Hoeganaes Corporation to present its latest developments in powder properties at PM2014 World Congress
advertisement

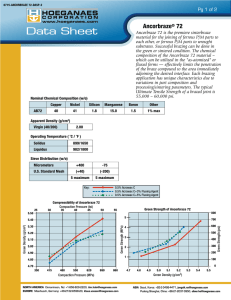
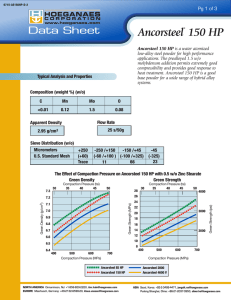
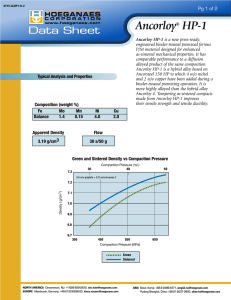
Hoeganaes Corporation to present its latest developments in powder properties at PM2014 World Congress US based metal powder producer Hoeganaes Corp has announced that it will be presenting a total of ten papers at the 2014 World Congress on Powder Metallurgy & Particulate Materials, Orlando, Florida, May 18‐ 22, 2014. The company will look in detail at a number of developments it has made in the production of powder for PM applications as well as discussing its work on producing metal powders for the fast growing Additive Manufacturing sector. The PM2014 World Congress is organised and sponsored by the Metal Powders Industries Federation (MPIF) and will feature over 450 industry experts presenting the latest developments in Powder Metallurgy, particulate materials, tungsten, hardmetals and Additive Manufacturing. The concurrent trade exhibition will include some 175 booths showcasing the leading suppliers of PM processing equipment, powders, products and Additive Manufacturing equipment. At last year’s PM2013 Conference, members of the Hoeganaes Research and Development team received both the Howard I. Sanderow Outstanding Technical Paper Award and the Excellence in Metallography Award. Hoeganaes will once again be a strong presence at this year’s event, presenting seven papers during the Technical Program as well as three Special Interest presentations. Technical Papers “The Effect of Bonding Method on the Properties of Low‐Alloy PM Steels.” Kylan McQuaig (speaker), Peter Sokolowski, Robert Causton, Hoeganaes Corporation. To reduce segregation, dusting, and overall inhomogeneity of PM mixes, the use of various bonding techniques has become increasingly common. This paper investigates the effect of bonding method on low‐alloy PM grade steels. The benefits and drawbacks of using polymer‐based binders vs diffusion alloying are examined in detail. Monday, May 19th. 10:00am‐11:15am. Session 2 “Diffusion Behavior and Microstructural Transformations of PM Steels Containing Silicon.” Thomas F. Murphy, FAPMI (speaker), Christopher T. Schade, Hoeganaes Corporation; Alan Lawley, FAPMI, Roger Doherty, Drexel University. Silicon as an alloying additive has been shown to be effective in improving the mechanical properties of both iron and low alloy PM steels. The effectiveness of the additives is dependent on the distribution of the elements throughout the material volume. The distribution of silicon and the other elements are quantified in mixes using different alloying methods. The mechanical properties of the various mixes are measured in an attempt to correlate the microstructure with the desired properties. Monday, May 19th. 2:15pm‐3:30pm. Session 7 “Production of High‐Density PM Automotive Components Utilizing Advanced Warm‐Die Compaction Technology.” Francis G. Hanejko (speaker), Sunil N. Patel, Michael L. Marucci, Hoeganaes Corporation; Gregory Falleur, PMTII, Suresh O. Shah, Cloyes Gear & Products. High density via warm die compaction has broadened potential applications for PM components. A key initiative in achieving higher part densities are advances in lubricants and premixing technology enabling reductions in the amount of lubricant required. Discussed in this paper is a new lube system that enables lubricant levels as low as 0.25% thus enabling higher green densities up to approximately 7.5 g/cm3. Coupled with high green densities, green strengths approaching 30 MPa are achieved, thus minimizing green cracking during compaction. This new powder premix has proven successful at Cloyes Gear in the production of automotive valve train components. Tuesday, May 20th. 8:00am‐9:15am. Session 17 “New Machinability Additive for PM Steels.” Bruce Lindsley (speaker), Hoeganaes Corporation. The subject of improved PM steel machinability is an ongoing focus as part tolerances become tighter, geometries more complex, and machining throughput affecting the cost competitiveness of PM products. One advantage of PM is that machinability additives can be easily admixed into the powder and therefore into the final part. A new machining additive with improved stability has been developed to complement MnS for use in PM steels. This paper describes the properties of this new machining additive. Tuesday, May 20th. 3:15pm‐4:30m. Session 32 “Development of Atomised Powders for Additive Manufacturing.” Christopher T. Schade (speaker), Chris Walton, Thomas F. Murphy, FAPMI, Hoeganaes Corporation. Powders for Additive Manufacturing require characteristics not typically found in atomised powders for press and sinter applications. In general, these powders require high apparent densities and better flow. This paper reviews both water and gas atomised powders produced specifically for Additive Manufacturing. Water versus gas atomisation, as well as powder characteristics such as particle shape, particle size distribution, surface roughness and chemistry are studied to determine the effectiveness of these powders for use in Additive Manufacturing. Wednesday, May 21st. 9:15am‐10:30am. Session 39 “Development of New Soft Magnetic Composite Material Possessing Higher Levels of Magnetic and Mechanical Performance.” Francis G. Hanejko (speaker), Hoeganaes Corporation. Greater usage of soft magnetic composites depends on attainment of higher magnetic permeability and induction via higher density, and greater mechanical strength. Mechanical strength relies on density in addition to the lubricant used during compaction. Described in this paper is a newly developed material capable of achieving >7.5 g/cm3 density while maintaining high resistivity. Another key aspect of this material is the high cured strength, approaching 130 MPa. The data presented in this paper will highlight the key magnetic and mechanical properties. Thursday, May 22th. 8:00am‐9:15am. Session 54 “Iron‐Silicon Water‐Atomised Powders for Electromagnetic Applications.” K.S. Narasimhan, FAPMI (speaker), Christopher T. Schade, Hoeganaes Corporation. Laminations made from iron‐silicon alloys have been used in a variety of electromagnetic applications. However, there is considerable waste of materials using existing production methods. Hoeganaes has developed water atomised Fe‐Si powders that can address the deficiencies of lamination steels and can be fabricated into near net shape for electromagnetic parts by typical powder metallurgy routes. This allows for the design of parts with three dimensional flux capabilities and the ability to be heat treated at 800°C without degrading the insulating characteristics, allowing for reduction of residual stresses resulting from the compaction process. Thursday, May 22th. 9:3am0‐10:45am. Session 61 Special Interest Sessions “Examination of Defects and Fracture Surfaces Using Non‐destructive Metallographic Techniques.” Thomas F. Murphy, FAPMI, Hoeganaes Corporation. Detecting the presence of a feature such as a crack, blemish, or surface defect using NDT methods is an important part of the PM process. This presentation offers metallographic techniques for examining and interpreting results of part and fracture surface analysis, including light optical and scanning electron microscopy. In addition, some dos and don'ts of sample preparation are included where preservation of sample integrity is important. Monday, May 19th. 3:45pm‐5:00pm. SIP1 “Techniques for the Examination of Fatigue Fractures.” Thomas F. Murphy, FAPMI, Hoeganaes Corporation; M. Andersson, Höganäs AB. The features present on and around fatigue fracture surfaces contain evidence of both the material behaviour under stress and the eventual cause of component failure. Evaluating these surface characteristics and the surrounding areas will be discussed in this presentation using several metallographic methods, including light and scanning electron microscopy. In addition, examples of techniques used to quantify the features on fracture surfaces will be presented. Tuesday, May 20th. 3:15pm‐4:30pm. SIP2 “Development of Alloy Systems for High‐Temperature Sintering.” Christopher T. Schade, K.S. Narasimhan, FAPMI, Hoeganaes Corporation. High temperature sintering has led to opportunities in alloy development not previously available to powder producers. The mechanical properties of alloys containing elements such as chromium, silicon, vanadium and manganese, which benefit from high temperature sintering and accelerated cooling are reviewed. The processing, microstructures, and mechanical properties are compared with those of conventional PM steels. Wednesday, May 21st. 9:15am‐10:30am. SIP3 Attendees can visit the Hoeganaes Corp. stand (booth 422) at the centre of the exhibition hall. Exhibit hours run 9.30am to 4.00pm Monday and Wednesday, 8.30am to 4.00pm Tuesday.