Within the realm of education, the terms objectives and outcomes... • Foster a common understanding or expectation among instructors,... Writing Effective Educational Objectives
advertisement

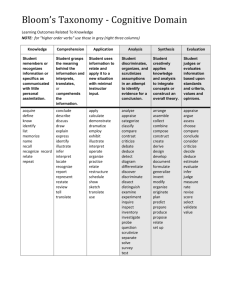
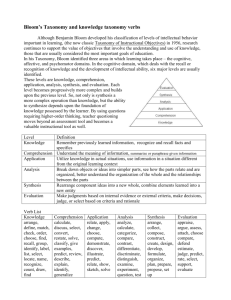
Writing Effective Educational Objectives Within the realm of education, the terms objectives and outcomes are generally interchangeable. The Purpose of Educational Objectives: • Foster a common understanding or expectation among instructors, students and administrators regarding what an educational activity aims to accomplish. • Define an activity’s place or role within a broader program. • Guide students about where they should focus their learning efforts. • Establish standards against which an activity can be evaluated. Three Types of Educational Outcomes: 1. Learning 2. Attitudinal 3. Behavioral Learning Objectives or Outcomes describe what students will be able to do after successfully completing an activity. Developing learning objectives should be the first step in planning any educational activity. They guide the design process by establishing priorities for pedagogy and content. Characteristics of Effective Course Objectives: • Focus entirely on students • Emphasize core skills and content • Relate directly back to program goals • Define learning levels • Measurable within the confines of the course • Specific • Realistic • Clearly and concisely written • Strive for higher order learning Writing Course Objectives: 1. Describe a performance using an action verb. Bloom’s skill cues are often helpful (See last page). 2. Specify the degree, contexts and/or conditions of learning. Examples: On completing the course, student will be able to: • Demonstrate a knowledge and understanding of microbiology as it relates to the general practice of medicine. This will specifically include: Bacterial structure and function; Bacterial growth and metabolism; Writing Effective Educational Objectives; 2.08 1 Genetic regulation and mechanism of genetic exchange; Antibiotics, antibiotic resistance and principle of sterilization; & Normal flora and virulence factors. • Evaluate clinical scenarios involving infections of the: Skin, Respiratory tract, Gastrointestinal tract & Urogenital tract. • Perform and explain a range of basic OMM techniques used to treat lesions of the thoracic spine and extremities. These techniques will utilize: Counterstrain, Muscle Energy, & High-Velocity Low-Amplitude. • Assess the conditions of and propose OMM treatment modalities for patients suffering from lesions of the thoracic spine and extremities. Common Mistakes • Use of vague passive verbs such as know, understand, or be familiar with. • Too broad or open-ended • Describe learning processes rather than outcomes • List content topics • Too many for one course • Emphasize lower order learning Writing Effective Educational Objectives; 2.08 2 Bloom’s Taxonomy of Higher Order Learning Competency Skills Demonstrated Skill/Question Cues Knowledge • • • recall information or ideas associate details define ideas or processes list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, label, match, associate, examine, tabulate, quote, name, attribute Comprehension • • • grasp meaning or relevance relate causes or motivations translate knowledge into new forms explain, summarize, interpret, paraphrase, restate, outline, predict, clarify, relate, distinguish, estimate, discuss, how, why • • use knowledge or ideas in new situations or areas solve problems using method or knowledge apply, demonstrate, calculate, complete, illustrate, show, solve, examine, deduce, change, classify, extend, discover, generalize, predict, prove, hypothesize • • • • discern similarities and differences identify parts and types see patterns and inconsistencies relate hidden meanings or causes • creat new theories or interpretations extrapolate from existing knowledge integrate knowledge from different areas analyze, separate, order, group, explain, categorize, compare, contrast, connect, classify, arrange, divide, dissect, rank, discriminate, prioritize, infer, interpret, differentiate synthesis, combine, integrate, modify, rearrange, substitute, plan, create, design, invent, compose, construct, formulate, prepare, propose Application Analysis Synthesis • • Evaluation • • • • • weigh evidence assess value of theories or ideas make choices based on reasoning and evidence recognize biases or subjectivity resolve discrepancies evaluate, assess, critique, resolve, decide, determine, rank, grade, test, appraise, prioritize, measure, recommend, convince, defend, judge, argue, support, conclude, justify Bloom, Benjamin S. (1984), Taxonomy of educational objectives. Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon. Writing Effective Educational Objectives; 2.08 3