BCB 444/544 Lecture 20 #20_Oct08 Protein Structure Basics,
advertisement

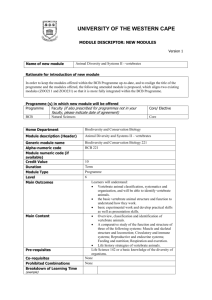
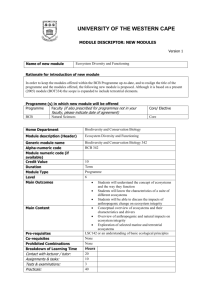
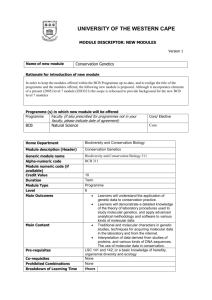
BCB 444/544 Lecture 20 Protein Structure Basics, Visualization, Classification & Comparison #20_Oct08 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 1 Required Reading (before lecture) Mon Oct 8 - Lecture 20 Protein Secondary Structure Prediction • Chp 14 - pp 200 - 213 Wed Oct 10 - Lecture 21 Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction • Chp 15 - pp 214 - 230 Thurs Oct 11 & Fri Oct 12- Lab 7 & Lecture 22 Protein Tertiary Structure Prediction • Chp 15 - pp 214 - 230 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 2 BCB 544 - Extra Required Reading Assigned Mon Sept 24 BCB 544 Extra Required Reading Assignment: for 544 Extra HW#1 Task 2 • Pollard KS, …., Haussler D. (2006) An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Nature 443: 167-172. • http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v443/n7108/abs/nature05113.html doi:10.1038/nature05113 • PDF available on class website - under Required Reading Link BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 3 BCB 544 Projects (Optional for BCB 444) • For a better idea about what's involved in the Team Projects, please look over last year's expectations for projects: http://www.public.iastate.edu/~f2007.com_s.544/project.htm Please note: wrong URL (instead of that shown above) was included in originally posted 544ExtraHW#1; corrected version is posted now • Criteria for evaluation of projects (oral presentations) are summarized here: http://www.public.iastate.edu/%7Ef2007.com_s.544/homework/HW7.pdf BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 4 Assignments & Announcements - #1 Students registered for BCB 444: Two Grading Options 1) Take Final Exam per original Grading Policies 2) Instead of taking Final Exam - you may participate in a Team Research Project If you choose #2, please do 3 things: 1) Contact Drena (in person) 2) Send email to Michael Terribilini (terrible@iastate.edu) 3) Complete 544 Extra HW#1 - Task 1.1 by noon on Mon Oct 1 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 5 Assignments & Announcements - #2 BCB 444s (Standard): 200 pts 200 100 500 pts Midterm Exams = 100 points each Homework & Laboratory assignments = 200 points Final Exam Total for BCB 444 BCB 444p (Project): 200 pts 200 190 590 pts Midterm Exams = 100 points each Homework & Laboratory assignments = 200 points Team Research Project Total for BCB 444p BCB 544: 200 pts 200 100 200 700 pts Midterm Exams = 100 points each Homework & Laboratory assignments Final Exam Discussion Questions & Team Research Projects Total for BCB 544 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 6 Assignments & Announcements #3 ALL: HomeWork #3 Due: Mon Oct 8 (Today) by 5 PM • HW544: HW544Extra #1 √Due: Task 1.1 - Mon Oct 1 by noon Due: Task 1.2 & Task 2 - Fri Oct 12 by 5 PM (not Monday) • 444 "Project-instead-of-Final" students should also submit: • HW544Extra #1 • Due: Task 1.1 - Mon Oct 8 (Today) by noon • Due: Task 1.2 - Fri Oct 12 by 5 PM (not Monday) Task 2 NOT required! BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 7 Chp 12 - Protein Structure Basics SECTION V STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS Xiong: Chp 12 Protein Structure Basics • • • • • • • • Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Dihedral Angles Hierarchy Secondary Structures Tertiary Structures Determination of Protein 3-Dimensional Structure Protein Structure DataBank (PDB) BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 8 Protein Structure & Function • Protein structure - primarily determined by sequence • Protein function - primarily determined by structure • Globular proteins: compact hydrophobic core & hydrophilic surface • Membrane proteins: special hydrophobic surfaces • Folded proteins are only marginally stable • Some proteins do not assume a stable "fold" until they bind to something = Intrinsically disordered Predicting protein structure and function can be very hard -- & fun! BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 9 Amino Acids • Each of 20 different amino acids has different "R-Group" or side chain attached to Ca BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 10 Peptide Bond is Rigid and Planar BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 11 Certain Side-chain Configurations are Energetically Favored (Rotamers) Ramachandran plot: "Allowable" psi & phi angles BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 12 Glycine is Smallest Amino Acid R group = H atom • Glycine residues increase backbone flexibility because they have no R group BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 13 Proline is Cyclic • Proline residues reduce flexibility of polypeptide chain • Proline cis-trans isomerization is often a rate-limiting step in protein folding • Recent work suggests it also may also regulate ligand binding in native proteins Andreotti (BBMB) BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 14 Cysteines can Form Disulfide (S-S) Bonds • Disulfide bonds (covalent) stabilize 3-D structures • In eukaryotes, disulfide bonds are often found in secreted proteins or extracellular domains BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 15 Globular Proteins Have a Compact Hydrophobic Core • Packing of hydrophobic side chains into interior is main driving force for folding • Problem? Polypeptide backbone is highly polar (hydrophilic) due to polar -NH and C=O in each peptide unit (which are charged at neutral pH=7, found in biological systems); these polar groups must be neutralized • Solution? Form regular secondary structures, • e.g., a-helix, b-sheet- both stabilized by H-bonds BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 16 Exterior Surface of Globular Proteins is Generally Hydrophilic • Hydrophobic core formed by packed secondary structural elements provides compact, stable core • "Functional groups" of protein are attached to this framework; exterior has more flexible regions (loops) and polar/charged residues • Hydrophobic "patches" on protein surface are often involved in protein-protein interactions BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 17 Protein Secondary Structures • aHelices • bSheets • Loops • Coils BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 18 aHelix: Stabilized by H-bonds Between every ~ 4th Residue in Backbone C = black O = red N = blue H = white Look: Charges on backbone are "neutralized" by hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) - red fuzzy vertical bonds BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 19 Types of aHelices "Standard" ahelix: 3.6 residues per turn H-bonds between C=0 of residue n and N-H of residue n + 4 (this neutralizes backbone chgs) Helix ends are polar; almost always on surface of protein Other types of helices? n + 5 = helix n + 3 = 310 helix BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 20 aHelix: R-Groups are on Outside BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 21 Certain Amino Acids are "Preferred" & Others are Rare in aHelices • Ala, Glu, Leu, Met = good helix formers • Pro, Gly Tyr, Ser = very poor • Amino acid composition & distribution varies, depending on on location of helix in 3-D structure BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 22 b-Sheets - also Stabilized by H-bonds Between Backbone Atoms Anti-parallel Parallel b-Sheets: R-Groups are Above & Below "Plane" BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 23 Coils • Regions of 2' structure that are not helices, sheets, or recognizable turns • Intrinsically disordered regions appear to play important functional roles BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 24 Loops & Turns • Connect helices and sheets • Vary in length & 3-D configurations • Are located on surface of structure • Are more "tolerant" of mutations • Are more flexible, can adopt multiple conformations • Tend to have charged and polar amino acids • Are frequently components of active sites • Some fall into distinct structural families (e.g., hairpin loops, reverse turns) BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 25 Globular Proteins are Built from Recurring Structural Patterns • Structural Motifs & supersecondary structures = combinations of 2' structural elements • Domains = combinations of motifs • Independently folding unit (foldon) • Functional unit BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 26 Simple Motifs Combine to Form Domains BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 27 6 Main Classes of Protein Structure 1) a-Domains Bundles of helices connected by loops 2) b-Domains Mainly antiparallel sheets, usually with 2 sheets forming sandwich 3) abDomains Mainly parallel sheets with intervening helices, also mixed sheets 4) abDomains Mainly segregated helices and sheets 5) Multidomain (a b Containing domains from more than one class 6) Membrane & cell-surface proteins BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 28 a-Domain Structures: 4-Helix Bundles BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 29 b-Sheets: Up-and-Down Sheets & Barrels BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 30 ab Domains: Leucine-rich Motifs can Form Horseshoes BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 31 Protein Structure Databases PDB - Protein Data Bank http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/ (RCSB) - THE protein structure database MMDB - Molecular Modeling Database http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=Structure (NCBI Entrez) - has "added" value MSD - Molecular Structure Database http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd Especially good for interactions & binding sites BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 32 PDB (RCSB) - recently "remediated" http://www.rcsb.org/pdb BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 33 Structure at NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 34 MMDB at NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/MMDB/mmdb.shtml BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 35 MMDB: Molecular Modeling Data Base • Derived from PDB structure records • "Value-added" to PDB records includes: • • • • • • Integration with other ENTREZ databases & tools Conversion to parseable ASN.1 data description language Data also available in mmCIF & XML (also true for PDB now) Correction of numbering discrepancies in structure vs sequence Validation Explicit chemical graph information (covalent bonds) • Integrated tool for identifying structural neighbors Vector Alignment Search Tool (VAST) BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 36 MSD: Molecular Structure Database http://www.ebi.ac.uk/msd/ BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 37 wwPDB: World Wide PDB http://www.wwpdb.org BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 38 Chp 13 - Protein Structure Visualization, Comparison & Classification SECTION V STRUCTURAL BIOINFORMATICS Xiong: Chp 13 Protein Structure Visualization, Comparison & Classification • Protein Structural Visualization • Protein Structure Comparison • Protein Structure Classification BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #20 - Protein Structure Basics & Classification 10/8/07 39