www.studyguide.pk Issues of Finance Overseas Direct Investment (ODI)
advertisement

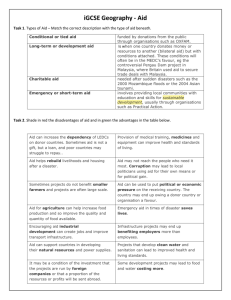
www.studyguide.pk Issues of Finance Overseas Direct Investment (ODI) Foreign investment from private firms. However, this goes to a very limited number of countries, usually NICs e.g. Brazil, Mexico, China & Hong Kong. This is mainly through investment in factories. ODI can be an important stimulus for economic & social development but is usually done for profits & often enables countries to be manipulated by TNCs. Problems: International Capital Movements – movement of money in & out of the country. Displacement of indigenous production. May control the extent of technology transfer. Social structure changed – change customs & beliefs. Can leader to greater inequalities. Can lead to dependency of a country on aid. Aid Aid is the flow of capital to LEDCs from a government or multi-lateral organisation. 1. Its objective is non-commercial from the point of view of the donor. 2. Characterised by concessional terms i.e. interest & repayment rates should be softer than commercial rates. There are several forms of aid: Bilateral Aid – One country gives to another country. Often the MEDC uses it for its own advantage so that it can dictate the conditions of aid. Multi-lateral aid – more than 1 country gives aid to a number of countries. Charity – These are from Non-government organisations (NGOs) but are small donations compared with other types of aid. Aid may also be short-term emergency aid or long-term aid to improve living standards. Aid is ver rarely allocated depending on the needs of the LEDC. For example it is not necessarily the poorest countries which receive aid as India gets most aid from the UK as it is a former colony. Usually for: Economic – promote exports. Political Strategic reasons. Most aid is given with the expectation of receiving something in return e.g. USA wants strategic help in the Middle East so helps Egypt & Turkey. Alternatively aid may be given as loans which are paid back or are tied to trade. The best aid is: Untied aid – spend on whatever they want. Longer repayments. More grants with the minimum number of strings attached. There are a few success stories e.g. Taiwan & S Korea where aid led to self-sustained growth. Rio Summit – 1992 LEDCs press for increase in aid for environmental reasons, as they want environmentally sustainable projects that don’t cause pollution. There is a gradual change towards real developments that help people e.g. medical aid, amenities & improvements in food production. However, the amount of aid given is falling.