Technical Note: Comparing R407C and R410A
advertisement

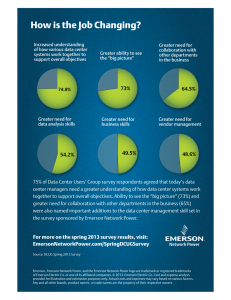
Technical Note: Comparing R407C and R410A Table of Contents Purpose pag. 3 1. R407C and R410Apag. 3 2. R407C and R410A Comparative Data pag. 3 3. Advantages and Disadvantages of the R407C and R410A pag. 4 3.1 R407Cpag. 4 3.2 R410Apag. 4 Conclusionpag. 4 2 Purpose The purpose of this document is to provide a brief overview of refrigerants R410A and R407C; describing their characteristics and comparing their environmental impact, regulatory compliance, and resulting system efficiency. 1. R407C and R410A The R407C is a non-ozone depleting blend of three HFC refrigerants (R32 wt 23%, R125 wt 25% and R134A wt 52%), designed to closely match R22 pressure and performance to allow for a smooth transition from R22 to R407C. Although this transition is suggested, the R407C’s performance characteristics are similar to that of the R22. The R410A is a non-ozone depleting blend of two HFC refrigerants (R32 wt 50% and R125 wt 50%), designed to provide benefits in efficiency and system size by increasing system pressure and taking advantage of thermodynamic and transport properties. Clearly, the R410A exhibits higher pressures and refrigeration capacity than the R407C. The properties and performance of the R407C and R410A are compared in Table 1. 2. R407C and R410A Comparative Data Properties/Performance R407C R410A Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) (CFC11=1.0) 0 0 Global Warming Potential (GWP) (CO2=1.0 [100 yr integrated time horizon]) 1600 1725 Total Equivalent Warming Impact (TEWI)a -16%a Maximum Allowable Concentration in the Workplace Flammable Toxicity 1000 ppm 1000 ppm No No Very Low Very Low +1 to +5 %a Relative Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER)a +90 to +135 psia Change in Discharge Pressurea Table 1. Properties and Performance of the R407C and R410A. a Compared to R407C. Source: DuPont Fluorochemicals 3 3. Advantages and Disadvantages of the R407C and R410A 3.1 R407C Advantages • Exhibits thermo-physical properties that are similar to the R22, thus, when changing from the R22 to the R407C, minimal alterations in the refrigeration system are required. An R22 system and an R407C system use many of the same components. Disadvantages • Multiple significant leaks (50 wt. %), and recharges may, in some cases, cause the refrigerant composition to change. This could have a minor impact on energy efficiency and heat transfer conditions. 3.2 R410A Advantages • The global warming potential value of the R410A is higher compared to the R407C, but the TEWI is lower. • Characteristics of the R410A permit the use of a smaller displacement compressor with a smaller coil area and lower refrigerant charge, while maintaining system efficiencies comparable to R407C equipment. Disadvantages • Operating pressures are higher than the R407C, which requires thicker walled tubing, high pressure compressors, and the use of components capable of withstanding these high pressures. An R407C and an R410A system use none of the same components, thus, the R407C system must be completely redesigned in order to use the R410A. Conclusion While the R407C and R410A offer almost equivalent capacity and performance characteristics, the R410A has a lower TEWI than the R407C. Both have the same A1 designation in the ASHRAE1 Standard 34: Designation and Safety Classification of Refrigerants. While both refrigerants are widely available, R410A is currently being used extensively for most new air cooled systems. 1 The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers establishing guidelines relating to HVAC systems. 4 Sources ■ ■ DuPont Fluorochemicals ASHRAE, The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers establishing guidelines relating to HVAC systems. Glossary ■ EER: Relative Energy Efficiency Ratio ■ GWP: Global Warming Potential ■ ODP: Ozone Depletion Potential ■ ppm: parts-per-million ■ psi: pound per square inch ■ TEWI: Total Equivalent Warming Impact 5 Ensuring The High Availability Of Mission-Critical Data And Applications. About Emerson Network Power Emerson Network Power, a business of Emerson (NYSE:EMR), delivers software, hardware and services that maximize availability, capacity and efficiency for data centers, healthcare and industrial facilities. A trusted industry leader in smart infrastructure technologies, Emerson Network Power provides innovative data center infrastructure management solutions that bridge the gap between IT and facility management and deliver efficiency and uncompromised availability regardless of capacity demands. Our solutions are supported globally by local Emerson Network Power service technicians. Learn more about Emerson Network Power products and services at www.EmersonNetworkPower.eu Locations Emerson Network Power Global Headquarters 1050 Dearborn Drive P.O. Box 29186 Columbus, OH 43229, USA Tel: +1 614 8880246 Emerson Network Power Thermal Management EMEA Via Leonardo Da Vinci, 16/18 Zona Industriale Tognana 35028 Piove di Sacco (PD) Italy Tel: +39 049 9719 111 Fax: +39 049 5841 257 ThermalManagement.NetworkPower.Eu@Emerson.com Emerson Network Power United Kingdom George CurlWay Southampton SO18 2 RY, UK Tel: +44 (0)23 8061 0311 Fax: +44 (0)23 8061 0852 While every precaution has been taken to ensure accuracy and completeness herein, Emerson assumes no responsibility, and disclaims all liability, for damages resulting from use of this information or for any errors or omissions. Specifications subject to change without notice. Globe Park Fourth Avenue Marlow Bucks SL7 1YG Tel: +44 1628403200 Fax: +44 1628403203 Uk.Enquiries@Emerson.com EmersonNetworkPower.eu Follow us on Social Media: Emerson. Consider it Solved. and Emerson Network Power are trademarks of Emerson Electric Co. or one of its affiliated companies. ©2014 Emerson Electric Co.