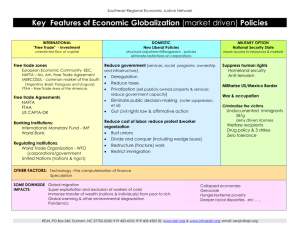
F T A
advertisement

BANCO INTERAMERICANO DE DESARROLLO DEPARTAMENTO DE INTEGRACIÓN Y PROGRAMAS REGIONALES INSTITUTO PARA LA INTEGRACIÓN DE AMÉRICA LATINA Y EL CARIBE II SEMINAR ON INTERNATIONAL AGRICULTURE TRADE NEGOTIATIONS ALADI - IDB/INTAL - IICA - BCEIE BUENOS AIRES, ARGENTINA MAY 22-24, 2001 FTAA AGRICULTURE NEGOTIATIONS PHASE I: PROGRESS AND PERSPECTIVES MARIO BERRIOS Inter-American Development Bank Integration, Trade and Hemispheric Issues Division PRESENTATION: INTRODUCTION: - Calendar - work accomplished - Mandate; Substantive Agenda PROGRESS REPORT: - progress during Phase I - Market access; Export Subsidies; Domestic Support; SPS; other issues - Linkages to other FTAA negotiations KEY ISSUES AND NEXT TASKS: - key issues - tasks for Phase II 2001-2002 PROSPECTS: POSSIBLE SCENARIOS - potential effects from WTO negotiations on FTAA agriculture ngts - trade negotiation authority - market conditions for agricultural commodities WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF FTAA AGRICULTURE TRADE? Schedule of agriculture trade negotiations Negotiating Phase FTAA WTO Pre-Negotiation Period 1994-98 1995-99 Start of Negotiations 1998 2000 Deadline to end negotiations End of 2004 Open implementation By December 2005 undecided Relationship to other areas of Same timetable negotiations Pending Work accomplished to date: • 10 negotiating sessions (August 1998 - Nov 2000) • proposals submitted by all participants (country or grouping) • dealt with all substantive areas under negotiation • specific progress made on 4 areas: - draft text Agriculture Chapter(made a public documnt) - draft outline on methods/modalities for tariff ngts - interaction between Negotiating Groups on Agriculture and Market Access - set target dates for (among others): - finish ngts in 2004, implement in 2005 - April 2002: define methodologies on: tariff ngts; elimination ES; defint/recomm treatment of OMDT; identification NTMs Mandate - issues for negotiation: FTAA goal: creation of a free trade zone, liberalization agric trade Area of negotiation Market Access WTO Continuation process FTAA reform - Tariffs; non-tariff barriers - coordination agric/non-agric market access ngts Export Review/ngtn ES - Agricultural ES affecting FTAA trade Subsidies commitmnts - Other measures and practices that have - reform process an effect equivalent to agricultural ES Review/ngtn DS Other trade-distorting practices for Other agricultural products commitmts support measures - reform process SPS Identifying/developing measures to facilitate trade, examining in depth WTO/SPS provisions - Special/differential - Facilitate the integration of smaller Others treatment for economies and their full participation developing country - Incorporate progress made in WTO ag - Non-trade concerns ngts ISSUES AND SCOPE OF DRAFT AGRICULTURE CHAPTER STRUCTURE OF DRAFT FTAA CHAPTER ON AGRICULTURE Six sections: • General provisions • Market access and NTMs • ES • Other measures and practices that distort trade • SPS • Institutional Issues • + Annexes • general comments: • 1 working document; different approaches still present • market access: consistency and link to NGMA • reference/consistency to WTO agreements noted Market access - what has been considered : •Tariff provisions: • tariff elimination and potential exceptions • working document on methods and modalities • link/consistency/coordination with NGMA modalities • issues: • base tariff/period; nomenclature; timetables; methods • NGAG: add specific MA provisions unique to agric • NTMs: • notification/counter-notification; listing; • methodology on how to deal with NTMs • Safeguards EXPORT SUBSIDIES - what has been considered: Definition: discussion on whether to include criteria related to: • de jure or de facto • reference to WTO AA Arts 1.e, 9, 9.1; WTO ASCV Annex I • Elimination of ES: • elimination on FTAA basis: • date implementation • how to offset ES imports from non-FTAA countries • FTAA countries’ ES competition in non-FTAA markets • non-circumvention: define disciplines on measures that have an effect equivalent to ES • areas of FTAA cooperation to eliminate ES at multilateral level: • mechanisms to prevent importation of ES products from nonFTAA countries from entering FTAA markets • disciplines on export credits/guarantees, food aid • use of dispute sett rights in case of nullific access in 3rd mkts OTHER MEASURES THAT DISTORT TRADE what has been considered • recognition of role of Domestic Support measures: • importance of DS to agric sector but role in distorting production and trade • key issue under discussion: negotiate disciplines/commitments in FTAA or WTO • proposals on negotiating goals / cooperation in WTO ngts: • max reduction; elimination blue box; overall limit; redefine green box • proposals to deal with DS in FTAA ngts: • definition and what exceptions may be allowed • elimination: methodology • disciplines to prevent circumvention • special and differential treatment Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures • issues: cooperate to implement WTO agmt; specific goals • General Provisions, rights and obligations • Implementation of WTO agreement • international standards • harmonization • equivalence • assessment of risk • pest or disease-free areas • transparency • control, inspection and approval procedures • safeguard measures • Technical assistance and cooperation • Consultations and Dispute settlement • Institutional Issues Institutional Issues - FTAA agreement on agriculture • Consultations and Dispute Settlement • FTAA new task to work on architecture of agreement: • institutional issues Linkages between agriculture and other FTAA negotiating areas • key links: • market access • subsidies, AD, CV • dispute settlement • potential new links: • intellectual property • investment • competition policy KEY ISSUES AND TASKS FOR PHASE II 2001-2002 • key issues: • negotiation on domestic support • elimination of Export Subsidies and mechanisms to enforce it • disciplines on export credits/guarantee/insurance programs • disciplines on Food Aid • treatment of SPS measures • sequencing, parallel or individual progress of different areas of ngts • some of the key tasks for Phase II 2001- 2002 • methods/modalities: proposal in April and start ngtn in May 2002 • ES: April 2002: propose methodology for elimination • OMDT: identify measures and methodology (April 2002) • NTMs: identific/inventory/methodology in April 2002 • hemispheric data base • notific/counterntif SPS measures and implementation WTO SPS agt What impact could WTO ngts have on FTAA agric ngts: 3 Possible scenarios • Key issue: • there are positive synergies between FTAA and WTO agr ngts for the general goal to reform trade in agricultural products 3 possible scenarios: • WTO Round 2002• Limited progress in WTO ag ngts by 2003 • No WTO Round in 2001-2004 WTO Round 2002 • parallel discussion of Domestic Support in WTO and FTAA ngts: • if WTO venue would be privileged to discuss DS: need for ambitious FTAA market access results • also at stake: whether or not to re-negotiate Art 13 peace clause • Limited progress in WTO ag ngts by 2003: • choices on peace clause: expire; extend ? • might provide additional impetus to complete FTAA ngts in 2004 • FTAA results by 2004 might contribute to WTO discussions • no progress / impasse in WTO negotiations • might provide added impetus to FTAA as more viable ag ngt • no significant FTAA results on DS support would require ambitious FTAA market access liberalization program • WTO negotiations produce results by 2003 • consideration on how to incorporate results from WTO agriculture negotiations in the FTAA No WTO round in 2001-2004 • No multilateral round in 2001-2004 might provide both challenges and opportunities for FTAA ngts • main challenges: • DS, ES, general subsidies, dispute settlement issues, export credits, food aid : results not available for incorporation in FTAA • possibility: • despite negative connotation, it may give impetus to FTAA as most viable way to reform and liberalize trade in agriculture in short/medium term KEY FACTORS INFLUENCING FTAA NGTS: • U.S. NEGOTIATING AUTHORITY • CONTEXT OF FARM BILL FOR APPROVAL IN 2002 • IMPORTANCE OF TIMING FOR FTAA NGTS: APR/MAY 2002 • SCOPE OF NEGOTIATING AUTHORITY: • ISSUES / MANDATE FOR WTO/BILATERAL/FTAA NGTS • CAPACITY OF COUNTRIES TO IMPLEMENT FTAA AGTM • WTO ROUND OR WTO SECTORAL NGTS • MARKET CONDITIONS - OECD FORECAST 2000-04: • CEREALS: ↑NOMINAL P ↑ LITTLE REAL P ↓STOCKS •OILSEEDS: ↑PRODUCTION/CONSUMP 5% SUSTAIN P •MEAT:↑MEAT P BUT UNCERTAINTY DISEASE ISSUE • HEMISPHERIC AND GLOBAL ECONOMIC CONDITIONS • FUTURE OF EU CAP: BUDGET LIMITS / ENLARGEMENT HOW IMPORTANT IS THE FTAA AS AN AGRICULTURAL TRADE ZONE ? WHAT IMPORTANCE COULD FTAA LIBERALIZATION OF AGRICULTURAL TRADE HAVE ON GLOBAL TRADE IN AGRICULTURE ? THE FTAA REGION IS AN IMPORTANT AREA OF AGRICULTURAL TRADE IT HAS APROXIMATELY: • 30% OF TOTAL WORLD EXPORTS • 20% “ : IMPORTS Regional Shares in World Trade in Agricultural Products, 1999 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Western Europe FTAA Asia Exports Imports Africa C./E. Eurpoe/Baltic states/CIS Middle East Source: Based on International Trade Statistics 2000 by the World Trade Organization But most of the FTAA trade agricultural trade at this time is heavily concentrated on 6 to 8 countries TABLE# Top10Intra-FTAAAgricultureExporters TABLE# Top10Intra-FTAAAgricultureImporters 25 20 20 Import Value ($billion) Export Value ($billion) 25 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 USA CAN MEX ARG BRA CHL COL CRI GTM ECU USA CAN MEX BRA COL VEN CHL ARG PER GTM Who are the top importers/exporters and products involved? There is a wide range of products traded: Total FTAA agricultural trade has been growing in recent years GRAPH1.1Intra-FTAAAgriculturalExports GRAPH2.1Intra-FTAAAgriculturalImports TotalAgriculturalImportsandTop5Importers TotalAgriculturalExportsandTop5Exporters 60 60 Total 50 Total 50 40 40 30 30 USA 20 20 USA CAN 10 10 CAN MEX BRA COL 0 95 96 97 Year 98 99 MEX ARG BRA 0 95 96 97 Year 98 99 Intra-RTA Agricultural trade has also been growing: …and Intra-RTA agricultural trade is the most important but extraRTA also looks active Probably no significant concerns on FTAA trade diversion should be in place since protection vis-à-vis third countries is within average protection and most growth is with FTAA By RTAs: RTAs also have an active export trade with the rest of the FTAA NAFTA remains the main importer from FTAA sources FTAA TRADE PROTECTION: TRQs Who has TRQs and on what? 13 countries: On what products are the TRQs and how many? How much of the TRQs’ import potential is used? Only around 60% Who has the TRQs and how much of the TRQs do they use? TRADE PROTECTION: APPLIED TARIFFS Applied tariff protection on the top intra-FTAA imports is high. On what products have we seen trade disputes?