (20) What is information in linkage analysis? List the factors that influence the information in a given cross. How can you improve information of a data set? Why backcrosses result only half the information of the complete classification? How do you obtain complete classification? When is it worthwhile to go for complete classification and how do you decide whether you should go for complete or incomplete classifications? Q18. (15) When do you need to apply: i) Grid search, ii) NewtonRaphson Iteration or iii) EM (expection maximization) algorithm? Determine the MLE of θ from the following equation by applying grid search. 2480θ 4 + 980 θ 2 – 61 = 0 What is the most important point to remember for obtaining an accurate calculation of θ? Questions 7 Q19. (25) Using the tables available in Allard (1957) determine the MLE of θ for the following data by applying Newton-Raphson iteration. Tall plants are dominant over dwarf in peas. Inflated pod is dominant over constricted pods. Tall and inflated pods = 1578 Tall and constricted pods = 602 Dwarf and inflated pods = 657 Dwarf and constricted pods = 10 The differentiated support function to consider here is: The traits are in repulsion phase linkage. Q20. (15) The size of a segregating population determines the accuracy of the recombination fraction between two linked traits. Determine the size of the segregating population required to determine the θ between two traits in repulsion with a standard error of 10%. The MLE of θ is 0.15. Questions 8 Developing Maps Q21. (20) In developing a linkage map what are the important points to consider? How do you determine what loci to place in a specific linkage group? What is the best way to order them in a linkage group? In a given interval only odd number of crossover events are recognized, not the even number events. How can you overcome this problem in constructing an accurate map? Describe the steps to consider in developing an accurate linkage map. Q22. (10) What are mapping functions? What are the assumptions in Morgan’s, Haldane’s and Kosambi’s functions? Out of these three functions which one is mostly used? What is the limitation of a mapping function?