World Hunger Introduction The World Food Problem (2009, Leathers and Foster) Sources:
advertisement

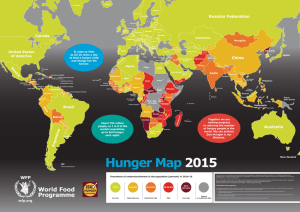
World Hunger Introduction Sources: The State of Food Insecurity 2015 (FAO) The World Food Problem (2009, Leathers and Foster) World Hunger Facts • Worldwide, about 800 million people are undernourished – Most in the Developing world • Don’t get enough calories each day – Susceptible to illness – Unable to lead productive lives • Chronic undernourishment – Due to extreme poverty • But undernourishment has been slowly declining since 1990 http://www.ehponline.org/docs/2004/112-14/hungry.jpg Decrease in Undernourishment since 1990 Undernourishment 1990-2015 Hunger has increased in Sub Saharan Africa World Hunger Issues • Poorest cannot afford food – Food prices up • Increased demand from emerging countries – Economic development • Population increase • Biofuels production • Reduced crop production – Climate change – Slow Economic Recovery • From recession of 2008 http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/faohome/home_photo/image_home_en.jpg World Hunger Facts • Over 20,000 people die each day due to causes related to undernutrition • ¾ of these are children under the age of 5 – About 6 million/year http://www.smh.com.au/ffximage/2005/06/30/poverty_wideweb__430x387.jpg Undernutrition and Child Death ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/a0200e/a0199e.pdf http://rehydrate.org/images/child-deaths-undernutrition.gif Common Scenario • Mother – Poorly educated – Food is scarce – Several children • Youngest child – – – – – http://static.flickr.com/73/193642829_3da338122c.jpg undernourished Disease resistance low Drinks unsanitary water Develops diarrhea Loses interest in eating Common Scenario • Mother removes solids from child’s diet – Not enough nourishment to fight disease – Diarrhea continues • Mother removes liquids – Dehydration – Death http://www.aa2sbu.org/aaezine/images/Fall2002/Starving_child_carried.jpg Malnutrition Cycle http://notaids.com/images/cycle.gif Importance of Maternal Health 1 in 6 babies in developing countries have low birthweight http://www.fao.org/docrep/008/a0200e/a0200e00.htm Causes of Hunger • Poverty – 2.3 billion people earn less than $2/day http://www.tribuneindia.com/2005/20050513/d.jpg Causes of Hunger • Extreme Poverty http://www.thp.org/africa/1bapr1-360.jpg – 1.3 Billion people earn less than $1.25/day – 75% of these live in rural areas • many unable to own land – Worst in Sub-Saharan Africa Extreme Poverty Percentage who earn less than $1.25/day http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Percentage_population_living_on_less_than_$1.25_per_day_2009.svg Causes of Hunger • Harmful Economic Systems – Control over incomes and resources by • Military • Wealthy • Politically powerful • Conflicts http://us-cdn.creamermedia.co.za/assets/articles/attachments/31567_i1683e.pdf Where are the Undernourished? World Hunger Map www.feedingminds.org/ img/map_world.jpg Sachs, J. 2005, The End of Poverty; Economic Possibilities for Our Time. Worldwide life expectancy http://www.theglobaleducationproject.org/earth/images/final-images/life-expectancy-map.gif Side effects of Hunger and Poverty ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/a0200e/a0199e.pdf Population Pressure • World Population has doubled in 40 years – Most of increase in developing countries • 5 billion people • Poverty and economic insecurity result in population growth http://www.sustainablescale.org/images/uploaded/Population/World%20Population%20Growth% 20to%202050.JPG – Children are a source of wealth to the poor Hope: Demographic Transition • Example: U.S. History – When U.S. became industrial, fewer kids/family needed • Lowered infant mortality • No need to rely on children’s labor • More opportunities for women • Happened without birth control http://bss.sfsu.edu/tygiel/Hist427/1920sphotos/fordassemblylinehist102.jpg Agricultural Revolution Hunters & Gatherers Conquest for land Agriculture Expanding population & environmental destruction Technology Culture Food production Population Growth Effect of the Agricultural Revolution Elite Wealth, Tribute Wealth: Own land, Well-fed Educated, Health care, Opportunities Food, Resources Conquered & Exploited: Peasants, Slaves, Workers Poverty: Landless, hungry, uneducated, unhealthy, no opportunities Effect of the Industrial Revolution Sachs, J. 2005, The End of Poverty; Economic Possibilities for Our Time. Issues • • • • • • • • • http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.resurgence.org/2005/egziahber233.jpg &imgrefurl=http://www.resurgence.org/selection/egziabher1005.htm&h=350&w=350&sz=1 1&hl=en&start=15&tbnid=svh3od2uZpp9bM:&tbnh=116&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq %3Dfeed%2Bthe%2Bworld%26svnum%3D10%26hl%3Den%26lr%3D%26ie%3DUTF-8 Nutrition Food Security Agriculture Environment Technology Education Culture Development Ethics Ethics • Is hunger and poverty morally acceptable? • Why or why not? • What should we do? http://www.whilechildrenstarve.org/images/starving-child-4.jpg