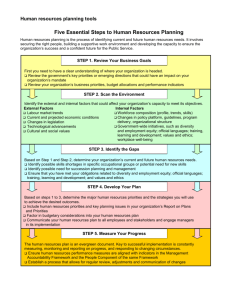
Templates to Assess Services Trade Policy and Performance
advertisement

Templates to Assess Services Trade Policy and Performance World Bank Research Program on Trade in Services OAS Trade Unit April 23, 2001 An assessment of policy and performance in services is frequently frustrated by the dearth of data. Empirical research has, in turn, been inhibited by the absence of clear guidelines on what data should be (and can be) collected. These templates seek to identify the key variables on which data is needed. They shall form the basis for research undertaken in collaboration with a number of institutions and regional networks. The template for each sector is divided into two parts. The first part deals with policies and market structure and covers three broad areas: the conditions of competition in the sector, notably policy restrictions on entry; restrictions on ownership, private and foreign; and regulation, especially elements designed to achieve social objectives in competitive markets. The emphasis is on policies affecting international trade and investment in services, rather than more general policies affecting the service sector. The second part deals with the performance of the sector, and covers prices, quality indicators, and measures of access, especially for the poor. The availability of data, particularly over time for a cross-section of countries, should make it possible to examine the relationship between policies and performance, and to identify priorities for reform. Critical feedback on the templates is welcome. 1 Telecommunications—Fixed Line Services Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. A. Market Access 1. Are there policy restrictions on new entry? Local services1 Long distance International Leased line2 Entry by any firm No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by foreign firms No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, number of foreign firms allowed 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give incumbents time to prepare for competition. To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Exclusive rights believed necessary to attract (strategic) investment Exclusive rights to allow the provision of universal service Other: ________________________________________ 3. Is interconnection to the public switched network allowed in principle? No Yes 4. Are there any restrictions on the provision of basic telecommunication services through networks other than the public switched network? Cable television network Internet Satellite Other: ______________ No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes If yes, please explain the nature of the restrictions: 5. Do market entrants have to use the incumbent carrier’s gateway(s) for international connections? No Yes 1 If policy restrictions on new entry in local services differ across regions within the country, please explain on a separate sheet. 2 Leased line services are defined as the ability of telecom service suppliers to sell or lease circuits for any type of bulk network capacity (cable, satellite, wireless) to third parties. 2 6. Is third party resale of lease line capacity permitted? No Domestic Yes International No Yes If yes, please specify the designated countries: ________________________________ B. Ownership 7. Is private ownership in the provision of services allowed? Local services Long distance International Leased line Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 8. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? Local services Long distance International Leased line Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) 9. Are there any restrictions on companies offering services in more than one market segment (local, long distance, international, leased line)? No Yes If yes, please explain the nature of these restrictions: ______________________________ C. Market Structure 10. Please list the characteristics of all facilities-based operators providing local services (starting with the incumbent PTO). Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Revenue Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 3 11. Please list the characteristics of all facilities-based operators providing long distance services (starting with the incumbent PTO). Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Revenue Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 12. Please list the characteristics of all facilities-based operators providing international services (starting with the incumbent PTO). Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Revenue Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 13. Please list the characteristics of all facilities-based operators providing leased line services (starting with the incumbent PTO). Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Revenue Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 14. If third party resale of leased-line capacity is permitted, how many resellers are in the market? Domestic:_____ International:_____ D. Regulation 15. Institutional status of sector regulator a) When was the regulator established? ___________ b) Is the sector regulator independent from the incumbent PTO? No c) If yes to b), is the regulator independent from the sector ministry? No d) How is the sector regulator financed? Yes Yes 4 License and other fees ___% State budget ___% Other (___________): ___% e) How many technical and economic professionals are employed? ________ 16. Please indicate regulatory responsibilities for the following functions: Operator Ministry Regulator Other (specify) Licensing Setting of interconnection rates Regulation of retail tariffs Dispute settlement and arbitration Regulation of cable television 17. How are licenses for fixed line services allocated? a) If the number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill. Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency: ________) Other: _____________________ b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? Competitive tender Discretionary decision by the licensing authority Other:_______________________________ c) Do licenses foresee specific network roll-out plans? No Yes d) Are foreign firms subject to different licensing requirements from domestic firms? No Yes If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign operators: e) Do licenses grant exclusivity periods? No Yes If yes, please indicate for the relevant market segments (local, long distance, international, leased line) when the exclusivity period will expire? _______________ 18. Regulation of network interconnection a) How are interconnection agreements among carriers determined? Private negotiations between parties Private negotiations, but general terms determined by regulatory agency Detailed terms of interconnection determined by the regulatory agency Other: ________________________________ 5 b) Which of the following aspects of interconnection are set by the regulatory agency? Technical standards Procedures for interconnection Time frames for interconnection Points of interconnection Price of interconnection Other: ______________ c) Are interconnection agreements required to be made public? No Yes d) Which of the following interconnection pricing rules are applied in your country? Reciprocal pricing3 Unbundling4 Imputation5 Other: _____________ 19. End-user tariffs a) How are end-user tariffs determined in your country? By market forces (i.e., not regulated) Price caps established by the regulator Rate of return regulation Other: _____________________ b) Is there a plan to rebalance tariffs in your country?6 No Yes If yes, please indicate when this plan is scheduled to be completed: ____________ 20. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups 3 Reciprocal pricing requires that all networks charge the same amount to terminate calls coming from other networks. 4 An ‘unbundling’ policy requires the dominant network operator to sell network components independently of each other, so that rival networks are not forced to buy services they do not need. 5 Imputation rules are designed to eliminate any markup on services components sold to competing firms over and above the implicit charges for internal use – and should tend to equalize prices charged by direct competitors. 6 Tariff rebalancing may take place when a dominant carrier provides both domestic and long distance/international services. It usually takes the form of the elimination of cross-subsidies from long distance/international services to the local segment of the domestic market. 6 User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Regional Integration Agreements in Fixed Line Services 21. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting fixed line services, and list the preferential measures.7 Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 22. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1990 (e.g., privatization of incumbent operator, introduction of competition, creation of an independent regulatory agency). Please attach copies of laws and regulations. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change 23. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of policy change 7 Please, specify how the treatment of fixed line service suppliers of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of fixed line service suppliers of non-member countries. 7 G. Universal Service 24. How does the government define universal service (or universal access)? 25. What are the policy instruments used to pursue the universal service objective? Roll-out obligations in services licenses Subsidies to operator(s), e.g., from universal service funds or state budgets Vouchers for target consumers Other: _________________________________ 26. On which service suppliers are universal service obligations imposed? Incumbent operator Private operators offering local services Private operators offering long distance and international services Other:__________________________________ H. Employment 27. Main employment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) How many people are employed in the provision of fixed line services? __________ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? ____________ What share of workers in this sector is employed by state-owned operators? ___________ What share of workers in this sector is employed by foreign-owned operators? __________ What is the annual average wage in this sector?____________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Investment 28. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in fixed line services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. 8 J. Prices 29. Please indicate the prices of the following services. Where relevant, distinguish between peak and off-peak charges. For a comprehensive assessment of telecommunications performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on prices for the various services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Service Installation charges Monthly subscription for business Monthly subscription for households 3-minute local call 3-minute domestic long distance call 3-minute call to Sao Paulo 3-minute call to Miami Average interconnection charge with main operator of local services Monthly leased line charges (capacity:____________) Price (in local currency) Date Comments K. Quality and Access to Services 30. Please fill in the following indicators of quality and access to services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Indicator Total number of main telephone lines in the country Number of main telephone lines in rural areas Number of main telephone lines in urban areas Number of payphones and/or call centers Waiting time for installation of basic telephone services Waiting list for installation of basic telephone services Percentage of network that is digitized Percentage of unsuccessful calls Are callback services available? Percentage of households with access to cable television Value Date Comments No Yes If yes, please since when? _____ 9 Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ Telecommunications—Mobile Services 10 Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. A. Market Access 1. Are there policy restrictions on new entry?8 Entry by any firm No Yes No Yes Analogue mobile Digital mobile If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by foreign firms No Yes No Yes If yes, number of foreign firms allowed 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give incumbents time to prepare for competition To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Exclusive rights believed necessary to attract (strategic) investment Limited availability of radio frequencies Other: ________________________________________ B. Ownership 3. Is private ownership in the provision of services allowed? Analogue mobile Digital mobile Existing operators No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 4. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? Analogue mobile Digital mobile Existing operators No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) C. Market Structure 5. Please list the characteristics of all operators providing analogue mobile services. 8 If policy restrictions on new entry in analogue or digital mobile differ across regions within the country, please explain on a separate sheet. 11 Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Market share Technology Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 6. Please list the characteristics of all operators providing digital mobile services. Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Technology (e.g., GSM, CMDA) Market share Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) D. Regulation 7. Please indicate regulatory responsibilities for the following functions: Operator Ministry Regulator Other (specify) Licensing Setting of interconnection rates Regulation of retail tariffs Dispute settlement and arbitration Spectrum Allocation 8. How are licenses for mobile services allocated? a) If the number of operators is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill. Payment of service license fee (indicate amount in local currency: ________) Other: _______________________________ b) If the number of operators is limited by policy, through what mechanism are service licenses allocated? Competitive tender Discretionary decision by the licensing authority Other:_______________________________ c) Are foreign firms subject to different licensing requirements from domestic firms? 12 No Yes If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign operators: d) Do licenses foresee specific network roll-out plans? No Yes e) Do licenses grant exclusivity periods? No Yes If yes, please indicate for the relevant market segments (digital, analogue) when the exclusivity period will expire? _______________ 9. Allocation of radio spectrum a) If radio frequencies are not awarded with the service license, through what mechanism are licenses for radio frequencies allocated? Auction Discretionary decision by the licensing authority First come, first served Other:_____________________________ b) Is there a separate fee for radio frequency licenses? No Yes If yes, please indicate the average fee paid by operators: _______ 10. Regulation of network interconnection a) How are interconnection agreements between mobile and fixed-line carriers determined? Private negotiations between parties Private negotiations, but general terms determined by regulatory agency Detailed terms of interconnection determined by the regulatory agency Other: ________________________________ b) How are interconnection agreements among mobile carriers determined? Private negotiations between parties Private negotiations, but general terms determined by regulatory agency Detailed terms of interconnection determined by the regulatory agency Other: ________________________________ c) Which of the following aspects of interconnection are set by the regulatory agency? Technical standards Procedures for interconnection Time frames for interconnection Points of interconnection Price of interconnection 13 Other: ______________ d) Are interconnection agreements required to be made public? No Yes e) Which of the following interconnection pricing rules are applied in your country? Reciprocal pricing9 Unbundling10 Imputation11 Other: _____________ f) Are mobile carriers allowed to charge for incoming mobile calls? No Yes If yes, do mobile carriers actually charge for incoming calls? No Yes 11. How are end-user tariffs for mobile services determined in your country? By market forces (i.e., not regulated) Price caps established by the regulator Rate of return regulation Other: _____________________ 12. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Regional Integration Agreements in Mobile Services 13. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting mobile services, and list the preferential measures.12 9 Reciprocal pricing requires that all networks charge the same amount to terminate calls coming from other networks. 10 An ‘unbundling’ policy requires the dominant network operator to sell network components independently of each other, so that rival networks are not forced to buy services they do not need. 11 Imputation rules are designed to eliminate any markup on services components sold to competing firms over and above the implicit charges for internal use – and should tend to equalize prices charged by direct competitors. 14 Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 14. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1990 (e.g., grant of additional mobile licenses, relaxation of ownership rules). Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change 15. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same areas. Among other things, describe the government’s plans for the introduction of third generation mobile services. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of policy change G. Employment 16. Main employment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) How many people are employed in the provision of mobile services? _________ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? __________ What share of workers in this sector is employed by state-owned operators? ___________ What share of workers in this sector is employed by foreign-owned service providers? ____ What is the annual average wage in this sector?_____________ 12 Please, specify how the treatment of mobile service suppliers of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of mobile service suppliers of non-member countries. 15 If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. H. Investment 17. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in mobile services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Prices 18. Please indicate the prices of the following services. Where relevant, distinguish between peak and off-peak charges. For a comprehensive assessment of mobile performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on prices for the various services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Service Acquisition of handset Monthly rental charges 3-minute domestic call 3-minute call to Sao Paulo 3-minute call to Miami Average roaming charges Average interconnection charge with fixed network Average interconnection charge between mobile networks Price (in local currency) Date Comments J. Quality and Access to Services 19. Please fill in the following indicators of quality and access to services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Indicator Total number of mobile subscribers in the country Number of mobile subscribers in rural areas Waiting period for acquisition of handset and initiation of service Percentage of unsuccessful Value Date Comments 16 calls Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ Telecommunications—Internet services Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. 17 A. Market Access 1. Are there policy restrictions on new entry of Internet service providers? If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by any firm No Yes Entry by foreign firms No Yes If yes, number of foreign firms allowed 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give incumbents time to prepare for competition To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Other: ________________________________________ B. Ownership 3. Is private ownership in the provision of services allowed? Maximum private equity permitted (%) Existing operators No Yes New entrants No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 4. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) Existing operators No Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes Yes C. Market Structure 5. a) What is the total number of Internet service providers? _________ b) How many Internet service providers are related to telecom operators? ___________ 6. Please list the characteristics of the six largest Internet services providers. Name of firm Year the firm first offered services Market share Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) D. Regulation 18 7. Licensing regime a) Is there a licensing regime for Internet service providers? No Yes b) If yes to a), which governmental agency issues licenses? ________________ c) If yes to a), please specify the main conditions new entrants have to fulfill: d) Are foreign firms subject to different licensing requirements from domestic firms? No Yes If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign operators: 8. Infrastructure and interconnection a) Are Internet service providers allowed to build their own networks? No Yes b) Are Internet service providers (other than the incumbent or affiliates) allowed to own or lease their own international data gateways? No Yes c) How are interconnection agreements among Internet service providers regulated? Private negotiations between parties Private negotiations, but general terms determined by regulatory agency Detailed terms of interconnection determined by the regulatory agency Other: ________________________________ d) How many peering points (locations where national and regional Internet traffic can be exchanged) are available? Private_________ Public____________ 9. Are there any policy initiatives to bolster Internet use? No Yes If yes, a) when were they introduced? ___________ b) what do they cover? Plan to introduce flat-rate access Discount local access charges for Internet use Other: ________________________________ 10. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ 19 b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Regional Integration Agreements in Internet Services 11. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting internet services, and list the preferential measures.13 Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 12. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1985 (e.g., grant of additional licenses for Internet services, relaxation of ownership rules). Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change 13. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of policy change 13 Please, specify how the treatment of internet service suppliers of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of internet service suppliers of non-member countries. 20 G. Employment 14. Main employment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) How many people are employed in the provision of Internet and data services? _________ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? __________ What share of workers in this sector is employed by state-owned service providers? ______ What share of workers in this sector is employed by foreign-owned service providers? ____ What is the average annual wage in this industry?_________ If time series data on these employment indicators are available, please attach them separately. H. Investment 15. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in Internet services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Prices 16. Please indicate the prices of the following services. Where relevant, distinguish between peak and off-peak charges. For a comprehensive assessment of Internet performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on prices for the various services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Service Average monthly charges for low bandwidth residential Internet access (Capacity:_________) Price (in local currency) Date Comments Additional (per minute) local telephone charges (if relevant) Average monthly charges for high bandwidth business Internet access (Capacity:_________) Additional connection charges (if relevant) I. Quality and Access to Services 17. Please fill in the following indicators of quality and access to services. 21 Indicator Number of Internet hosts Number of household subscribers Total number of Internet users Number of users that access the Internet via the fixed telephone network Number of users that access the Internet via leased lines Number of users that access the Internet via the cable network Annual value of e-commerce transactions Value Date Comments Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ 22 Air Transport Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. Please report all monetary values in their reported currencies. Within this section of the questionnaire, two concepts will be frequently encountered: commercial presence and cross-border supply. They are alternative modes of supply and are defined by the WTO in the context of the GATS schedules of commitments. To avoid confusion, a preliminary discussion of the two concepts is necessary. Foreign suppliers provide services according to the “cross-border” mode if they operate from their own country without establishing a local branch or subsidiary or acquiring shares in a firm located in the country to which the service is destined. The “commercial presence” mode of supply means exactly the contrary, i.e. the foreign firms establish locally in the country where they want to supply the service and open a branch, subsidiary or participate to the capital of a local firm (the share can go up to 100%). A. Market Access Commercial presence 1. Are there policy restrictions to new entry (refer only to commercially-established operators)? Entry by any Service Firm International air transport15 No Yes Domestic air transport No Yes Provision of fuel No Yes Luggage and freight loading No Yes and unloading Aircraft repair and No Yes maintenance Selling and marketing of air No Yes transport services16 Computer reservation No Yes system 14 If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by firms with foreign participation14 No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, number of firms with foreign participation allowed No Yes No Yes No Yes This category also includes branches and subsidiaries of foreign suppliers. Include designation among restrictions. 16 Refers to selling and marketing activities undertaken by the airline company itself (GATS definition). 15 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? Use the definitions below to fill in the table: 1—To give protected operators time to prepare for competition. If so, please specify time. 2—To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees 3—Exclusive rights believed necessary to attract (strategic) investment If so, please specify time given. 4—It is believed that market can sustain only a limited number of operators 5—Strategic activity reserved to the state Service International air transport Domestic air transport Provision of fuel Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system 1 2 3 4 Reasons 5 Other (describe in brief) Cross-border supply 3. Are there restrictions on cross-border entry of foreign airlines on the scheduled air transport market? No Yes If yes, what are the instruments used to implement restrictions? Air Services Agreements (ASAs) Other: _________________________________________________ 4. Are there restrictions on cross-border entry of foreign service providers on the non-scheduled (charter) air transport market? International air transport Domestic air transport Entry by foreign firm No Yes No Yes If yes, total number of foreign providers allowed 5. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To prepare incumbent airline(s) for competition: Scheduled services Non-scheduled services 24 Market is believed to sustain a limited number of airline(s) Other (explain) 6. Are there restrictions to cross-border supply of computer reservation system (CRS) services by foreign suppliers? No Yes If yes, please specify: 7. Bilateral Air Service Agreements (ASAs) Type of bilateral ASAs Number of signed bilateral ASAs Number of operational bilateral ASAs Predetermined (TP)17 Bermuda (B)18 “Point to Point” Open Skies (POS)19 “Multiple Point” Open Skies (MOS)20 Other 8. Please list the countries with which (bilateral) Open Skies Agreements have been signed: 9. Is the country member of any plurilateral open skies agreement group? No Yes If yes, please list other members of the group: 10. Please fill in the following information referring to clauses in operational ASAs: a) Tariff clauses in ASAs 17 each country designates one single company to operate on the bilateral route; limited number of points/routes operated by designated airlines as listed in the bilateral’s annex; capacity and frequency to be agreed ex ante; few 5th freedom granted 18 each country designates one or several airlines on each route; limited number of points/routes operated by designated airlines as listed in the bilateral’s annex; there is no ex ante capacity control on each route, capacity offered is often negotiated via commercial agreements between airlines; several 5th freedoms may be granted, but total capacity must be proportional to the needs of the main bilateral route 19 multiple designation of airlines; free access to designated routes, between specific points, either departure or arrival points may be left open and unrestricted; no frequency or capacity control; extensive 5th freedom rights are granted 20 multiple designation of airlines; airlines can fly on any route between two states; no frequency or capacity control; unrestricted 5th freedom 25 Total number of bilateral ASAs Total number of plurilateral open skies agreement groups21 Double approval22 Country of origin23 No approval needed Double disapproval24 Other mechanism of setting tariffs (please describe in brief) b) Capacity clauses imposed on foreign airlines Total number of bilateral ASAs Total number of plurilateral open skies agreement groups No capacity constraints Capacity constraints c) Number of foreign airlines designated Total number of bilateral ASAs Total number of plurilateral open skies agreement groups Single Double Multiple d) Routes specification for the foreign airlines Total number of bilateral ASAs Total number of plurilateral open skies agreement groups Routes not specified Routes specified e) Freedoms of the air granted to foreign airlines Total number of bilateral ASAs Unrestricted Restricted freedom freedom Total number of plurilateral open skies agreement groups Unrestricted Restricted freedom freedom Third freedoms25 21 Include air transport liberalization within EU in this category. Both states must approve a tariff. 23 Only the state in which the transportation originates needs to approve the tariff. 24 Both states concerned must disapprove a tariff to prevent it from coming into effect. 25 The right of an airline of one country to carry traffic (passenger, cargo, mail) from its country to another country. 22 26 Fourth freedoms26 Fifth freedom27 Sixth freedom28 Seventh freedom29 Cabotage30 B. Ownership 11. Is private ownership in the provision of services through commercial establishment allowed? Services International air transport Domestic air transport Provision of fuel Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 12. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services through commercial establishment allowed? Maximum Existing foreign equity Services operators permitted (%) International air transport No Yes Domestic air transport No Yes Provision of fuel No Yes Luggage and freight loading No Yes and unloading Aircraft repair and No Yes maintenance Selling and marketing of air No Yes transport services Computer reservation No Yes system New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) No Yes No Yes No Yes 26 The right of an airline of one country to carry traffic (passenger, cargo, mail) from another country to its own country. 27 The right of an airline of one country to carry traffic between two other countries providing the flight originates and terminates in its own country. 28 The right of an airline of one country to carry traffic between two other countries via its own country. 29 The right of an airline of one country to carry traffic between two other countries without the flight originating or terminating in its own country. 30 The right of an airline of one country to carry domestic traffic between two points within the territory of another country. 27 13. Does the government have a special government voting right in the airlines? No Yes 14. Please mark in the table below, the appropriate ownership structure for the 5 most important international airports in terms of traffic: Assets ownership/Service provision Publicly owned/publicly operated Publicly owned/ privately operated (e.g., by concession) Privately owned/privately operated Airports C. Market Structure 15. Please list below the characteristics of all commercially-established carriers operating on domestic and international routes. Name Year carrier first offered services Designated to provide international services Market share NatInterional national Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) 31 No No No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes 16. a) Do commercial carriers participate in international carrier alliances? No Yes If yes, please specify alliance(s) and partner airlines: b) Do commercial carriers participate in codesharing agreements? No Yes If yes, please specify partner airlines: 17. Please indicate the total number of foreign airlines providing the following services crossborder: Services International air transport Domestic air transport 31 Scheduled services Non-scheduled services Percentage of international passengers transported to/from the country 28 18. Please indicate the total number of commercially-established operators providing the following services in the main international airport: Services Provision of fuel Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system Total number 19. Please list the characteristics of the 6 most important commercially-established operators for the following services: Name of firm Year of service commencement Market share Provision of fuel Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system 29 20. Capacity of the main international airport a) How many passengers can the terminal building handle at the peak hours? __________ b) Apron capacity: __________________ D. Regulation 21. Institutional status of sector regulator When was the regulator established? Is the regulator an institutionally independent agency?32 How is the sector regulator financed? License and other fees (%) State budget (%) Other _________________ (%) How many technical and economic professionals are employed? For carriers For airports No Yes No Yes 22. What are the main requirements that an airline must fulfill in order to become an international carrier and have the right to be designated in ASAs? 23. How are flight and gate slots allocated in airports? By grandfathering rights By slot auction By a combination of grandfathering rights and slot auction By authorities discretion By flag carrier discretion By airport discretion By IATA guidelines Other:_______________________________ 24. Carrier alliances a) Are alliances and other carrier agreements allowed? b) Is codesharing allowed? No Yes No Yes “Institutionally independent” means that the regulator is not part of the ministry and is not linked to the operating entity (national airlines/airports). 32 30 25. Price regulation a) Does the government regulate airfares? On domestic routes No Yes On international routes No Yes b) If yes to a), is fare discounting allowed? On domestic routes No Yes On international routes No Yes c) If no to a) how are abuse of monopoly power and/or predatory pricing dealt with? 26. Allocation of licenses for commercially-established operators providing air transport services a) If the number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions, including important licensing requirements, that the new entrants must fulfill: Service International air transport Domestic air transport Provision of fuel Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency) Other (describe in brief) b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? Service International air transport Domestic air transport Provision of fuel Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation Competitive tender First come, first served Public hearings Other discretionary mechanism Other (describe in brief) 31 system 27. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Past and Future Changes in Policy 28. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1990 (e.g., domestic liberalization, implementation of open skies agreements, joining of regional agreements on air transport, privatization of state-owned airlines and airport facilities etc.) Please attach copies of laws and regulations. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of change Description of change 29. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of change F. Subsidies and Universal Service 30. How does the government define universal service (or universal access)? 31. Does the government subsidize domestic airlines? 32 No Yes If yes, please indicate the airlines. 32. Has the government covered operational losses of airlines in the past five years? No Yes If yes, please indicate the amount in 1995 and in 2000. 33. Does the government oblige large national airlines to provide universal service? No Yes G. Regional Integration Agreements in Air Transport Services 34. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting air transport services, and list the preferential measures. Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures H. Employment 35. Main employment indicators (for the years 1990-2000). How many people are employed by the main national carrier?______________________ How many people are directly employed in the provision of airport services? _________ What share of the total labor force is directly employed in the provision of airport services? __________ What share of workers is employed by foreign-owned operators providing airport services? __________ What is the annual average wage in this sector?________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Investment 36. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) Service Total amount of investment Total amount of foreign direct investment Total stock of foreign direct investment International air transport Domestic air transport Provision of fuel 33 Luggage and freight loading and unloading Aircraft repair and maintenance Selling and marketing of air transport services Computer reservation system If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. J. Prices 37. Please fill in the table below. If possible distinguish between season and off-season airfares. For a comprehensive assessment of air transport performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on prices and/or price indices for the various services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Service Roundtrip standard economy class fare between the two most important domestic cities Roundtrip standard economy class fare to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Roundtrip standard economy class fare to New York Roundtrip standard economy class fare to London Roundtrip standard economy class fare to Hong Kong Roundtrip business class fare between the two most important domestic cities Roundtrip business class fare to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Roundtrip business class fare to New York Roundtrip business class fare to London Roundtrip business class fare to Hong Kong Freight rate between the two most important domestic cities Freight rate to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Price (in local currency) Date Comments 34 Freight rate to New York Freight rate to London Freight rate to Hong Kong K. Quality and Access to Services 38. Please fill in the following indicators of quality and access to services. Indicator Value Date Share of exports/import carried by air Number of departures and landings in a peak day for the most important international airport Number of departures and landings in a peak hour for the most important international airport Number of passengers carried on domestic routes by: *national airlines *foreign airlines Number of passengers carried on international routes by: *national airlines *foreign airlines Freight carried on domestic routes by: *national carriers *foreign carriers Freight carried on international routes by: *national carriers *foreign carriers Percentage of on-time flights at main international airport Comments Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:_________________________________________________________________ Maritime Transport 35 Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. Please report all monetary values in their reported currencies. Within this section of the questionnaire, two concepts will be frequently encountered: commercial presence and cross-border supply. They are alternative modes of supply and are defined by the WTO in the context of the GATS schedules of commitments. To avoid confusion, a preliminary discussion of the two concepts is necessary. Foreign suppliers provide services according to the “cross-border” mode if they operate from their own country without establishing a local branch or subsidiary or acquiring shares in a firm located in the country to which the service is destined. The “commercial presence” mode of supply means exactly the contrary, i.e. the foreign firms establish locally in the country where they want to supply the service and open a branch, subsidiary or participate to the capital of a local firm (the share can go up to 100%). A. Market Access Commercial presence 1. Are there policy restrictions to new entry (refer only to commercially-established operators)? Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Entry by any Firm No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by Firms with foreign participation33 No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, number of firms with foreign participation allowed 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? Use the definitions below to fill in the table: 1—To give the incumbent(s) time to prepare for competition. If so, please specify how much time is given. 2—To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees 3—Exclusive rights believed necessary to attract (strategic) investment. If so, please specify how many and how long exclusive rights are provided. Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling 33 1 2 3 Reasons Other (describe in brief) This category also includes branches and subsidiaries of foreign suppliers. 36 Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Cross-border supply 3. Describe restrictions on cross-border supply imposed on foreign shipping companies: Restriction Application of principle of reciprocity Restrictions on the number of foreign suppliers (indicate how many foreign suppliers are allowed) Application of UN Liner Code (provide quota applicable to foreign suppliers) Bilateral agreements including cargo-sharing clauses (provide total number and list countries affected) Cargo reservation if different from the application of UN Liner Code and bilateral agreements (provide quota applicable to foreign suppliers) International Shipping Cabotage Liner Tramp Liner Tramp No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Other:___________________ 4. If cross-border entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give the incumbent(s) time to prepare for competition. If so, please specify the duration given. For national security reasons. Other (please specify) International Shipping No Yes Cabotage No Yes No No Yes Yes 5. Please fill in the following table with information referring to the main international port (in terms of traffic): Port service Pilotage Towing Are the following services mandatory for ships entering the port? No Yes No Yes Is access to service discriminatory for foreign carriers as opposed to domestic ones? No Yes No Yes 37 Tug assistance Navigation aids Berthing Waste disposal Anchorage Other (please specify) No No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes B. Ownership 6. Is private ownership in the provision of services through commercial establishment allowed? Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Maximum Existing private equity operators permitted (%) No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 7. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services through commercial establishment allowed? Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) 8. Please fill in the table below, for the 5 most important international maritime ports with respect to the amount of traffic. Port Port Authority Public Private Public Private Public Private Port type34 Landlord Tool Service Other Landlord Tool Service Other Landlord Tool Service Other 34 In the case of landlord ports, the port authority typically owns and manages infrastructure, private firms are able to own superstructure, and provide port services as well as rent port assets by concessions or licenses. In the case of tool ports, port authority owns infrastructure and superstructure, private firms provide services by renting port assets through concessions and licenses. In the case of service ports, the port authority owns assets and supplies services by directly hiring employees. 38 Public Private Public Private Landlord Tool Service Other Landlord Tool Service Other C. Market Structure 9. Please list the characteristics of the 6 most important shipping lines in terms of market share in the total maritime traffic (include foreign cross-border suppliers as well as commerciallyestablished companies). Company Year of service Residency commencement (domestic/foreign) International shipping Market share Cabotage 10. Please indicate the total number of commercially established operators providing the following services in the main international port (in terms of traffic)35: International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vesse1s ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ ________ 11. Please list the characteristics of the 6 most important commercially established operators in terms of market share. Name of firm Year of service commencement Market share Owners of capital and their respective shares (domestic/foreign) International shipping 35 Exclude from port ranking the ports that are fully specialized on tanker or other bulk shipping services. 39 Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels 12. How many conferences exist in the maritime services market? 13. What is the market share of conferences? __________% 14. Apart from conferences, are global alliances present in the market? If so what is their market share? 40 D. Regulation 15. Characteristics of the sector regulator Institutional status of sector regulator When was the regulator established? Is the regulator an institutionally independent agency?36 How is the sector regulator financed? License and other fees (%) State budget (%) Other ________________ (%) How many technical and economic professionals are employed? For carriers For ports No No Yes Yes 16. What are the conditions that a vessel or fleet must fulfill in order to fly the national flag (if a national merchant fleet does not exist or an “open registry” system is in place, please specify). 17. If applicable, what are the conditions that a vessel or fleet must fulfill in order to be transferred to open registries? 18. Is authorization required for the transfer to the open registries? No Yes If yes, who authorizes? 19. If applicable, what are the conditions that a vessel or fleet must fulfill in order to be included in the “second registry”? 20. Is any compensation mechanism instituted for vessels national flagged? No Yes If yes, please specify the type of compensation mechanism. “Institutionally independent” means that the regulator is not part of the ministry and is not linked to the operating entity (national carriers/port authorities) 36 41 21. Regulation of carrier agreements a) Do agreements between transport carriers (such as conferences) benefit from exemptions to competition law? No Yes If yes, what types of carrier agreements benefit from exemptions? b) What types of conference agreements are allowed? Open Closed Both open and closed c) Are tariffs established by carrier agreements required to be filed or notified? No Yes d) Does the government enforce tariffs agreed upon within carrier agreements? No Yes e) Is fare discounting allowed? No Yes f) Does the regulatory agency monitor conferences’ activities? No Yes 22. How are licenses for commercially-based operators providing maritime services allocated? a) If the number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill. Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and Warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency) Other (describe in brief) b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? 42 Service International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels Competitive tender First come, first served Discretionary decision Other (describe in brief) c) Can the licenses be sold, once allocated? No Yes 23. If the cross-border service provision by foreign carriers requires the appointment of a domestic agent, describe conditions that the agent must fulfill. Services Conditions International shipping Cabotage 24. What are the licensing requirements for the cross-border service provision by foreign suppliers? Services License requirements International shipping Cabotage 25. Does port state control principle exist? No Yes If yes, please specify reasons. 26. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ 43 E. Regional Integration Agreements in Maritime Transport Services 27. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting maritime transport services, and list the preferential37 measures. Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures 28. Do regional integration agreements harmonize rules and standards among parties to the agreements? No Yes F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 29. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1990 (e.g., elimination of cargo sharing, UN Liner Code implementation and phasing out, privatization of state-owned shipping companies, elimination of restrictions applied to foreign service suppliers etc.) Please attach copies of laws and regulations. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of change Description of change 30. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of change 37 Please, specify how the treatment of maritime transport service providers of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of maritime transport service providers of non-member countries. 44 G. Subsidies and Universal Service 31. How does the government define universal service (or universal access)? 32. Does the government subsidise domestic shipping companies? No Yes If yes, please indicate the shipping company. 33. Has the government covered operational losses of shipping companies in the past five years? No Yes If yes, please indicate the amount in 1995 and in 2000. H. Employment 34. Main employment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) How many people are employed in the provision of maritime transport services? _______ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? _______ What share of workers is employed by state-owned operators? _______ What share of workers is employed by foreign-owned operators? _______ How many workers are employed at the main international port? _______ What share of workers employed in port services are unionized? _______ What is the annual average wage in this sector? _________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Investment 35. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) Services Total amount of investment Total amount of foreign direct investment Total stock of foreign direct investment International shipping Cabotage Cargo handling Storage and warehousing Freight forwarding Pilotage, towing and tying Maintenance and repair of vessels If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. J. Prices 36. Please fill in the table below. For a comprehensive assessment of maritime transport performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on prices or price indices for the 45 various services. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Indicator Value Date Comments Liner freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Liner freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Hong Kong Liner freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Rotterdam Liner freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to New York Dry bulk charter rate for standard shipment from main international port to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Dry bulk charter rate for standard shipment from main international port to Hong Kong Dry bulk charter rate for standard shipment from main international port to Rotterdam Dry bulk charter rate for standard shipment from main international port to New York Tanker freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Sao Paulo (or relevant neighboring country) Tanker freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Hong Kong Tanker freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to Rotterdam Tanker freight rate for standard shipment from main international port to New York Cargo handling rates applicable at the main international port Forwarding rate applicable at the main international port Other available port service charges at main international port (pilotage, storage etc.) 46 K. Quality and Access to Services 37. Please fill in the following indicators of quality and access to services. Indicator Average duration of cargo turnover at main international port38 Share of international trade, by quantity and/or value, carried by sea Share of international trade, by quantity and/or value, carried by liners Average amount of dry bulk loaded at the main international port Average amount of dry bulk unloaded at the main international port Average amount of tanker freights loaded at the main international port Average amount of tanker freights unloaded at the main international port Share of liner shipping, by quantity and/or value, carried by conferences Share of liner shipping, by quantity and/ or value, carried by global alliances Share of liner shipping, by quantity and/or value, which is containerized Value Date Comments Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ 38 Measured from the moment the goods reach the port until the departure of the vessel 47 Financial Services: Banking Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. Please report all monetary values in their reported currencies. A. Market Access Macroeconomic policies 1. Are there restrictions on capital flows? Capital inflows Capital outflows Short term Short term No Yes Long term No Yes If yes, what type of restrictions? Is the authority allowed to impose temporary restrictions? No Yes Long term No Yes Commercial presence 2. Are there policy restrictions on new entry of banks? Entry by any bank No If yes, total number of banks allowed Yes Entry by foreign banks No Yes If yes, total number of foreign banks allowed 3. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give state-owned or national banks time to prepare for competition To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Exclusive rights to allow the provision of universal service To reduce potential systemic risk believed to arise from over-banking Inadequate regulatory and supervisory capacity No perceived economic need for new banks Other: ________________________________________ 4. Which of the following legal forms of establishment are allowed for foreign banks? Subsidiaries Branches Representative Office All 5. Are there restrictions on the number of foreign bank branches? No Yes If yes, what is the maximum number of foreign bank branches permitted? _____ 6. Are there restrictions on the number of foreign bank ATMs? No Yes If yes, what is the maximum number of foreign bank ATMs permitted? _____ 7. Are foreign banks allowed to raise capital domestically? No Yes 48 8. Which of the following services are commercial banks permitted to provide domestically? Real estate lending Insurance services Securities services Foreign currency lending Foreign exchange services Credit card services Leasing services Other (specify)_________ Domestic banks No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Foreign banks No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Cross-border banking trade 9. Are the following allowed to borrow cross-border from foreign banks? Domestic banks Domestic corporations Domestic households No No No Yes Yes Yes If applicable, please specify borrowing limits: _____________ 10. Are banks subject to any qualifications in order to be able to access foreign capital? No Yes If yes, please specify_________________ 11. Are the following allowed to make cross-border deposits with foreign banks? Domestic banks Domestic corporations Domestic households No No No Yes Yes Yes If applicable, please specify deposit limits: ______ B. Ownership 12. Is private ownership in the provision of services allowed? Existing banks No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New banks No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 13. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? 49 Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) Existing banks No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes 14. Are banks allowed to hold equity in the following firms? Domestic banks Foreign banks Non-financial firms No Yes No Yes Financial firms No Yes No Yes If yes, please indicate maximum stake permitted in each case. C. Market Structure 15. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest banks in the market for deposits: Name of bank Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Market share in total deposits (%) Return over equity (%) Total number of banks in the market for deposits: ______ 16. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest banks in the market for loans: Name of bank Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Market share in total loans39 (%) Return over equity (%) Total number of banks in the market for loans: ______ 17. Please provide the following information on the actual number of banks: Number of fully state-owned banks: _____ Number of privatized banks: _____ Number of fully domestically owned40 private banks: _____ Number of foreign minority-owned41 banks: _____ 39 40 Include consumer and business loans. Banks that are not state owned where the paid-up share capital is entirely held by domestic residents. 50 Number of foreign majority-owned42 banks: _____ D. Regulation 18. Characteristics of regulator: Name of regulator Year of establishment % of Regulator’s finances from: License and other fees: _____ Budgetary allocation: _____ Other (specify): _____ Is the regulator independent of the ministry of finance/economy or other regulatory bodies? No Yes Number of professional regulatory and supervisory staff: _______ 19. How are banking licenses allocated? a) If the number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill. Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency: ________) Presentation of detailed business plan. Minimum capital Compatible home country regulation Other: _____________________ b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? First come, first served basis Competitive bidding Discretionary decision by the licensing authority Other:_______________________________ c) Once the licenses have been allocated, are there restrictions on banks ability to sell or dispose of these licenses? No Yes If yes, please specify: d) Are foreign banks subject to different licensing requirements from domestic banks ? No 41 42 Yes Banks where foreigners hold under 50% of the paid-up share capital of the bank. Banks where 50% or more of the paid-up share capital of the bank is held by foreigners. 51 If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign banks. e) Are separate licenses required to establish branches in each state/province? No Yes 52 20. Please provide information on the following indicators of prudential regulation for the latest year available. Category Capital adequacy requirement Loan Classification Requirement44 Liquidity ratio45 Single exposure Limit46 Foreign exchange risk exposure limit47 Required to join deposit insurance scheme? Lender of last Resort facility Available? No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Required frequency of publication of financial statements48 43 State owned banks Nationally Owned banks Foreign owned: Branches Subsidiaries 43 Capital Adequacy ratios for a bank are usually measured by the ratio of capital to risk-weighted assets. Refers to the number of days after which an unpaid loan has to be classified as a non-performing loan. 45 Refers to the percentage of assets to be held against deposits for liquidity purposes. 46 Refers to percentage limits on lending to an individual company. 47 Refers to the percentage of foreign exchange assets to be held as a proportion of deposits 48 Please indicate whether financial statements have to be published annually or quarterly. 44 53 21. Are banks required to disclose critical information? Related to performance Related to changes in ownership Other No No No Yes Yes Yes 22. Is home country supervision of foreign banks recognized? No Yes If yes, please list the countries whose bank supervisory systems are recognized. 23. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Regional Integration Agreements in Banking Services 24. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting banking services, and list the preferential49 measures. Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 49 Please specify how the treatment of banks of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of banks of non-member countries. 54 25. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1985 (e.g., privatization of state-owned banks, introduction of competition, entry of foreign banks, creation of an independent regulatory agency, liberalization of capital account, etc.). Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change 26. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same, or other areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Anticipated date Description of policy change 27. Administered allocation of resources a) Category Controls on Ceilings on deposit rates? lending rates? State owned banks Private nationally owned banks Foreign banks No Yes No Yes Subject to directed lending? No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes List of sectors benefiting from directed lending b) Does the government subsidize nationally owned banks? No Yes G. Employment 28. Main employment indicators How many people are employed in the banking sector? __________ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? ____________ What share of banking labor force is employed by state-owned banks? _____________ 55 What share of banking labor force is employed by foreign banks? _____________ What is the annual average wage in the banking sector? ______________ If time series data on these employment indicators are available, please attach them separately. H. Investment 29. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in banking services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. I. Prices and Performance Indicators: 30. Please provide information on the following price indicators for the latest year available. For a comprehensive assessment of banking sector performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on these prices measures. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Category Average monthly bank charges for a basic checking account Average monthly ex – post spread50 as a % of bank assets Non-performing Loans as a % of total bank assets Ratio of no. of employees to operating income Nationally Owned banks Foreign owned: Branches Subsidiaries J. Quality and Access to Banking Services 31. Which of the following services have been introduced by foreign banks in the last 10 years? Credit cards Debit cards Online banking ATM network other (specify) 32. Do foreign banks participate in rural lending? No Yes If yes, what is the share of foreign banks in total rural loans? _________ 33. Please indicate if the following banks make education loans to the poor: 50 The Ex-Post Spread of a bank is defined as the accounting value of the difference of the realized interest revenue and total interest cost of that bank and is also referred to as the Net Interest Margin. 56 Domestic banks: No Foreign banks: No Yes Yes 34. Do spreads between lending and deposit rates differ between large business firms and low-income households? No Yes If yes, please give sample spreads for a large business firm and a poor household below. Spread for large business:______ % Spread for low-income household: _____ % 35. Indicate the following: Number of banks per 1000 of the population: _____ Average wait time for loan approval: _____ Average wait time for credit card approval: _____ No. of bank failures during 1990-2000: _____ Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ 57 Financial Services: Insurance Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. Please report all monetary values in their reported currencies. A. Market Access Commercial presence 1. Are there policy restrictions on new entry of insurance providers in the following segments? Entry by any insurance providers If yes, total number of firms allowed Entry by foreign insurance providers No Yes No Yes If yes, total number of foreign firms allowed Direct life insurance No Yes Direct non-life No Yes insurance Re-insurance No Yes No Yes 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give incumbents time to prepare for competition To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Exclusive rights to allow the provision of universal service Excessive entry is believed to threaten financial stability Perception of no economic need for new insurance companies Other: ________________________________________ 3. Which of the following legal forms of establishment are allowed for foreign insurance companies? Subsidiaries Branches Representative Office All 4. Which of the following services are insurance companies permitted to provide domestically? Re-insurance Life insurance Property insurance Cargo insurance Medical insurance Automobile insurance Export credit insurance Pension insurance Investment services Other (specify)____________ Domestic insurance companies No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Foreign insurance companies No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes 5. Do the assets of foreign insurance companies established in the domestic country have to be held locally? No Yes 58 If applicable, please indicate the share of assets required to be held locally: _______ 6. Underwriting associations a) Do domestic underwriting associations51 exist? No Yes b) If yes to a), are foreign insurance companies established in the domestic country given memberships in domestic underwriting associations? No Yes Cross-border insurance trade 7. Can domestic residents purchase the following kinds of insurance cross-border from a foreign insurance company? No No No No Life insurance Medical insurance Property insurance Cargo insurance Only through resident intermediary Only through resident intermediary Only through resident intermediary Only through resident intermediary Yes Yes Yes Yes Are any of these purchases subject to limits? No No No No Life insurance Medical insurance Property insurance Cargo insurance Yes Yes Yes Yes What type? ______________ What type? ______________ What type? ______________ What type? ______________ 8. Are cross-border foreign insurance suppliers allowed to solicit business through advertising in the domestic country? No Yes Are there any limits on this type of advertisement? No Yes 9. Are insurers operating in the domestic country required to offer re-insurance business to nationally owned re-insurers before re-insuring abroad? No Yes B. Ownership 10. Is private ownership in the provision of insurance services allowed? Existing providers Life insurance Property insurance No No Yes Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New entrants No No Maximum private equity permitted (%) Yes Yes 51 Some countries have underwriting associations whereby a large proportion of insurance contracts in one or more classes of insurance is placed with members of these associations. 59 Health/medical Insurance Re-insurance No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes 11. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? Life insurance Property insurance Health/medical insurance Re-insurance Existing operators No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) C. Market Structure 12. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest insurance companies in the market for life insurance: Name Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Share in total life insurance premiums (%) Total number of life insurance providers: ______ 13. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest insurance companies in the market for non-life insurance: Name Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Share in total non-life insurance premiums (%) Total number of non-life insurance providers: ______ 14. Please list the characteristics of the insurance distribution/intermediary network. Distributor Whether present? Number of distributors 60 Tied Agents52 Independent Agents Brokers Banks No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes 15. Please provide the following information on the actual number of insurance companies: Number of fully state-owned insurance companies: _____ Number of privatized insurance companies: _____ Number of fully domestically owned53 private insurance companies: _____ Number of foreign minority-owned54 insurance companies: _____ Number of foreign majority-owned55 insurance companies: _____ D. Regulation 16. Characteristics of regulator Name of insurance regulator Year of establishment % of Regulator’s finances from: License and other fees Budgetary allocation Other (specify) Is the insurance regulator independent of the concerned ministry or other regulatory bodies? Number of professional regulatory and supervisory staff No Yes 17. How are insurance licenses allocated? a) If the number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill: Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency: ________) Presentation of a detailed business plan Minimum capital Compatible home country regulation Other: _____________________ b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? 52 Agents that sell insurance exclusively for one company. It is claimed that the predominance of tied agents and lack of independent agents and brokers in Japan and some European countries constitute a major structural barrier to entry. 53 Insurance companies that are not state owned where the paid-up share capital is entirely held by domestic residents. 54 Insurance companies where foreigners hold under 50% of the paid-up share capital of the company. 55 Insurance companies where 50% or more of the paid-up share capital of the company is held by foreigners. 61 First come, first served basis Competitive bidding Discretionary decision by the licensing authority Other:_______________________________ c) Once the licenses have been allocated, are there restrictions on the ability of insurance firms to sell or dispose of these licenses? No Yes If yes, please specify. d) Are foreign companies subject to different licensing requirements from domestic insurance companies? No Yes If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign insurance companies: e) Are separate licenses required to establish branches in each state/province? No Yes 18. Administered allocation of resources Category State owned insurance companies Private nationally owned insurance companies Foreign insurance companies Government controls on insurance prices? No Yes Re-insurance that must be ceded to the state-owned re-insurers (as a % of gross premiums) 56 Value of government insurance contracted ($) No Yes No Yes 56 Some countries mandate that companies must compulsorily re-insure either all or part of their portfolio with a state run insurance company. The requirement can also be imposed the other way, namely by requiring that only a certain percentage of gross premiums can be re-insured with private or foreign reinsurers 62 19. Please list the following indicators of prudential regulation based on the latest information available. Category State-owned insurance companies Private nationally Owned insurance companies Foreign owned Branches Subsidiaries Minimum capital requirement Capital adequacy requirement57 Liquidity reserve requirements Covered by insolvency guarantee Scheme58? Required frequency of publication of financial statements59 No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes 57 Capital Adequacy ratios for an insurance company are usually measured by the ratio of capital to risk-weighted assets. Sometimes, it is also posed as a solvency margin requirement. Solvency margins may be specified in absolute amounts or as a percentage of premiums. 58 The insurance sector’s equivalent of bank deposit insurance. 59 Please indicate whether financial statements have to be published annually or quarterly. 63 20. Are the following life-insurance providers subject to restrictions on the type of instruments in which they can invest? Domestic life insurance providers No Yes Foreign life insurance providers No Yes If yes, % of fund allowed to be invested abroad? _____ If yes, please list the type of financial instruments in which those investments can be made. 21. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ E. Regional Integration Agreements in Insurance Services 22. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting insurance services, and list the preferential60 measures. Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 23. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1985 (e.g., privatization of state-owned insurance companies, introduction of competition, 60 Please, specify how the treatment of insurance providers of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of insurance providers of non-member countries. 65 entry of foreign insurance, creation of an independent regulatory agency, changes in prudential regulation). Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of change Description of change 24. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same, or other areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of change Description of change G. Employment 25. Main employment indicators How many people are employed in the insurance sector? ________ What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? ________ What share of insurance workers is employed by state-owned insurance providers? _______ What share of insurance workers is employed by foreign insurance providers? _________ What is the annual average wage in the insurance sector? ______________ If time series data on these employment indicators are available, please attach them separately. H. Investment 26. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in insurance services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000. 66 I. Prices and Performance Indicators 27. Please list the following price and performance indicators for the latest year available. For a comprehensive assessment of insurance sector performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on these measures. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Category State owned insurance providers National Private Owned insurance providers Foreign Owned insurance providers Average monthly Premium on a 10 year life insurance policy Average monthly health insurance premium Loss ratio61 Retention ratio62 J. Quality and Access to Insurance Services 28. Which of the following new services have been introduced by foreign insurance companies in the last 10 years? Private health insurance Automobile insurance Private pension insurance 29. Please indicate the following: a) Share of adult population or households covered by life insurance contracts: _____ Share of household savings channeled through life insurance: _____ Total Premiums as a percentage of GDP: _____ b) If available, indicate average time (in days) for claims processing in the following segments: Life insurance: ______ Property insurance: _____ Automobile insurance: _____ Health insurance: ______ c) In which of the following segments is insurance mandated by law? Life insurance: ______ Property insurance: _____ Automobile insurance: _____ Health insurance: ______ d) Do foreign insurance companies participate in insuring poor and rural households? 61 62 The Loss Ratio of an insurance company is defined as the ratio of losses incurred to premiums earned. Defined as the ratio of net premiums to gross premiums. 67 No Yes If yes, what is the percentage of foreign insurance companies in the value of total rural insurance contracts? _____ Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address:__________________________________________________________________ 68 Financial Services: Securities Note: Unless specified, please give information for the latest year available and indicate which year. If insufficient space is provided, please attach additional information on separate sheets. Please report all monetary values in their reported currencies. A. Market Access Commercial presence 1. Are there policy restrictions on new entry of securities services providers in the following segments? Investment banking Stock brokerage Mutual funds Entry by any providers No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, total number of providers allowed Entry by foreign providers No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, number of foreign providers allowed 2. If entry is restricted, what are the reasons provided by the government? To give incumbents time to prepare for competition To increase government revenue from privatization or license fees Excessive entry is believed to threaten financial stability Perception of no economic need for new securities firms Other: ________________________________________ 3. Which of the following legal forms of establishment are allowed for foreign securities firms? Subsidiaries Branches Representative Office All 4. Which of the following services are securities firms permitted to provide? Underwriting new issues Securities dealing Stock brokerage services Risk management Mergers and acquisition advisory services Mutual funds (or unit trusts) Information services63 Other_______________ Domestic securities firms No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Foreign securities firms No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes No No No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes 5. Are foreign commercial or universal banks allowed to deal in domestic securities? 63 Financial information services include the provision of trading information and credit rating services. 69 No No Foreign commercial banks Foreign universal banks64 Yes Yes 6. Are foreign owned securities firms obliged to use the services of a domestic resident financial intermediary (broker-dealer) in the following segments: No No No No Inter-bank market Foreign exchange market Stock market Derivatives market Yes Yes Yes Yes Cross-border securities services trade 7. Are the following activities permitted? No Yes No Yes Purchase by domestic residents of securities issued abroad Domestic companies raising capital abroad If yes, please specify the restrictions. 8. Are foreign securities firms permitted to provide the following services cross-border to domestic companies and residents: Securities dealing in the domestic market Mergers and acquisitions advisory services Investment advisory services Credit rating services 9. a) Are settlement and clearance utilities available? No No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes b) If yes to the above, are cross-border foreign securities dealers permitted to use domestic settlement and clearance utilities without using the services of a domestic financial intermediary? No Yes B. Ownership 10. Is private ownership in the provision of the following securities services allowed? Investment banking Stock brokerage Mutual funds Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum private equity permitted (%) 64 Universal banks are banks which provide insurance and securities services in addition to traditional deposit taking and lending. 70 11. Is foreign ownership in the provision of services allowed? Investment banking Stock brokerage Mutual funds Existing operators No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) New entrants No Yes No Yes No Yes Maximum foreign equity permitted (%) C. Market Structure 12. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest mutual funds or investment trust funds (in terms value) in the market.65 Name of fund Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Value of fund as a % of total stock market capitalization Total number of mutual or investment funds: ______ 13. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest securities firms in the market for new equity issues. Name Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Share in annual value of new issues underwritten Total number of securities firms in the market for new equity issues: ___________ 14. Please list the characteristics of the 6 largest securities firms in the derivatives market: Name Year of establishment Domestically owned equity (%) Foreign equity (%) Share in annual value of derivatives traded 65 Investment trust funds are usually closed ended (have a limited size or number of units) and although they invest in a diversified portfolio of equities and other assets as mutual funds do, they are more like a regular company with a set number of shares in issue and their shares are usually listed on the stock exchange. 71 Total number of securities firms in the derivatives market: ___________ 15. Please provide the following information on the actual number of operators: Number of government-owned mutual funds: _____ Number of domestically owned66 private mutual funds: _____ Number of foreign owned mutual funds: _____ Number of fully domestically owned67 private investment banks: _____ Number of foreign minority-owned68 investment banks: _____ Number of foreign majority-owned69 investment banks: _____ D. Regulation 16. Characteristics of regulator Name of securities regulator Year of establishment % of Regulator’s finances from: License and other fees Budgetary allocation Other (specify) Is the regulator independent of the ministry of finance or other regulatory bodies? Number of professional regulatory and supervisory staff No Yes 66 Investment Banks where the paid-up share capital is entirely held by domestic residents. Investment Banks that are not state owned where the paid-up share capital is entirely held by domestic residents. 68 Investment Banks where foreigners hold under 50% of the paid-up share capital of the bank. 69 Investment Banks where 50% or more of the paid-up share capital of the bank is held by foreigners. 67 72 17. How are licenses to securities firms allocated? a) If number of providers is not restricted by policy, specify the main conditions new entrants must fulfill. Payment of license fee (indicate amount in local currency: ________) Presentation of a detailed business plan Minimum capital Compatible home country regulation Other: _____________________ b) If the number of providers is limited by policy, through what mechanism are licenses allocated? First come, first served basis Competitive bidding Discretionary decision by the licensing authority Other:_______________________________ c) Once the licenses have been allocated, are there restrictions on the ability of insurance firms to sell or dispose of these licenses? No Yes If yes, please specify. d) Are foreign securities firms subject to different licensing requirements from domestic securities firms? No Yes If yes, please specify what additional requirements have to be met by foreign securities firms: 18. Credit rating a) Is private credit rating permitted? No Yes b) Is private credit rating subject to regulation or approval by an other public or private body? No Yes 73 19. Please list the following indicators of prudential regulation based on the latest information available. Minimum capital requirement Capital adequacy ratio70 (%) Required frequency of publication of financial statements71 Category Government owned mutual funds Domestic privately owned mutual funds Foreign owned mutual funds Investment banks Domestic Foreign 20. 70 71 Are securities firms required to disclose critical information? Related to performance No Yes Related to changes in ownership No Yes Other No Yes Capital Adequacy ratios are usually measured by the ratio of capital to risk-weighted assets. Please indicate whether financial statements have to be published annually or quarterly. 74 21. Are the following mutual funds required to invest in shares of publicly held companies? Government owned mutual funds Domestic privately owned mutual funds Foreign owned mutual funds No Yes No Yes No Yes If yes, % of fund equity required to be invested in public company shares? _____ If yes, % of fund equity required to be invested in public company shares? _____ If yes, % of fund equity required to be invested in public company shares? _____ 22. Are mutual funds subject to other restrictions on their investments abroad? No Yes If yes, % of fund allowed to be invested abroad? _____ If yes, type of financial instruments in which those investments can be made? _____ 23. Public consultation and transparency a) Which of the following are consulted in advance of regulatory decisions? Service providers Consumer groups User industries Other: _____________________ b) How are laws and regulatory decisions made public? Published on the regulator’s website Published in an official gazette Other: _____________________ 75 E. Regional Integration Agreements in Financial Services 24. Please indicate if there are any preferential arrangements affecting securities services, and list the preferential72 measures. Name of agreement Partner country(s) in agreement Date of entry into force Preferential measures F. Past and Future Changes in Policy 25. Please indicate major changes in market access policies, ownership rules, and regulation since 1985 (e.g., introduction of competition, entry of foreign mutual funds and investment banks, creation of an independent regulatory agency, changes in prudential regulation). Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change 26. Please indicate announced or anticipated changes in the same, or other areas. Area of policy change (market access, ownership or regulation) Year of policy change Description of policy change G. Employment 27. Main employment indicators How many people are employed in the securities sector? ________ 72 Please, specify how the treatment of securities firms of member countries of the agreement differs from the treatment of securities firms of non-member countries. 76 What share of the total labor force is employed in this sector? __________ What share of securities workers is employed by foreign securities firms? __________ What is the annual average wage in this sector? ______________ If time series data on these employment indicators are available, please attach them separately. H. Investment 28. Investment indicators (for the years 1990-2000) What is the total amount of investment in securities services? _____________ What is the total amount of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ What is the total stock of foreign direct investment in this sector? ___________ If time-series data from 1990 to 2000 is not available, please collect indicators for the years 1990, 1995 and 2000 I. Prices and Performance Indicators 29. Please list the following price and performance indicators for the latest year available. For a comprehensive assessment of securities services performance, it would be extremely useful to have historical data on these measures. If time series data are available, please attach them separately (preferably electronically). Category Domestic operators Foreign operators Average brokerage Commissions (%) Average underwriting Commissions (%) Securities Dealing fees Average initial Subject to charge73 on a price fixing mutual fund by regulator? No Yes No Yes J. Quality and Access to Securities Services 30. Which of the following services have been introduced in the last 10 years? Over the counter (OTC) markets Computerized stock exchange trading Online Investing Electronic settlement and clearance systems Derivatives trading 73 Refers to the percentage charge imposed on buyers of the fund by the manager to cover the costs of administration and marketing plus commissions paid to intermediaries. The initial charge is usually factored into the buying price of the mutual fund units. If the initial charge is 5%, then out of every $100 invested, $5 is retained by the management of the mutual fund to cover the costs listed above. 77 Other:______________________________________ 31. Indicate the following: Number of stock exchanges in the country: _____ Total stock market capitalization: _____ Number of listed companies in the stock exchange: _____ Number of foreign listed companies in the stock exchange: _____ Share of foreign listed companies in total stock market capitalization: _____% Number of domestic companies whose assets are rated: ____ Growth in the value of stocks traded in OTC markets: ____% Number of penalized insider-trading cases in the last 5 years: _____ Please, provide the name and contact information of the respondent of this questionnaire, or of a specialist from whom we can obtain clarifications if necessary. Name_________________________________________________________________________ Telephone_____________________________________________________________________ Fax___________________________________________________________________________ E-mail address 78